Lead-acid batteries offer reliable, cost-effective power with a heavier weight and shorter lifespan compared to lithium-ion batteries, which provide higher energy density, faster charging, and longer cycle life ideal for portable and electric vehicle applications. Your choice depends on balancing budget constraints with performance needs, where lithium-ion excels in efficiency and longevity but at a higher initial investment.
Table of Comparison
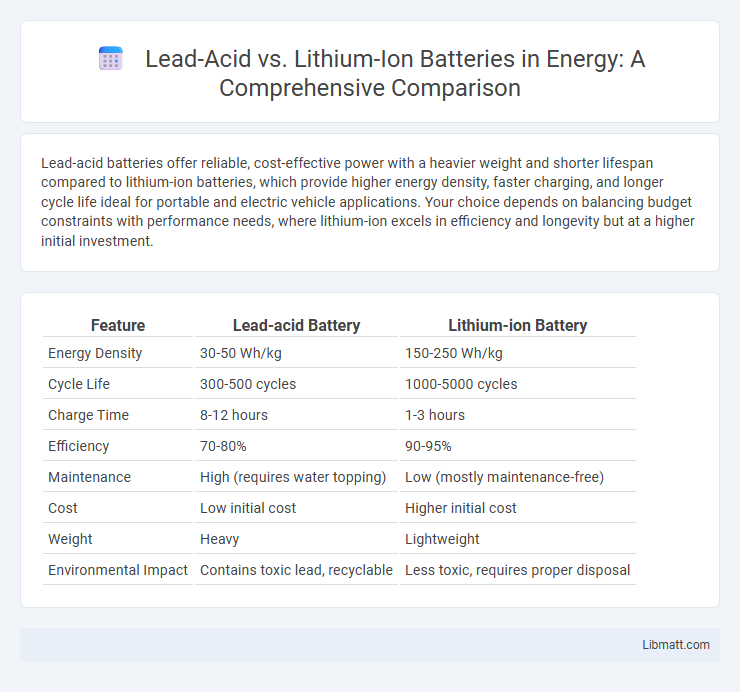
| Feature | Lead-acid Battery | Lithium-ion Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | 30-50 Wh/kg | 150-250 Wh/kg |
| Cycle Life | 300-500 cycles | 1000-5000 cycles |
| Charge Time | 8-12 hours | 1-3 hours |
| Efficiency | 70-80% | 90-95% |
| Maintenance | High (requires water topping) | Low (mostly maintenance-free) |
| Cost | Low initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Weight | Heavy | Lightweight |
| Environmental Impact | Contains toxic lead, recyclable | Less toxic, requires proper disposal |
Introduction to Lead-acid and Lithium-ion Batteries
Lead-acid batteries, known for their cost-effectiveness and reliability, use lead plates submerged in sulfuric acid to store energy, making them ideal for automotive and backup power applications. Lithium-ion batteries feature higher energy density, lighter weight, and longer cycle life, utilizing lithium compounds for energy storage, which suits portable electronics and electric vehicles. Understanding the differences in chemistry, performance, and use cases can help you choose the right battery technology for your needs.
Basic Working Principles
Lead-acid batteries store electrical energy through a chemical reaction between lead dioxide and sponge lead, submerged in sulfuric acid, producing electrical current via the movement of ions. Lithium-ion batteries operate by shuttling lithium ions between the anode and cathode during charge and discharge cycles, enabling higher energy density and efficiency. Understanding these basic working principles helps you choose the optimal battery type for applications requiring specific energy storage and power delivery characteristics.
Energy Density Comparison
Lithium-ion batteries offer significantly higher energy density compared to lead-acid batteries, typically ranging from 150 to 250 Wh/kg versus 30 to 50 Wh/kg for lead-acid. This higher energy density enables longer runtime and reduced weight, making lithium-ion more efficient for portable and automotive applications. Your choice in energy storage can impact device performance and overall system weight due to this substantial difference.
Lifespan and Cycle Durability
Lead-acid batteries typically offer a lifespan of about 3-5 years with 300-500 charge cycles, while lithium-ion batteries can last 8-15 years and endure 2,000-5,000 cycles. The higher cycle durability of lithium-ion batteries results in more consistent performance and less frequent replacements, making them ideal for applications requiring long-term energy storage. Your choice of battery technology impacts maintenance costs and overall reliability depending on usage demands.
Charging and Discharging Efficiency
Lithium-ion batteries exhibit superior charging and discharging efficiency, typically around 90-95%, compared to lead-acid batteries, which range between 70-85%. This higher efficiency results in faster charging times and reduced energy loss during discharge for lithium-ion technology. Improved cycle life and deeper discharge capabilities further enhance the overall efficiency and performance of lithium-ion batteries in various applications.
Weight and Size Differences
Lead-acid batteries are significantly heavier and bulkier compared to lithium-ion batteries, making lithium-ion the preferred choice for applications where weight and space are critical. Lithium-ion batteries offer a higher energy density, allowing your devices or vehicles to achieve longer runtimes and increased efficiency without the added bulk. Choosing lithium-ion batteries enhances portability and performance due to their compact size and lightweight design.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-term
Lead-acid batteries offer a lower initial cost compared to lithium-ion batteries, making them a budget-friendly option for short-term use. However, lithium-ion batteries provide greater long-term value due to higher energy density, longer cycle life, and reduced maintenance costs. Your overall investment benefits from lithium-ion technology's efficiency and durability despite the higher upfront price.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Lead-acid batteries have a higher environmental footprint due to toxic lead content but benefit from an established, efficient recycling system recovering up to 99% of lead materials. Lithium-ion batteries, although less toxic and lighter, pose challenges with recyclability and require advanced processes to recover valuable metals like cobalt and lithium, often resulting in lower recycling rates. Your choice between these batteries affects sustainability, where lead-acid offers immediate recyclability and lithium-ion presents long-term environmental benefits with improving recycling technologies.
Safety and Maintenance Requirements
Lead-acid batteries require regular maintenance, including monitoring electrolyte levels and ensuring proper ventilation to prevent acid leaks and gas buildup, which can pose safety risks. Lithium-ion batteries offer enhanced safety features such as built-in protection circuits to prevent overcharging and thermal runaway, resulting in lower maintenance demands. Your choice between these batteries impacts both ongoing care efforts and overall operational safety, with lithium-ion batteries generally providing a safer and more maintenance-friendly solution.
Best Applications for Each Battery Type
Lead-acid batteries are best suited for automotive starters, backup power supplies, and off-grid renewable energy storage due to their low cost and high surge current capabilities. Lithium-ion batteries excel in portable electronics, electric vehicles, and grid storage applications where high energy density, longer cycle life, and lightweight design are critical. Selecting the appropriate battery depends on specific application requirements such as weight constraints, energy demands, and budget considerations.
Lead-acid vs Lithium-ion Battery Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com