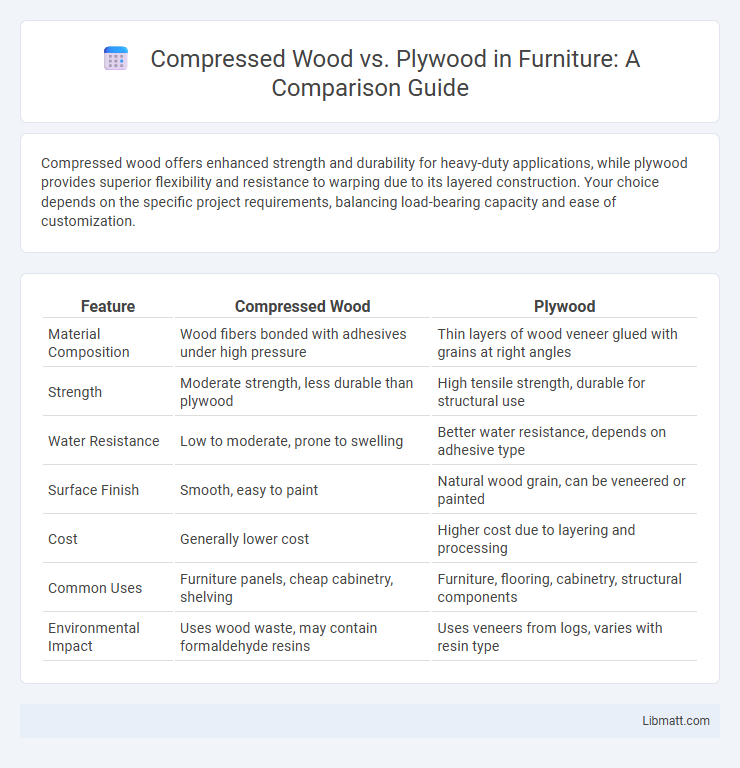
Compressed wood offers enhanced strength and durability for heavy-duty applications, while plywood provides superior flexibility and resistance to warping due to its layered construction. Your choice depends on the specific project requirements, balancing load-bearing capacity and ease of customization.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Compressed Wood | Plywood |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Wood fibers bonded with adhesives under high pressure | Thin layers of wood veneer glued with grains at right angles |
| Strength | Moderate strength, less durable than plywood | High tensile strength, durable for structural use |
| Water Resistance | Low to moderate, prone to swelling | Better water resistance, depends on adhesive type |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, easy to paint | Natural wood grain, can be veneered or painted |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to layering and processing |
| Common Uses | Furniture panels, cheap cabinetry, shelving | Furniture, flooring, cabinetry, structural components |
| Environmental Impact | Uses wood waste, may contain formaldehyde resins | Uses veneers from logs, varies with resin type |
Introduction to Engineered Wood: Compressed Wood vs Plywood
Engineered wood products like compressed wood and plywood offer enhanced strength and durability compared to natural wood. Compressed wood is created by applying heat and pressure to wood fibers or particles, resulting in a dense, uniform material ideal for structural applications. Plywood consists of multiple thin layers of wood veneer glued together with alternating grain directions, providing superior stability and resistance to warping in furniture and construction projects.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Compressed wood consists of wood fibers or particles bonded under high pressure and heat using adhesives or resins, resulting in a dense, solid material. Plywood is made by layering thin veneers of wood, each grain rotated typically 90 degrees to the adjacent layer, and then glued and pressed firmly together to enhance strength and stability. The manufacturing of compressed wood emphasizes compression and resin bonding, whereas plywood production requires precise veneer peeling, grain alignment, and multi-layer lamination steps.
Structural Strength and Durability Comparison
Compressed wood offers enhanced density and uniformity, resulting in superior structural strength compared to conventional plywood, which consists of layered veneers bonded together. Plywood exhibits good durability but can be prone to delamination under prolonged moisture exposure, whereas compressed wood provides improved resistance to warping and swelling due to its engineered compression process. For applications requiring maximum load-bearing capacity and long-term stability, compressed wood may better support Your structural needs.
Moisture Resistance and Environmental Suitability
Compressed wood offers enhanced moisture resistance due to its dense structure and resin bonding, making it suitable for humid environments and reducing the risk of warping or swelling. Plywood, composed of multiple wood veneers glued in alternating grain directions, provides moderate moisture resistance but may delaminate if exposed to prolonged dampness without proper sealing. Environmentally, compressed wood utilizes wood fibers and adhesives that can vary in eco-friendliness, while plywood often incorporates sustainably sourced veneers and low-VOC adhesives, supporting green building certifications.
Weight and Handling Differences
Compressed wood typically weighs more than plywood due to its density and the manufacturing process that tightly compacts wood fibers. Plywood offers lighter weight and greater ease of handling, making it preferable for projects requiring frequent positioning or transport. Your choice depends on whether weight reduction or material strength is more critical for your application.
Surface Finish and Aesthetic Versatility
Compressed wood offers a smooth, consistent surface finish ideal for painting and laminating, making it suitable for custom decorative applications. Plywood displays natural wood grain patterns and can be stained or varnished to enhance its aesthetic appeal, providing versatile options for visible surfaces. The choice between compressed wood and plywood depends on whether a uniform finish or natural wood texture is desired in interior design and furniture projects.
Cost Analysis: Budget Considerations
Compressed wood generally offers a lower-cost alternative compared to plywood due to its manufacturing process using wood fibers and adhesives, resulting in reduced material expenses. Plywood typically incurs higher prices because of its layered construction and greater durability, which suits applications requiring strength and moisture resistance. For budget-conscious projects, compressed wood can provide adequate performance while minimizing upfront costs, but long-term durability may influence overall value.
Common Applications in Construction and Furniture
Compressed wood, known for its high density and strength, is commonly used in flooring, structural panels, and load-bearing components in construction, providing durability and resistance to impact. Plywood's layered composition makes it ideal for furniture, cabinetry, and interior walls due to its stability, flexibility, and smooth surface finish. Both materials enhance sustainability by utilizing wood fibers efficiently, catering to various design and functional needs in modern building and furniture manufacturing.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Compressed wood uses recycled wood fibers and adhesives, reducing waste and the demand for virgin timber, making it a more sustainable option compared to plywood, which often relies on veneers from freshly cut trees. Manufacturing compressed wood typically emits fewer carbon emissions due to lower energy requirements during production, contributing to a smaller environmental footprint. While plywood offers strength and durability, compressed wood's utilization of reclaimed materials supports forest conservation and decreases landfill volumes.
Choosing the Right Material: Key Factors to Consider
When choosing between compressed wood and plywood, consider durability, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness for your specific project. Compressed wood offers a dense, smooth surface ideal for indoor use, while plywood provides superior strength and resistance to warping, making it suitable for structural applications. Your decision should balance these factors with the environmental conditions and load requirements to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
compressed wood vs plywood Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com