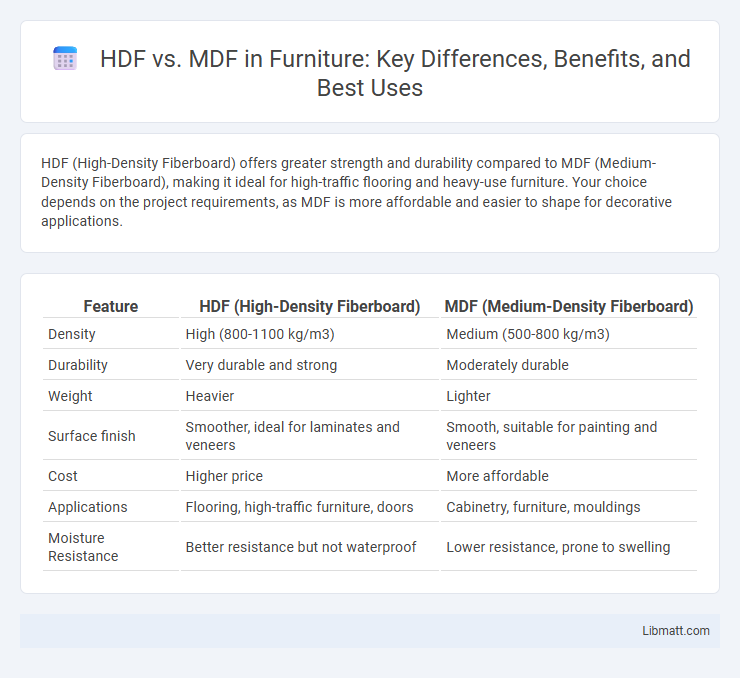
HDF (High-Density Fiberboard) offers greater strength and durability compared to MDF (Medium-Density Fiberboard), making it ideal for high-traffic flooring and heavy-use furniture. Your choice depends on the project requirements, as MDF is more affordable and easier to shape for decorative applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | HDF (High-Density Fiberboard) | MDF (Medium-Density Fiberboard) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | High (800-1100 kg/m3) | Medium (500-800 kg/m3) |
| Durability | Very durable and strong | Moderately durable |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Surface finish | Smoother, ideal for laminates and veneers | Smooth, suitable for painting and veneers |
| Cost | Higher price | More affordable |
| Applications | Flooring, high-traffic furniture, doors | Cabinetry, furniture, mouldings |
| Moisture Resistance | Better resistance but not waterproof | Lower resistance, prone to swelling |
Introduction to HDF and MDF
HDF (High-Density Fiberboard) and MDF (Medium-Density Fiberboard) are engineered wood products made from wood fibers bonded with resin under heat and pressure. HDF is denser and harder than MDF, offering greater durability and resistance to impact, making it ideal for high-traffic areas and heavy-use applications. Your choice between HDF and MDF depends on the required strength, finish quality, and budget for furniture, flooring, or cabinetry projects.
What is HDF?
High-Density Fiberboard (HDF) is a type of engineered wood product made by compressing wood fibers under high pressure and heat, resulting in a dense, durable panel. HDF has a higher density than Medium-Density Fiberboard (MDF), typically exceeding 800 kg/m3, making it stronger and more resistant to impact and moisture. Commonly used in flooring, furniture, and cabinetry, HDF provides a smooth surface ideal for veneers, laminates, and paint finishes.
What is MDF?
MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard) is an engineered wood product made by breaking down hardwood or softwood residuals into wood fibers, combining them with wax and resin binder, and applying high temperature and pressure to form dense, flat panels. MDF is known for its smooth surface, uniform density, and excellent machining qualities, making it ideal for furniture, cabinetry, and decorative projects where a consistent finish is required. You can choose MDF when you need a cost-effective, versatile material that provides strength and ease of customization compared to traditional solid wood.
Key Differences Between HDF and MDF
HDF (High-Density Fiberboard) has a higher density and smoother surface compared to MDF (Medium-Density Fiberboard), making it more durable and suitable for high-traffic areas or furniture requiring strength. MDF is easier to machine and less expensive, often used for decorative projects and interior applications where moisture resistance is not critical. Understanding these key differences can help you select the right material for your woodworking or construction needs.
Density and Composition Comparison
High-Density Fiberboard (HDF) typically has a density ranging from 800 to 1,000 kg/m3, while Medium-Density Fiberboard (MDF) falls between 600 and 800 kg/m3, making HDF denser and stronger. Both HDF and MDF are engineered wood products made from wood fibers combined with resin binders, but HDF's fibers are more tightly compressed during manufacturing, resulting in greater hardness and durability. The higher density and improved fiber bonding in HDF enhance its resistance to impact and moisture compared to MDF, which features a softer and less compact structure.
Durability and Strength: HDF vs MDF
High-Density Fiberboard (HDF) exhibits superior durability and strength compared to Medium-Density Fiberboard (MDF) due to its higher density, typically ranging from 800 to 1,000 kg/m3, which enhances resistance to impact and wear. MDF, with a density between 600 to 800 kg/m3, offers good stability but is more prone to damage from moisture and mechanical stress. The denser, compact fiber structure of HDF makes it ideal for flooring and heavy-duty applications where robustness is critical.
Applications and Uses
HDF (High-Density Fiberboard) is extensively used in furniture manufacturing, cabinetry, and decorative applications due to its smooth surface and high density, which allows for superior painting and laminating. MDF (Medium-Density Fiberboard) is commonly employed in interior projects such as shelving, molding, and speaker boxes because of its ease of machining and versatility. Both materials are preferred in construction and woodworking but differ in strength and finish quality, with HDF offering greater durability and MDF providing cost-effective solutions.
Cost Comparison: Which is More Affordable?
Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF) typically offers a more affordable option compared to High-Density Fiberboard (HDF) due to its lower manufacturing density and raw material costs. While MDF is widely used for interior applications like cabinetry and furniture because of its smooth surface and ease of machining, HDF's higher density provides superior durability and moisture resistance, often resulting in a higher price point. For budget-conscious projects, MDF remains the preferred choice, whereas HDF is favored when enhanced strength and longevity justify the additional expense.
Pros and Cons of HDF and MDF
High-Density Fiberboard (HDF) offers superior strength, density, and moisture resistance, making it ideal for flooring and heavy-duty furniture; however, it is typically more expensive and harder to work with compared to MDF. Medium-Density Fiberboard (MDF) provides a smooth surface for painting and is easier to machine and shape, but it is less durable and more susceptible to water damage and swelling. Choosing between HDF and MDF depends on project requirements such as durability, budget, and exposure to moisture.
Which One Should You Choose?
HDF (High-Density Fiberboard) offers greater strength and moisture resistance compared to MDF (Medium-Density Fiberboard), making it ideal for flooring and exterior applications. MDF provides a smoother surface for detailed woodworking and is more cost-effective, suited for indoor furniture and cabinetry. Choosing between HDF and MDF depends on durability requirements, environmental exposure, and budget for your specific project.
HDF vs MDF Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com