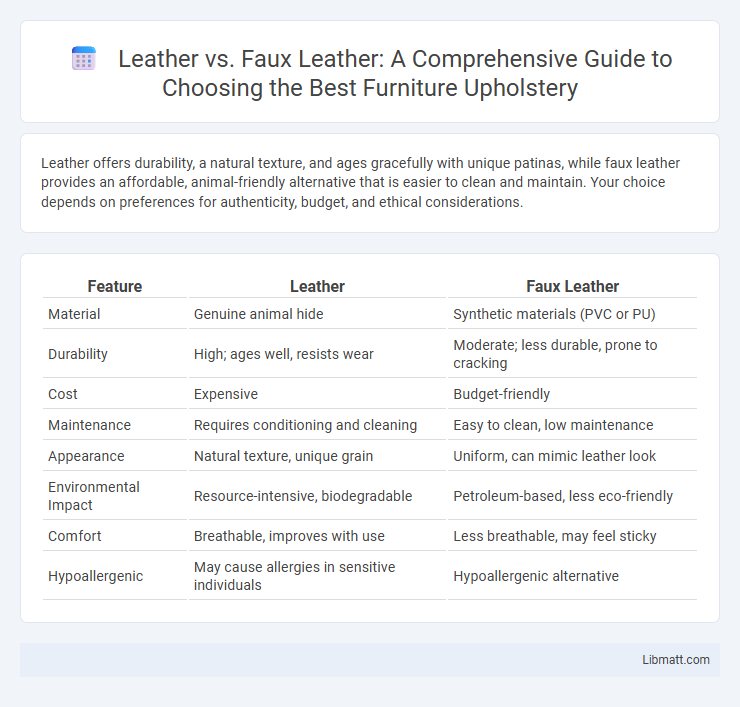
Leather offers durability, a natural texture, and ages gracefully with unique patinas, while faux leather provides an affordable, animal-friendly alternative that is easier to clean and maintain. Your choice depends on preferences for authenticity, budget, and ethical considerations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Leather | Faux Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Genuine animal hide | Synthetic materials (PVC or PU) |
| Durability | High; ages well, resists wear | Moderate; less durable, prone to cracking |
| Cost | Expensive | Budget-friendly |
| Maintenance | Requires conditioning and cleaning | Easy to clean, low maintenance |
| Appearance | Natural texture, unique grain | Uniform, can mimic leather look |
| Environmental Impact | Resource-intensive, biodegradable | Petroleum-based, less eco-friendly |
| Comfort | Breathable, improves with use | Less breathable, may feel sticky |
| Hypoallergenic | May cause allergies in sensitive individuals | Hypoallergenic alternative |
Introduction to Leather and Faux Leather
Leather is a natural material made from animal hides, prized for its durability, breathability, and unique texture that improves with age. Faux leather, also known as synthetic leather, is crafted from plastic-based materials like polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), offering a cruelty-free and often more affordable alternative. Understanding the differences in origin and characteristics helps you make informed choices for fashion, furniture, or accessories.
What is Genuine Leather?
Genuine leather is made from the natural hide of animals, primarily cows, and undergoes a tanning process to enhance durability and flexibility. It features unique grain patterns and breathability, which contribute to its long-lasting quality and comfort. Unlike faux leather, genuine leather develops a patina over time, adding character and value to the material.
What is Faux Leather?
Faux leather, also known as synthetic leather, is a man-made material designed to mimic the appearance and texture of genuine leather using plastic-based substances like polyurethane or polyvinyl chloride (PVC). It offers a more affordable and animal-friendly alternative while being easier to maintain and resistant to water and stains. Your choice between leather and faux leather depends on preferences for durability, environmental impact, and ethical considerations.
Appearance and Texture Comparison
Leather features a natural grain pattern with unique textures created by animal hide characteristics, offering a rich, supple feel that develops a patina over time. Faux leather mimics real leather's appearance but tends to have a more uniform texture and a slightly synthetic surface, often feeling stiffer and less breathable. High-quality faux leather can closely resemble genuine leather visually, but it lacks the natural variances and aging qualities that define authentic leather.
Durability: Leather vs Faux Leather
Leather offers superior durability due to its natural fibers that withstand wear and tear over time, often lasting decades with proper care. Faux leather, made from synthetic materials like polyurethane, tends to deteriorate faster, usually showing signs of cracking and peeling within a few years. When choosing between leather and faux leather, consider your need for long-lasting material that maintains its quality under frequent use.
Maintenance and Cleaning Needs
Leather requires regular conditioning to prevent drying and cracking, using specialized leather cleaners and conditioners to maintain its natural oils. Faux leather is easier to clean with simple soap and water, but it can be prone to cracking over time without proper care. Both materials benefit from avoiding prolonged exposure to direct sunlight and heat to preserve their appearance and durability.
Environmental Impact
Leather production contributes significantly to deforestation, greenhouse gas emissions, and water pollution due to livestock farming and tanning processes. Faux leather, often made from polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or polyurethane (PU), involves fossil fuel consumption and generates microplastics, raising concerns about its long-term environmental sustainability. Choosing between leather and faux leather requires weighing ecological costs of animal agriculture against the challenges of synthetic material waste and toxicity.
Cost Differences
Leather typically costs significantly more than faux leather due to its natural origin, durability, and labor-intensive tanning process. Faux leather offers a budget-friendly alternative, made from synthetic materials that simulate authentic leather's appearance at a fraction of the price. Your choice between the two often depends on whether long-term investment or short-term affordability is the priority.
Popular Uses in Fashion and Furniture
Leather remains a top choice in luxury fashion items such as handbags, jackets, and shoes due to its durability, natural texture, and aging qualities. Faux leather gains popularity in budget-friendly and vegan fashion accessories, including belts and purses, while also dominating upholstery in contemporary furniture for its easy maintenance and animal-friendly appeal. Both materials are widely used in furniture designs, where genuine leather offers a premium look and feel, and faux leather provides diverse color options and resistance to scratches and stains.
Making the Right Choice: Leather or Faux Leather
Choosing between leather and faux leather depends on factors such as durability, maintenance, cost, and environmental impact. Genuine leather offers long-lasting strength and natural breathability but requires regular conditioning and higher investment, while faux leather provides a budget-friendly, animal-friendly alternative that resists stains and moisture but may lack the same durability and aging quality. Consider personal preferences, ethical values, and intended use to make an informed decision that balances longevity, appearance, and sustainability.
Leather vs Faux Leather Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com