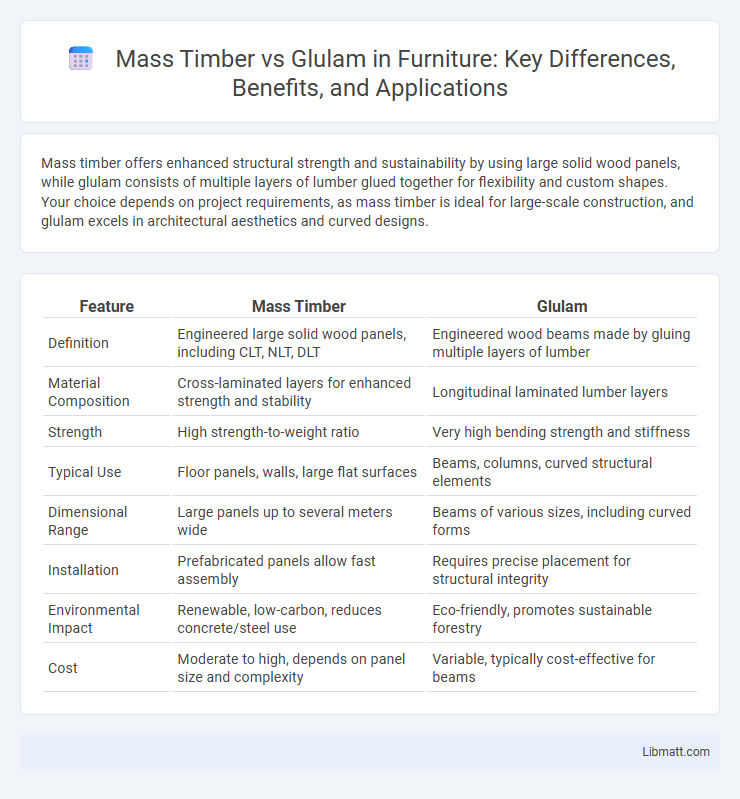
Mass timber offers enhanced structural strength and sustainability by using large solid wood panels, while glulam consists of multiple layers of lumber glued together for flexibility and custom shapes. Your choice depends on project requirements, as mass timber is ideal for large-scale construction, and glulam excels in architectural aesthetics and curved designs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mass Timber | Glulam |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Engineered large solid wood panels, including CLT, NLT, DLT | Engineered wood beams made by gluing multiple layers of lumber |
| Material Composition | Cross-laminated layers for enhanced strength and stability | Longitudinal laminated lumber layers |
| Strength | High strength-to-weight ratio | Very high bending strength and stiffness |
| Typical Use | Floor panels, walls, large flat surfaces | Beams, columns, curved structural elements |
| Dimensional Range | Large panels up to several meters wide | Beams of various sizes, including curved forms |
| Installation | Prefabricated panels allow fast assembly | Requires precise placement for structural integrity |
| Environmental Impact | Renewable, low-carbon, reduces concrete/steel use | Eco-friendly, promotes sustainable forestry |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depends on panel size and complexity | Variable, typically cost-effective for beams |
Overview of Mass Timber and Glulam
Mass timber refers to a category of engineered wood products that includes cross-laminated timber (CLT), nail-laminated timber (NLT), dowel-laminated timber (DLT), and glue-laminated timber (glulam), designed for structural applications. Glulam is a specific type of mass timber made by bonding layers of dimensional lumber with durable, moisture-resistant adhesives, offering exceptional strength and design versatility for beams, columns, and arches. Both mass timber and glulam contribute to sustainable construction practices by using renewable wood resources while providing high load-bearing capacities and aesthetic appeal.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Mass timber consists of large panels made from multiple layers of wood veneers, strands, or boards bonded together with adhesives, optimizing structural strength and sustainability. Glulam, or glued laminated timber, is composed of several layers of dimensional lumber bonded longitudinally with durable adhesives to form strong, versatile beams and columns. Both rely on precise manufacturing processes involving moisture control, adhesive application, and pressing to ensure high-performance structural integrity.
Structural Performance Comparison
Mass timber and glulam both offer exceptional structural performance, with mass timber providing superior strength-to-weight ratios due to its large solid panels, which enhance load distribution and seismic resistance. Glulam, composed of laminated wood layers, offers remarkable flexibility in design and high bending strength, making it ideal for long spans and curved structures. Your project's structural needs will determine the best choice, as mass timber excels in stability and glulam delivers customizable strength for complex architectural forms.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Mass timber and glulam both offer sustainable building solutions by utilizing renewable wood resources and storing carbon dioxide, reducing overall greenhouse gas emissions compared to steel or concrete. Mass timber's large panels are manufactured with minimal adhesives, enhancing recyclability and reducing chemical emissions, while glulam uses laminated smaller wood pieces bonded with eco-friendly adhesives to maximize wood utilization and reduce waste. Both materials contribute to energy-efficient construction, lower embodied energy, and promote sustainable forest management, reinforcing their environmental benefits.
Fire Resistance and Safety Standards
Mass timber products, including cross-laminated timber (CLT) and glulam, are engineered for enhanced fire resistance by charring predictably to maintain structural integrity during exposure. Glulam beams, often subjected to rigorous testing under standards such as ASTM E119 and NFPA 285, demonstrate excellent load-bearing capacity and slower combustion compared to conventional materials. Compliance with fire safety standards like the International Building Code (IBC) ensures both mass timber and glulam meet critical requirements for structural safety and occupant protection in construction.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Appeal
Mass timber offers extensive design flexibility through large panel sizes and varied configurations, enabling architects to create open, airy spaces with unique geometric forms. Glulam, composed of multiple layers of laminated wood, provides exceptional strength and can be shaped into curves and arches, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of your project with warm, natural textures. Both materials allow for innovative designs, but mass timber excels in scale and seamless finishes, while glulam shines in intricate structural beauty.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Mass timber generally offers a competitive cost advantage over glulam due to its efficient manufacturing process and reduced waste. Your overall project budget can benefit from mass timber's faster installation times and lower labor costs compared to the more labor-intensive fabrication of glulam beams. Evaluating lifecycle expenses reveals that mass timber's sustainability and potential for prefabrication often result in better long-term economic value.
Applications in Modern Construction
Mass timber and glulam are pivotal in modern construction for sustainable, efficient building solutions. Mass timber, composed of large solid wood panels like cross-laminated timber, excels in multi-story buildings due to its strength and fire resistance, while glulam, made of glued laminated timber beams, is ideal for long-span structures such as bridges and sports facilities. Your choice depends on project scale and structural demands, with mass timber offering integrated panel systems and glulam providing customized beam shapes for architectural versatility.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Mass timber offers superior durability due to its engineered cross-laminated layers that resist warping and shrinkage, making it ideal for long-term structural stability. Glulam combines multiple timber laminations with strong adhesives, providing excellent resistance to heavy loads and moisture when properly treated, but it requires periodic inspections to prevent delamination or decay. Your choice between mass timber and glulam should factor in the specific environmental conditions and maintenance commitments needed to ensure lasting performance.
Choosing the Right Material: Mass Timber or Glulam
Mass timber offers versatility and sustainability with large engineered panels, while glulam provides exceptional strength through layered wood laminations ideal for beams and columns. Your project's structural requirements and aesthetic goals determine the best choice, as mass timber excels in wide spans and uniform surfaces, whereas glulam allows for customized shapes and load-bearing capacity. Evaluating factors like load, design flexibility, and environmental impact ensures selecting the optimal engineered wood material.
mass timber vs glulam Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com