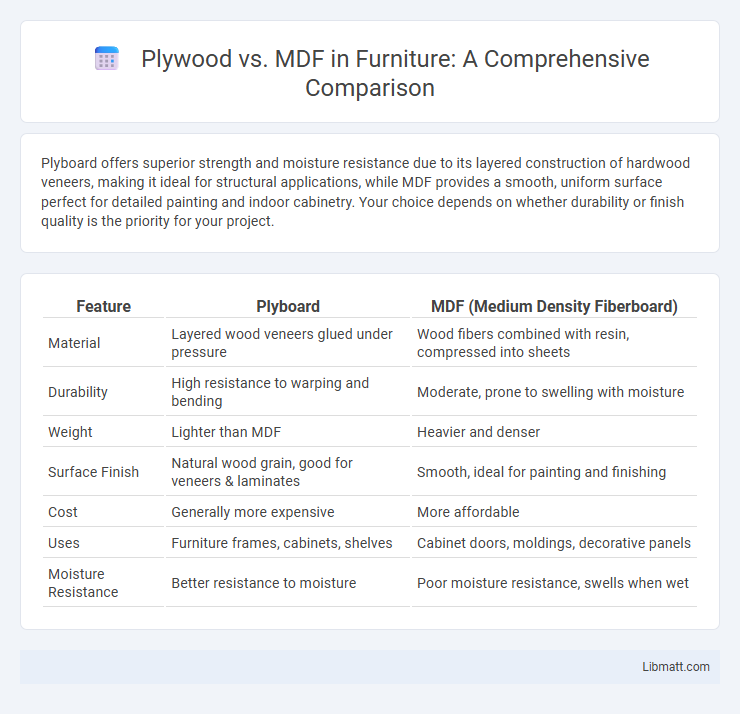
Plyboard offers superior strength and moisture resistance due to its layered construction of hardwood veneers, making it ideal for structural applications, while MDF provides a smooth, uniform surface perfect for detailed painting and indoor cabinetry. Your choice depends on whether durability or finish quality is the priority for your project.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Plyboard | MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard) |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Layered wood veneers glued under pressure | Wood fibers combined with resin, compressed into sheets |
| Durability | High resistance to warping and bending | Moderate, prone to swelling with moisture |
| Weight | Lighter than MDF | Heavier and denser |
| Surface Finish | Natural wood grain, good for veneers & laminates | Smooth, ideal for painting and finishing |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | More affordable |
| Uses | Furniture frames, cabinets, shelves | Cabinet doors, moldings, decorative panels |
| Moisture Resistance | Better resistance to moisture | Poor moisture resistance, swells when wet |
Introduction to Plyboard and MDF
Plyboard consists of multiple layers of wood veneers glued together with grains oriented at right angles for enhanced strength and durability. MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard) is engineered from wood fibers combined with resin and compressed under high pressure to create a smooth, dense surface ideal for precise cutting and painting. Understanding the differences between plyboard and MDF helps you choose the right material for furniture, cabinetry, or interior paneling projects based on strength, finish, and application needs.
Key Differences Between Plyboard and MDF
Plyboard consists of thin layers of wood veneer glued together, providing superior strength, moisture resistance, and durability compared to MDF, which is made from fine wood fibers compressed with resin. MDF offers a smoother surface ideal for painting and detailed cutting but is less resistant to water and heavy loads. The choice between plyboard and MDF hinges on the specific requirements for strength, finish quality, and environmental exposure in furniture or construction projects.
Material Composition Overview
Plywood consists of thin layers of wood veneer glued together with alternating grain directions for enhanced strength and durability. MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard) is made from finely ground wood fibers combined with resin and compressed under high pressure, resulting in a smooth, uniform surface ideal for painting. Understanding the material composition helps you choose the best option for your woodworking or furniture project based on strength, finish, and cost.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Plyboard offers superior durability and strength due to its cross-laminated structure, making it highly resistant to warping and heavy loads compared to MDF, which consists of fine wood fibers bonded with resin and is denser but more prone to damage under stress. MDF provides a smooth surface ideal for intricate finishes but lacks the tensile strength and moisture resistance that plyboard delivers, especially in structural applications. Your choice should consider plyboard for projects requiring long-lasting support, while MDF suits decorative or indoor elements with less mechanical strain.
Cost and Affordability
Plyboard generally offers better durability and moisture resistance, but it comes at a higher cost compared to MDF, which is more affordable and widely available for budget-conscious projects. MDF provides a smooth surface ideal for painting and interior applications while keeping expenses low, making it a practical choice for your cost-sensitive woodworking needs. Evaluating your project's requirements against material prices ensures you select the best balance of affordability and performance.
Workability and Ease of Use
Plyboard offers superior workability due to its natural wood grain, allowing for easier cutting, nailing, and drilling with minimal splitting. MDF, being a dense composite material, provides a smooth, uniform surface ideal for painting and detailed routing but requires sharper tools and careful handling to avoid chipping. Both materials are versatile, with plyboard favored for structural projects and MDF preferred in fine cabinetry and intricate moldings.
Applications and Common Uses
Plywood is widely used in construction, cabinetry, and furniture making due to its strength, durability, and resistance to moisture, making it ideal for structural applications and outdoor projects. MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard) is preferred for interior applications like molding, cabinetry, and decorative paneling because of its smooth surface, ease of machining, and affordability. Both materials are essential in woodworking but serve different purposes based on their physical properties and intended use.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Plyboard is generally considered more environmentally friendly than MDF due to its use of larger wood veneers that require less adhesive resin, reducing formaldehyde emissions. MDF production involves fine wood fibers bonded with synthetic resins, which can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and contribute to indoor air pollution. Sustainable sourcing and certification, such as FSC or PEFC, play a critical role in minimizing the environmental footprint of both materials by ensuring responsible forest management.
Aesthetic and Finish Options
Plywood offers a natural wood grain finish that can be easily stained or varnished to enhance its appearance, making it ideal for visible furniture and cabinetry. MDF provides a smooth and consistent surface perfect for painting and intricate designs, giving you more flexibility for customized aesthetic finishes. Choosing between plywood and MDF depends on whether you prefer the textured, authentic look of wood or the sleek, uniform finish of engineered board.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Plyboard offers superior strength, moisture resistance, and durability, making it ideal for structural projects and areas exposed to humidity, such as kitchens and bathrooms. MDF provides a smooth, uniform surface perfect for detailed painting and indoor furniture where precision and finish matter most. Selecting between plyboard and MDF depends on project requirements, prioritizing load-bearing capacity and moisture exposure for plyboard, or a refined finish and easy machining for MDF.
Plyboard vs MDF Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com