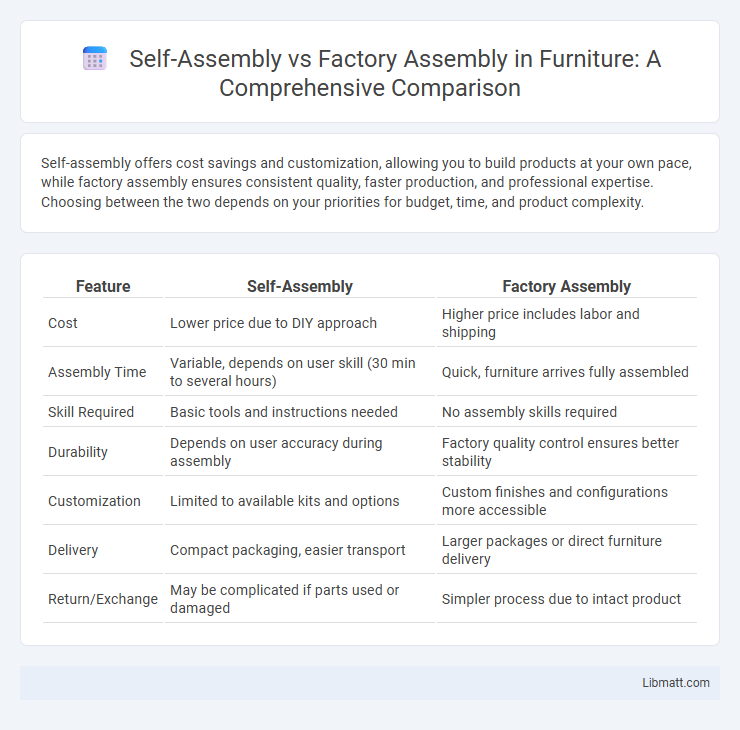
Self-assembly offers cost savings and customization, allowing you to build products at your own pace, while factory assembly ensures consistent quality, faster production, and professional expertise. Choosing between the two depends on your priorities for budget, time, and product complexity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Self-Assembly | Factory Assembly |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lower price due to DIY approach | Higher price includes labor and shipping |
| Assembly Time | Variable, depends on user skill (30 min to several hours) | Quick, furniture arrives fully assembled |
| Skill Required | Basic tools and instructions needed | No assembly skills required |
| Durability | Depends on user accuracy during assembly | Factory quality control ensures better stability |
| Customization | Limited to available kits and options | Custom finishes and configurations more accessible |
| Delivery | Compact packaging, easier transport | Larger packages or direct furniture delivery |
| Return/Exchange | May be complicated if parts used or damaged | Simpler process due to intact product |
Introduction to Self-Assembly and Factory Assembly
Self-assembly involves building products by individuals using pre-packaged parts, emphasizing customization and cost savings, while factory assembly relies on automated processes and skilled labor to produce items at scale with consistent quality. Self-assembly suits consumers seeking hands-on involvement and budget-friendly options, whereas factory assembly prioritizes efficiency, speed, and uniformity in mass production. Your choice depends on factors like desired level of involvement, product complexity, and delivery timelines.
Core Principles of Self-Assembly
Self-assembly relies on the intrinsic ability of components to organize themselves into structured patterns through local interactions and chemical affinities without external guidance. Core principles include reversible bonding, molecular recognition, and energy minimization, which drive components to reach a stable, ordered state autonomically. Understanding these principles can help you harness self-assembly for innovative material design and nanotechnology applications.
Key Processes in Factory Assembly
Factory assembly involves standardized manufacturing processes such as automated component fitting, quality inspections, and precision calibration to ensure product consistency and efficiency. Skilled technicians and robotic systems work in tandem to optimize assembly lines, reducing human error and production time. Your products benefit from streamlined workflows, rigorous testing, and scalable output in factory assembly environments.
Advantages of Self-Assembly
Self-assembly offers significant cost savings by eliminating factory labor fees and reducing transportation expenses due to compact packaging. It allows for greater customization and flexibility, enabling you to tailor components to specific needs or preferences during the assembly process. This approach can also lead to faster delivery times and environmental benefits by minimizing packaging waste and reducing the carbon footprint associated with assembled product shipments.
Benefits of Factory Assembly
Factory assembly ensures consistent quality control through standardized processes and experienced technicians, reducing errors and defects. It significantly accelerates production time by utilizing specialized equipment and streamlined workflows, leading to faster product availability. Factory assembly also enhances cost efficiency by minimizing material waste and optimizing labor, resulting in lower overall manufacturing expenses.
Challenges Faced in Self-Assembly
Self-assembly faces challenges such as limited precision and variability in component alignment, which can hinder consistent product quality. Environmental factors like temperature and humidity fluctuations often impact the reliability and repeatability of the assembly process. Scalability remains an issue due to the dependence on molecular interactions and slower production rates compared to automated factory assembly lines.
Limitations of Factory Assembly
Factory assembly faces limitations such as high setup costs and reduced customization options compared to self-assembly, restricting flexibility for unique or small-scale production runs. It often requires specialized machinery and skilled labor, increasing dependency on factory availability and maintenance schedules. Moreover, delays in factory workflows can impact lead times, reducing responsiveness to urgent market demands.
Applications and Real-World Examples
Self-assembly is widely used in nanotechnology and biotechnology, enabling the formation of complex molecular structures such as DNA origami and lipid bilayers, while factory assembly dominates in automotive and electronics manufacturing, streamlining mass production with precision machinery. Real-world applications of self-assembly include drug delivery systems and the creation of wearable sensors, whereas factory assembly lines are integral to producing smartphones and automobiles efficiently. Understanding the differences in these methods can help you choose the best approach for your product development needs.
Cost and Efficiency Comparison
Self-assembly often reduces initial costs by eliminating labor expenses, but efficiency may decline due to longer assembly time and potential errors. Factory assembly benefits from streamlined processes, higher precision, and faster production rates, though it usually entails higher upfront costs for labor and machinery. Your choice depends on balancing budget constraints against desired quality and turnaround time.
Future Trends in Assembly Methods
Future trends in assembly methods emphasize increased automation and integration of smart technologies in both self-assembly and factory assembly processes. Advances in robotics, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are driving more flexible, scalable, and efficient assembly systems that reduce human intervention and errors. The rise of modular designs and adaptive manufacturing platforms supports seamless transitions between self-assembly and factory assembly, optimizing production speed and customization.
Self-assembly vs factory assembly Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com