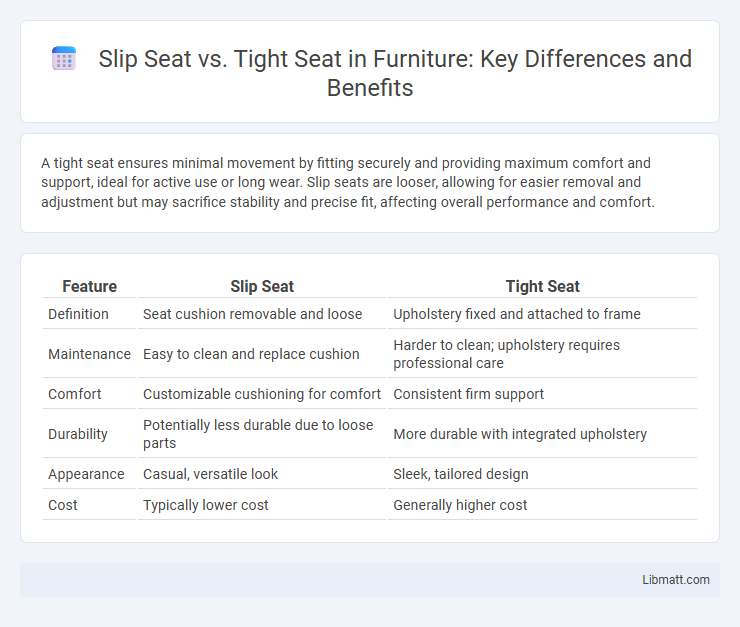
A tight seat ensures minimal movement by fitting securely and providing maximum comfort and support, ideal for active use or long wear. Slip seats are looser, allowing for easier removal and adjustment but may sacrifice stability and precise fit, affecting overall performance and comfort.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Slip Seat | Tight Seat |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Seat cushion removable and loose | Upholstery fixed and attached to frame |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean and replace cushion | Harder to clean; upholstery requires professional care |
| Comfort | Customizable cushioning for comfort | Consistent firm support |
| Durability | Potentially less durable due to loose parts | More durable with integrated upholstery |
| Appearance | Casual, versatile look | Sleek, tailored design |
| Cost | Typically lower cost | Generally higher cost |
Introduction to Slip Seat and Tight Seat
Slip seat and tight seat are two common seating configurations used in workplace and transportation settings to optimize space and flexibility. A slip seat setup allows multiple users to share a single workstation or seat without permanent assignments, enhancing resource efficiency in dynamic environments. Conversely, a tight seat is assigned exclusively to one individual, offering personalized comfort and consistency but less adaptability for fluctuating user demands.
Defining Slip Seat: What Does It Mean?
Slip seat refers to an airline seating policy where passengers are not assigned fixed seats before boarding, allowing airlines to allocate seats dynamically based on operational needs. This flexible seating approach helps optimize aircraft capacity, accommodate last-minute changes, and streamline boarding processes. Understanding slip seat policies can help you anticipate seat assignments and improve your travel experience.
Understanding Tight Seat: Key Features
Tight seat refers to seating designed with a snug fit, often utilizing materials like neoprene or memory foam to provide firm support and prevent slipping. This type of seat maintains consistent positioning, enhancing stability and comfort during activities such as cycling or rowing. Your performance benefits from the reduced movement and improved contact, ensuring better control and reduced fatigue.
Operational Differences Between Slip Seat and Tight Seat
Slip seat operations allow employees to use shared workstations flexibly, improving space utilization and reducing real estate costs. Tight seat setups assign specific desks to individual employees, enhancing personalization and equipment consistency but limiting adaptability. Your choice depends on operational priorities like workforce mobility, collaboration needs, and resource allocation.
Pros and Cons of Slip Seat Trucking
Slip seat trucking offers flexibility by allowing drivers to use different trucks without being assigned a specific vehicle, which can increase operational efficiency and reduce downtime. However, it may lead to less familiarity with individual trucks, potentially affecting maintenance awareness and driver comfort. While tight seat trucking promotes consistency and accountability by assigning drivers to specific trucks, it can limit adaptability and increase vehicle idle time when drivers are unavailable.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Tight Seat Assignments
Tight seat assignments maximize space utilization by ensuring every seat is occupied, reducing empty spots and increasing passenger capacity on flights or events. This method can streamline boarding processes and enhance revenue per flight or venue but may reduce passenger comfort due to limited flexibility in seating choices. Passengers often perceive tight seat assignments as restrictive, leading to decreased satisfaction and less opportunity for accommodating special requests or last-minute changes.
Impact on Driver Work-Life Balance
Slip seating allows multiple drivers to share the same seat, increasing flexibility and reducing individual assignment stress, which can enhance work-life balance by allowing varied schedules and more efficient use of resources. Tight seating assigns a fixed seat to each driver, providing a stable and consistent workspace that can improve comfort and a sense of ownership but may limit schedule flexibility and increase commuting stress. Drivers using slip seating may experience less control over their work environment, impacting rest and recovery, while tight seating supports routine but can reduce adaptability to personal life demands.
Effects on Fleet Efficiency and Utilization
Slip seating increases fleet efficiency by allowing multiple employees to share a single workstation or vehicle without assigned spots, reducing idle time and maximizing utilization rates. Tight seating limits flexibility by assigning fixed seats, often resulting in underutilized resources and decreased operational agility. Optimizing seat allocation policies can lead to higher productivity and cost savings across fleet management systems.
Which Is Better: Slip Seat vs Tight Seat?
Slip seats offer flexibility by allowing quick adjustments and easy boarding for multiple users, making them ideal for dynamic environments. Tight seats provide a secure, fixed position that enhances stability and comfort, perfect for consistent, long-duration use. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize adaptability or firm support in your seating needs.
Choosing the Right Seating Arrangement for Your Fleet
Choosing between slip seat and tight seat configurations depends on your fleet's operational needs and employee workflow. Slip seats offer flexibility by allowing multiple drivers to share vehicles without assigned seating, increasing utilization and reducing downtime. Tight seats provide dedicated workstations, enhancing driver comfort and personalization but may limit vehicle sharing and scheduling flexibility in your fleet.
slip seat vs tight seat Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com