Solar control coated glass blocks a significant portion of infrared and ultraviolet rays while maintaining high visible light transmission, enhancing energy efficiency and reducing glare without darkening your view. Tinted glass, on the other hand, absorbs and reduces visible light across all wavelengths, resulting in darker interiors but less effective heat rejection compared to solar control coatings.
Table of Comparison
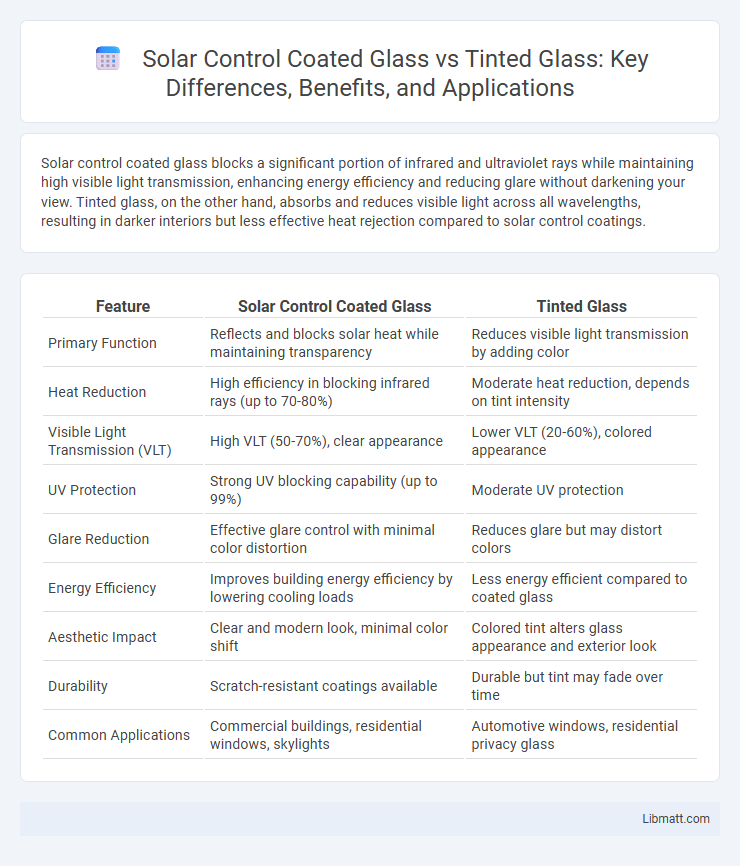
| Feature | Solar Control Coated Glass | Tinted Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Reflects and blocks solar heat while maintaining transparency | Reduces visible light transmission by adding color |
| Heat Reduction | High efficiency in blocking infrared rays (up to 70-80%) | Moderate heat reduction, depends on tint intensity |
| Visible Light Transmission (VLT) | High VLT (50-70%), clear appearance | Lower VLT (20-60%), colored appearance |
| UV Protection | Strong UV blocking capability (up to 99%) | Moderate UV protection |
| Glare Reduction | Effective glare control with minimal color distortion | Reduces glare but may distort colors |
| Energy Efficiency | Improves building energy efficiency by lowering cooling loads | Less energy efficient compared to coated glass |
| Aesthetic Impact | Clear and modern look, minimal color shift | Colored tint alters glass appearance and exterior look |
| Durability | Scratch-resistant coatings available | Durable but tint may fade over time |
| Common Applications | Commercial buildings, residential windows, skylights | Automotive windows, residential privacy glass |
Introduction to Solar Control Glass and Tinted Glass
Solar control coated glass features a specialized low-emissivity coating that reflects infrared heat while allowing visible light to pass through, enhancing energy efficiency and indoor comfort. Tinted glass incorporates color pigments throughout the glass to reduce glare and solar heat gain by absorbing a portion of sunlight, which can also affect the natural light entering your space. Choosing between these options depends on your priorities for light transmission, heat reduction, and aesthetic preferences in architectural applications.
How Solar Control Coated Glass Works
Solar control coated glass works by applying a thin, transparent metallic layer that reflects infrared radiation while allowing visible light to pass through, reducing heat gain inside buildings. This specialized coating helps maintain indoor temperature by blocking solar heat without significantly darkening your view, unlike tinted glass which absorbs and reduces light transmission. Your energy efficiency improves as solar control coated glass minimizes reliance on air conditioning, enhancing comfort and lowering utility costs.
The Science Behind Tinted Glass
Tinted glass works by incorporating metal oxides or other compounds during manufacturing that absorb and filter specific wavelengths of solar radiation, reducing heat and glare transmission. This selective absorption lowers solar heat gain inside buildings or vehicles, improving energy efficiency and occupant comfort. Compared to solar control coated glass, which uses thin coatings to reflect infrared radiation, tinted glass primarily relies on bulk material properties to manage light and heat.
Key Differences Between Solar Control Coated and Tinted Glass
Solar control coated glass uses a thin, transparent metallic layer to reflect infrared and ultraviolet rays, enhancing energy efficiency without significantly reducing visible light transmission. Tinted glass contains color additives that absorb both solar heat and visible light, resulting in reduced glare and darker appearance but lower natural light penetration. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize heat rejection with clear views or reduced brightness with a shaded effect.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Solar control coated glass significantly outperforms tinted glass in energy efficiency by reflecting a higher percentage of solar heat while allowing ample natural light, reducing cooling costs and maintaining indoor comfort. Tinted glass absorbs and blocks some solar energy, which can lower heat gain but often results in darker interiors and increased reliance on artificial lighting. Choosing solar control coated glass optimizes your building's energy consumption by balancing heat rejection and daylight transmission more effectively than tinted glass.
Light Transmission and Visual Comfort
Solar control coated glass significantly reduces solar heat gain while maintaining high visible light transmission, ensuring optimal daylight without excessive glare. Tinted glass absorbs and blocks a portion of sunlight, which lowers light transmission and can create a dimmer interior environment, potentially affecting visual comfort. Your choice between these glasses impacts how natural light is managed, balancing energy efficiency with clear views and indoor comfort.
Heat Reduction Capabilities
Solar control coated glass reduces heat by reflecting infrared radiation while maintaining high visible light transmission, making it highly effective for energy-efficient cooling. Tinted glass absorbs solar energy, resulting in moderate heat reduction but lower visible light transmission, which can darken interiors. Solar control coatings offer superior heat rejection without compromising natural daylight, ideal for climate-sensitive architectural applications.
Aesthetic Impact on Building Design
Solar control coated glass enhances building aesthetics by maintaining clarity and brightness while reducing glare and heat, preserving natural light without altering color perception. Tinted glass, conversely, imparts a colored or shaded appearance that can impact the building's facade by reducing visible light transmission and modifying exterior hues. Choosing solar control coated glass supports a sleek, modern design with energy efficiency, whereas tinted glass offers a distinctive stylistic effect alongside solar heat reduction.
Cost Considerations and Long-Term Value
Solar control coated glass typically has a higher upfront cost than tinted glass due to advanced manufacturing processes that enhance energy efficiency by reflecting infrared radiation while maintaining visible light transmission. Although tinted glass is less expensive initially, it may reduce natural daylight and offer limited heat reduction, potentially increasing cooling costs over time. Investing in solar control coated glass delivers superior long-term value through lower energy bills, improved indoor comfort, and increased property value, offsetting the higher installation price.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Project
Solar control coated glass offers superior heat rejection and UV protection, making it ideal for energy-efficient buildings that reduce cooling costs. Tinted glass provides aesthetic appeal and glare reduction but may compromise natural light and energy performance. You should evaluate factors such as climate, building orientation, and energy goals to determine which glass best suits your project's needs.
Solar control coated glass vs tinted glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com