Curved glass features a smooth, continuous curve formed by heating and shaping a single glass sheet, offering aesthetic appeal and structural strength for modern architectural designs. Bent laminated glass combines multiple layers bonded with interlayers, enhancing safety and flexibility while maintaining the curved form, making it ideal for applications requiring both durability and impact resistance.
Table of Comparison
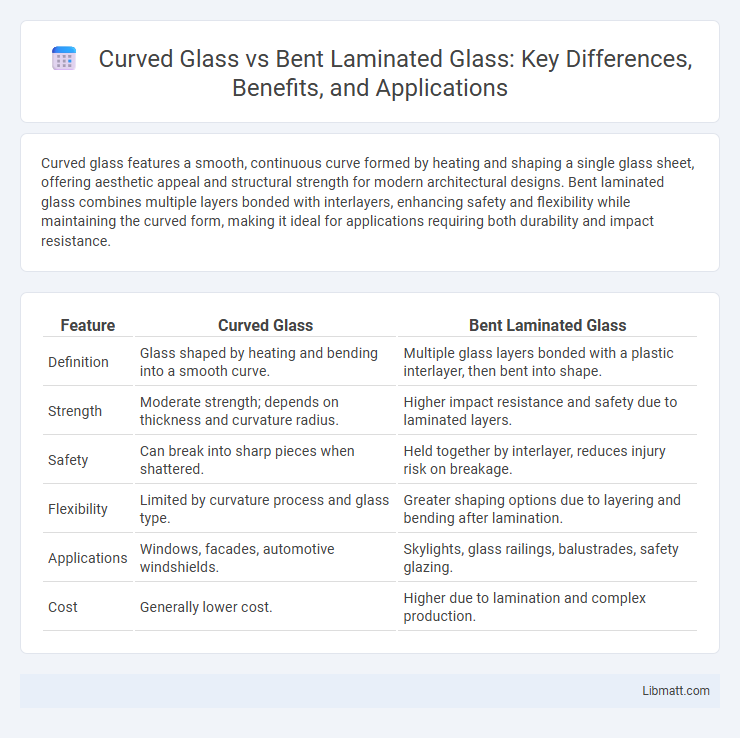
| Feature | Curved Glass | Bent Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Glass shaped by heating and bending into a smooth curve. | Multiple glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, then bent into shape. |
| Strength | Moderate strength; depends on thickness and curvature radius. | Higher impact resistance and safety due to laminated layers. |
| Safety | Can break into sharp pieces when shattered. | Held together by interlayer, reduces injury risk on breakage. |
| Flexibility | Limited by curvature process and glass type. | Greater shaping options due to layering and bending after lamination. |
| Applications | Windows, facades, automotive windshields. | Skylights, glass railings, balustrades, safety glazing. |
| Cost | Generally lower cost. | Higher due to lamination and complex production. |
Introduction to Curved Glass and Bent Laminated Glass
Curved glass is shaped by heating and bending flat glass sheets into smooth, continuous curves, commonly used in architectural facades and automotive windshields. Bent laminated glass combines the strength of multiple glass layers with interlayer bonding, molded into precise angles or curves for enhanced safety and design flexibility in structural applications. Both types offer distinct aesthetic and functional advantages, with curved glass emphasizing fluid form and bent laminated glass providing impact resistance and durability.
Manufacturing Processes: Curved vs Bent Laminated Glass
Curved glass is produced by heating flat glass sheets until pliable and then shaping them over molds or forms to achieve the desired curvature, followed by controlled cooling to maintain structural integrity. Bent laminated glass combines the bending process with lamination, where multiple glass layers are heated and bent simultaneously before being bonded with interlayers to enhance strength and safety. The lamination step in bent laminated glass adds complexity to manufacturing, requiring precise alignment and curing to ensure durability and optical clarity.
Structural Properties and Durability Comparison
Curved glass offers high structural rigidity and excellent load-bearing capacity due to its uniform bend, while bent laminated glass combines multiple layers with interlayers that enhance impact resistance and prevent shattering. Bent laminated glass provides superior durability against impacts and environmental stressors, maintaining structural integrity even when cracked, whereas curved glass may be more prone to breakage without the protective laminate. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize the sleek, continuous form of curved glass or the enhanced safety and longevity of bent laminated glass in demanding architectural applications.
Aesthetic Differences and Design Flexibility
Curved glass offers smooth, continuous bends achievable through heat treatment, enabling sleek, modern aesthetics with uniform curvature ideal for high-end architectural applications. Bent laminated glass combines multiple glass layers bonded with interlayers, allowing more complex, multi-directional shapes and enhanced structural safety while maintaining transparent design versatility. Both materials provide distinct design flexibility, with curved glass emphasizing elegance and uniform curvature, and bent laminated glass prioritizing customized shapes and durability for innovative facade designs.
Safety Features: Curved vs Bent Laminated Glass
Bent laminated glass offers enhanced safety features compared to curved glass due to its multilayered structure, which prevents shattering and holds fragments together in case of breakage. Curved glass, while visually appealing, lacks the laminated interlayer, making it more prone to dangerous shards upon impact. The laminated composition of bent glass significantly improves resistance to impact, providing superior protection in architectural and automotive applications.
Common Applications in Architecture and Interior Design
Curved glass is commonly used in storefronts, facades, and large architectural features where smooth, continuous shapes enhance aesthetic appeal and allow for panoramic views. Bent laminated glass, with its added structural strength and safety features, is favored for interior partitions, balustrades, and staircases where both design flexibility and impact resistance are critical. Your choice between these materials should consider the specific architectural demands and safety codes relevant to your project's environment.
Cost Considerations and Budget Implications
Curved glass typically incurs higher costs due to the specialized machinery and precise manufacturing processes required, leading to increased labor and production time. Bent laminated glass offers a cost-effective alternative by combining layers of glass with flexible interlayers, reducing raw material waste and fabrication expenses. If your project demands budget efficiency without sacrificing aesthetic appeal, bent laminated glass presents a strategic choice over traditional curved glass options.
Energy Efficiency and Thermal Performance
Curved glass typically offers moderate energy efficiency due to its shape, which can influence solar heat gain and natural light penetration, but may require additional treatments for enhanced thermal performance. Bent laminated glass, composed of multiple layers bonded with interlayers, provides superior thermal insulation and energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer and improving thermal break properties. Both types can incorporate low-emissivity coatings and gas fills to optimize thermal performance, with bent laminated glass often preferred in applications demanding higher energy efficiency standards.
Maintenance and Longevity
Curved glass requires regular cleaning with non-abrasive materials to maintain its clarity and smooth surfaces, while bent laminated glass benefits from its durable interlayer that resists delamination and enhances structural integrity over time. Both glass types are designed for longevity, but bent laminated glass typically offers superior resistance to impact and environmental wear, reducing maintenance frequency. Your choice should consider the specific application environment, as bent laminated glass provides enhanced safety and durability, ensuring longer-lasting performance with minimal upkeep.
Choosing the Right Glass: Factors to Consider
Curved glass offers seamless, smooth contours ideal for aesthetic architectural designs, while bent laminated glass provides enhanced safety and structural integrity through multiple bonded layers. When choosing the right glass, consider factors such as the desired curvature precision, impact resistance requirements, thickness, and installation environment. Cost differences and maintenance needs also influence the selection between curved glass and bent laminated options for both commercial and residential projects.
curved glass vs bent laminated glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com