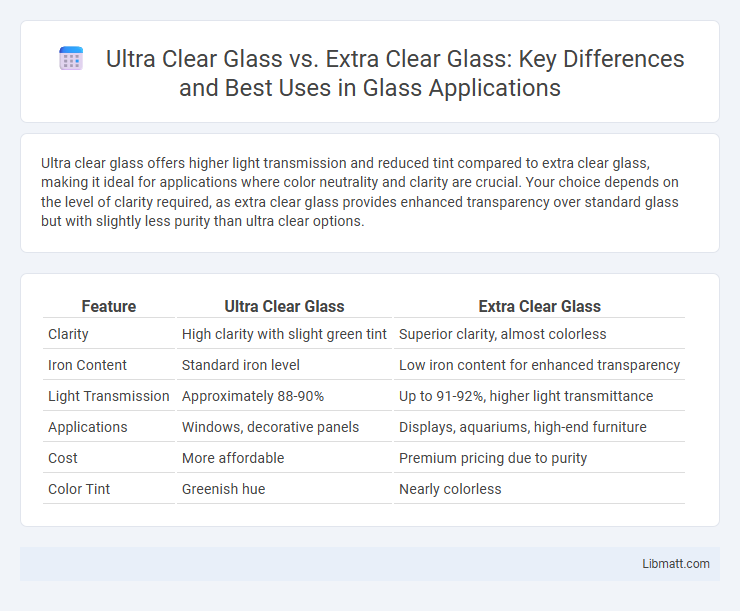
Ultra clear glass offers higher light transmission and reduced tint compared to extra clear glass, making it ideal for applications where color neutrality and clarity are crucial. Your choice depends on the level of clarity required, as extra clear glass provides enhanced transparency over standard glass but with slightly less purity than ultra clear options.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ultra Clear Glass | Extra Clear Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Clarity | High clarity with slight green tint | Superior clarity, almost colorless |
| Iron Content | Standard iron level | Low iron content for enhanced transparency |
| Light Transmission | Approximately 88-90% | Up to 91-92%, higher light transmittance |
| Applications | Windows, decorative panels | Displays, aquariums, high-end furniture |
| Cost | More affordable | Premium pricing due to purity |
| Color Tint | Greenish hue | Nearly colorless |
Introduction to Ultra Clear Glass vs Extra Clear Glass
Ultra clear glass offers a higher purity level with reduced green tint due to lower iron content compared to extra clear glass, making it ideal for applications requiring maximum transparency and color accuracy. Extra clear glass still maintains excellent clarity but may exhibit a slight green hue that is less desirable for high-end displays or artistic installations. Understanding the difference helps you choose the best glass type to enhance visual performance in architectural and decorative projects.
What is Ultra Clear Glass?
Ultra Clear Glass, also known as low-iron glass, contains significantly reduced iron content compared to standard glass, resulting in higher light transmittance and enhanced clarity. This type of glass exhibits minimal greenish tint, making it ideal for applications requiring true color representation, such as display cases, aquariums, and architectural facades. Its purity and transparency outperform Extra Clear Glass, which has slightly higher iron levels and less optical clarity.
What is Extra Clear Glass?
Extra clear glass is characterized by its minimal green tint, achieved by reducing iron content to less than 0.03%, enhancing light transmission up to 91% compared to 83-85% in standard clear glass. This ultra-low iron composition offers superior color neutrality and clarity, making it ideal for applications like aquariums, display cases, and frameless glass installations where true color representation is critical. Its high transparency and reduced green hue differentiate it from regular ultra clear glass, which may have slightly higher iron levels and less light transmission efficiency.
Key Differences Between Ultra Clear and Extra Clear Glass
Ultra clear glass contains a higher purity of raw materials, resulting in a lower iron content that reduces the greenish tint found in extra clear glass. Extra clear glass typically has an iron oxide content around 0.03%, while ultra clear glass can have levels as low as 0.01%, providing superior light transmittance of up to 91-92%. The reduced green tint and increased clarity of ultra clear glass make it ideal for applications requiring true color representation, such as display cases and high-end architectural projects.
Composition and Light Transmission
Ultra clear glass, also known as low-iron glass, contains significantly reduced iron content compared to extra clear glass, resulting in enhanced light transmission of up to 91%. Extra clear glass typically has higher iron levels, limiting its light transmission to around 89%, which can cause a slight greenish tint. The reduced iron in ultra clear glass minimizes color distortion, making it ideal for applications requiring maximum transparency and true color visibility.
Visual Clarity and Color Accuracy
Ultra clear glass offers superior visual clarity and color accuracy compared to extra clear glass due to its reduced green tint caused by lower iron content. This results in more true-to-life colors and enhanced transparency, making ultra clear glass ideal for applications requiring pristine optical quality, such as high-end displays and museum cases. Extra clear glass, while still offering good clarity, exhibits slight color distortion with a subtle green hue, which may affect color perception in critical viewing environments.
Applications and Use Cases
Ultra clear glass is ideal for applications requiring maximum light transmission and true color representation, such as high-end display cases, aquariums, and luxury storefronts, where clarity and visual impact are critical. Extra clear glass is commonly used in windows, solar panels, and architectural projects that benefit from reduced green tint and enhanced transparency but do not demand absolute color neutrality. Your choice between ultra clear and extra clear glass should depend on the specific optical performance and aesthetic requirements of your project.
Durability and Maintenance
Ultra clear glass, also known as low-iron glass, offers higher clarity and reduced green tint compared to extra clear glass, enhancing visibility and aesthetic appeal. Both types demonstrate strong durability with comparable resistance to scratches and impacts, but ultra clear glass typically requires less maintenance due to its superior resistance to staining and discoloration. For applications demanding long-lasting transparency and minimal upkeep, ultra clear glass provides a more durable and maintenance-friendly solution than extra clear glass.
Cost Comparison
Ultra clear glass typically costs more than extra clear glass due to higher purity levels and reduced iron content, enhancing transparency and color fidelity. This premium pricing reflects advanced manufacturing processes that minimize greenish tint, making ultra clear glass ideal for display and architectural applications where clarity is paramount. Your choice depends on budget constraints and the importance of optical performance for your project.
How to Choose Between Ultra Clear and Extra Clear Glass
Choosing between ultra clear and extra clear glass depends on the desired level of light transmission and color neutrality; ultra clear glass typically offers higher clarity with minimal green tint, ideal for showcasing artwork or high-end displays. Extra clear glass, while still providing excellent transparency, contains slightly more iron content, resulting in a subtle greenish hue but often at a lower cost. Evaluate the specific application requirements, budget, and aesthetic preferences to determine which glass type aligns best with your project goals.
ultra clear glass vs extra clear glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com