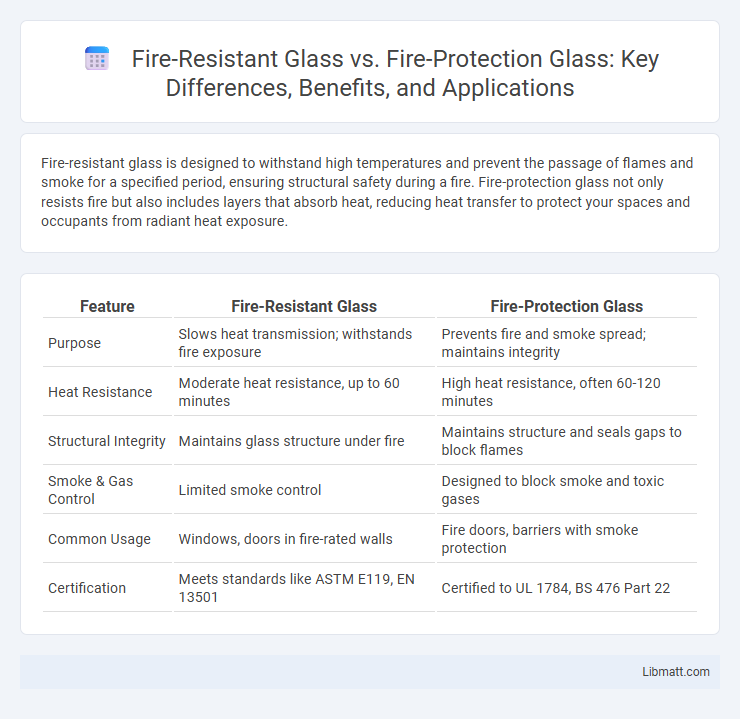
Fire-resistant glass is designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent the passage of flames and smoke for a specified period, ensuring structural safety during a fire. Fire-protection glass not only resists fire but also includes layers that absorb heat, reducing heat transfer to protect your spaces and occupants from radiant heat exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fire-Resistant Glass | Fire-Protection Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Slows heat transmission; withstands fire exposure | Prevents fire and smoke spread; maintains integrity |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate heat resistance, up to 60 minutes | High heat resistance, often 60-120 minutes |
| Structural Integrity | Maintains glass structure under fire | Maintains structure and seals gaps to block flames |
| Smoke & Gas Control | Limited smoke control | Designed to block smoke and toxic gases |
| Common Usage | Windows, doors in fire-rated walls | Fire doors, barriers with smoke protection |
| Certification | Meets standards like ASTM E119, EN 13501 | Certified to UL 1784, BS 476 Part 22 |
Introduction to Fire-Resistant and Fire-Protection Glass
Fire-resistant glass is specifically designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent flames and smoke from passing through for a certain period, making it essential for fire containment in buildings. Fire-protection glass, while also resistant to fire, emphasizes limiting heat transfer and protecting occupants by maintaining visibility and structural integrity during a fire event. Your choice between these glasses should depend on whether containment or heat insulation is the primary safety requirement in your project.
Key Differences Between Fire-Resistant and Fire-Protection Glass
Fire-resistant glass is designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of fire and smoke for a specified period, typically offering insulation and integrity ratings, while fire-protection glass primarily aims to provide a barrier against fire and heat without necessarily offering insulation. Fire-resistant glass usually contains special intumescent interlayers or multiple glazing layers that expand when exposed to heat, maintaining structural stability, whereas fire-protection glass often focuses on holding off flames and reducing radiant heat transmission. The key difference lies in fire-resistant glass's ability to both resist flames and insulate, whereas fire-protection glass mainly prevents flame spread with less emphasis on thermal insulation.
How Fire-Resistant Glass Works
Fire-resistant glass works by incorporating special interlayers that expand under high temperatures to create an insulating barrier, preventing the spread of flames and smoke. This glass maintains its structural integrity for a specified duration, typically ranging from 20 to 120 minutes, depending on the classification. The fire-resistance mechanism ensures that heat transfer is minimized, protecting occupants and property during fire emergencies.
How Fire-Protection Glass Functions
Fire-protection glass functions by forming a dense, insulating barrier during a fire, preventing the spread of flames, smoke, and heat for a specified time. It contains special interlayers or coatings that expand or char when exposed to high temperatures, maintaining structural integrity and visibility. This glass is essential in fire-rated doors and windows to ensure occupant safety and compliance with fire safety standards.
Applications and Use Cases for Fire-Resistant Glass
Fire-resistant glass is designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of flames for a specified period, making it ideal for applications in fire doors, partitions, and windows in commercial buildings and healthcare facilities. This glass is commonly used in areas where maintaining structural integrity during a fire is critical, such as escape routes and fire barriers. Your choice of fire-resistant glass ensures enhanced safety and compliance with fire codes in environments prone to fire hazards.
Common Uses for Fire-Protection Glass
Fire-protection glass is commonly used in commercial buildings, hospitals, schools, and high-occupancy environments where strict fire safety regulations require barriers that prevent the spread of flames and smoke. This type of glass is designed to maintain structural integrity and block heat transfer, providing critical evacuation time during a fire emergency. Your choice of fire-protection glass enhances safety by meeting fire containment standards such as UL 752 and NFPA 80.
Performance Ratings and Standards Comparison
Fire-resistant glass and fire-protection glass are evaluated using specific performance ratings and standards that measure their ability to withstand high temperatures and prevent flame penetration. Fire-resistant glass typically meets standards such as UL 9 and BS 476 Part 22, with fire ratings ranging from 20 to 120 minutes, indicating its capacity to maintain integrity and insulation during fire exposure. Fire-protection glass is often rated under standards like ASTM E119 and EN 13501-2, focusing on its ability to prevent the spread of smoke and radiant heat, with performance levels that complement structural fire safety requirements.
Installation Requirements and Considerations
Fire-resistant glass and fire-protection glass each demand specific installation requirements to ensure optimal performance in fire safety. Fire-resistant glass must be installed within certified framing systems and typically requires precise sealing and support to maintain its integrity under high temperatures. Your choice between these glass types should consider compatibility with surrounding materials, building codes, and inspection protocols to ensure compliance and effective fire containment.
Cost Factors: Fire-Resistant vs Fire-Protection Glass
Fire-resistant glass generally incurs higher costs due to its ability to withstand extreme heat for extended periods, often requiring specialized manufacturing processes and materials like ceramic or tempered glass. Fire-protection glass tends to be more affordable but may offer shorter fire rating durations, relying on intumescent layers that expand to block heat and smoke. Installation expenses and compliance with building codes also influence overall pricing between fire-resistant and fire-protection glass options.
Choosing the Right Glass Type for Your Project
Fire-resistant glass offers high-temperature resistance, preventing flames from passing through and maintaining structural integrity in fire scenarios. Fire-protection glass provides not only heat resistance but also limits smoke and toxic gas spread, enhancing safety for occupants. Your choice between these glass types depends on specific building codes, fire safety requirements, and the level of protection needed for your project.
Fire-resistant glass vs fire-protection glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com