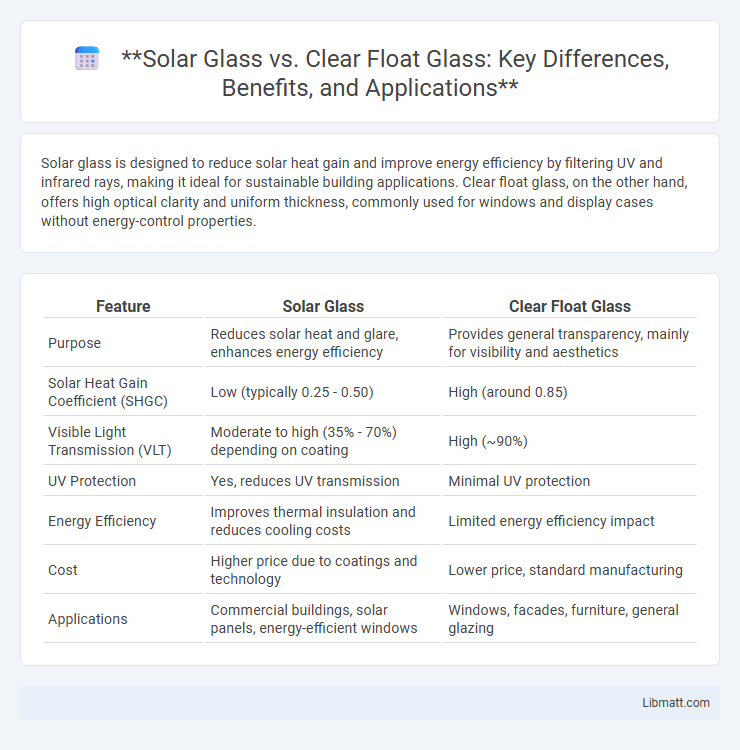
Solar glass is designed to reduce solar heat gain and improve energy efficiency by filtering UV and infrared rays, making it ideal for sustainable building applications. Clear float glass, on the other hand, offers high optical clarity and uniform thickness, commonly used for windows and display cases without energy-control properties.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Solar Glass | Clear Float Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Reduces solar heat and glare, enhances energy efficiency | Provides general transparency, mainly for visibility and aesthetics |
| Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) | Low (typically 0.25 - 0.50) | High (around 0.85) |
| Visible Light Transmission (VLT) | Moderate to high (35% - 70%) depending on coating | High (~90%) |
| UV Protection | Yes, reduces UV transmission | Minimal UV protection |
| Energy Efficiency | Improves thermal insulation and reduces cooling costs | Limited energy efficiency impact |
| Cost | Higher price due to coatings and technology | Lower price, standard manufacturing |
| Applications | Commercial buildings, solar panels, energy-efficient windows | Windows, facades, furniture, general glazing |
Introduction to Solar Glass and Clear Float Glass
Solar glass is engineered with coatings and tints to reduce solar heat gain and enhance energy efficiency, making it ideal for greenhouse glazing and building facades. Clear float glass, produced by floating molten glass on a bed of molten metal, offers high optical clarity and smooth surfaces without any coatings, widely used in windows and storefronts. The primary distinction lies in solar glass's heat-control properties versus clear float glass's natural transparency.
Key Differences Between Solar Glass and Clear Float Glass
Solar glass incorporates a special coating or film that reflects or absorbs solar radiation to improve energy efficiency, while clear float glass is a standard transparent glass with no such thermal control properties. The solar glass typically exhibits higher solar heat rejection coefficients, reducing heat gain and cooling loads in buildings, unlike clear float glass which allows more solar heat to penetrate. Durability and cost differences also exist, as solar glass often includes treatments enhancing UV resistance and longevity but usually comes at a higher price point than basic clear float glass.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Solar glass incorporates a coating or embedded film designed to filter infrared rays, composed primarily of silica with metal oxide layers, whereas clear float glass consists mainly of pure silica, soda ash, and limestone melted and floated on molten tin to achieve smooth, clear surfaces. The manufacturing process for solar glass involves additional steps such as sputtering or pyrolytic coating to deposit energy-efficient layers, while clear float glass follows the classic float glass process without these treatments. These differences in composition and production result in solar glass providing better thermal insulation and energy savings compared to conventional clear float glass.
Light Transmission Properties
Solar glass typically features a low-emissivity coating that reduces visible light transmission to about 40-70%, effectively minimizing heat and glare while maintaining adequate natural light. Clear float glass allows higher light transmission, often exceeding 80%, but lacks the solar control properties, resulting in increased solar heat gain. The choice depends on balancing natural illumination needs with energy efficiency and thermal comfort requirements.
Solar Energy Efficiency and Performance
Solar glass improves solar energy efficiency by incorporating coatings that selectively filter infrared and ultraviolet rays, reducing heat transfer while maximizing visible light transmission. Clear float glass lacks these specialized coatings, resulting in higher solar heat gain and lower energy performance in applications requiring thermal regulation. The enhanced performance of solar glass makes it a preferred choice for energy-conscious architectural designs aiming to optimize natural light and reduce cooling costs.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Solar glass features a tempered surface and special coatings that significantly enhance its durability and resistance to harsh weather conditions compared to clear float glass. Clear float glass, while offering excellent clarity, lacks the reinforced strength and UV protection found in solar glass, making it more susceptible to damage from temperature fluctuations, moisture, and impact. Choosing solar glass improves the lifespan and performance of your windows or architectural projects in demanding outdoor environments.
Applications in the Construction Industry
Solar glass offers superior energy efficiency by reducing heat gain and enhancing natural light control, making it ideal for sustainable building facades and skylights. Clear float glass is commonly used in standard windows and partitions due to its cost-effectiveness and clarity but lacks the advanced thermal performance of solar glass. Your choice between these materials impacts building energy consumption, occupant comfort, and compliance with green building standards.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Solar glass significantly reduces environmental impact by enhancing energy efficiency through solar control properties, lowering cooling costs and reducing carbon emissions in buildings. Clear float glass, while recyclable, lacks these energy-saving features, leading to higher energy consumption and increased greenhouse gas output. Choosing solar glass for your projects supports sustainability goals by minimizing reliance on non-renewable energy sources and promoting eco-friendly building practices.
Cost Comparison and Economic Viability
Solar glass typically costs 10-20% more than clear float glass due to its specialized coating that enhances energy efficiency by reflecting infrared radiation. Despite the initial higher investment, solar glass can reduce cooling expenses and improve building energy ratings, making it economically viable for projects aiming for long-term savings. Your choice between the two should consider not only upfront cost but also potential energy cost reductions and sustainability goals.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Project
Choosing between solar glass and clear float glass depends on your project's energy efficiency and light transmission needs. Solar glass offers superior solar control by reducing heat gain and UV radiation, ideal for energy-saving buildings. Clear float glass provides excellent clarity and natural light but lacks the solar protection needed for temperature regulation.
solar glass vs clear float glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com