Vision glass offers clear, transparent views and natural daylight for your interior spaces, enhancing visibility and aesthetic appeal. Spandrel glass conceals structural elements and insulation, providing a uniform exterior appearance without transparency.
Table of Comparison
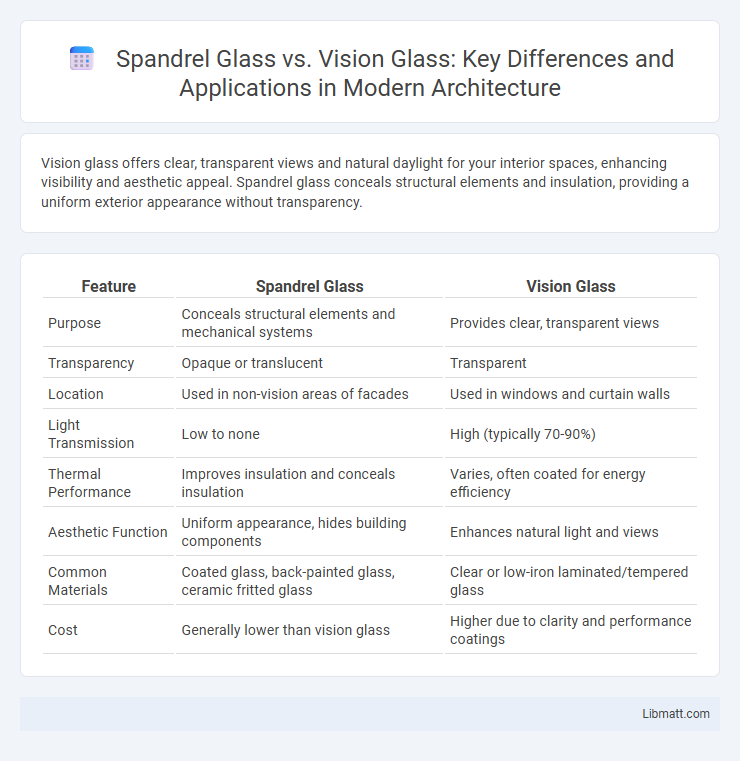
| Feature | Spandrel Glass | Vision Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Conceals structural elements and mechanical systems | Provides clear, transparent views |
| Transparency | Opaque or translucent | Transparent |
| Location | Used in non-vision areas of facades | Used in windows and curtain walls |
| Light Transmission | Low to none | High (typically 70-90%) |
| Thermal Performance | Improves insulation and conceals insulation | Varies, often coated for energy efficiency |
| Aesthetic Function | Uniform appearance, hides building components | Enhances natural light and views |
| Common Materials | Coated glass, back-painted glass, ceramic fritted glass | Clear or low-iron laminated/tempered glass |
| Cost | Generally lower than vision glass | Higher due to clarity and performance coatings |
Introduction to Spandrel Glass and Vision Glass
Spandrel glass and vision glass play distinct roles in modern architectural design, with vision glass allowing clear views and natural light into building interiors, while spandrel glass conceals structural elements like columns and floor slabs. Spandrel glass typically features opaque or reflective coatings that match the appearance of adjacent vision glass, ensuring a uniform exterior facade. Understanding the differences between these glass types helps you select the right combination for aesthetics, energy efficiency, and functionality in building projects.
Key Differences Between Spandrel Glass and Vision Glass
Spandrel glass is opaque and designed to conceal structural elements, insulation, or mechanical equipment, while vision glass is transparent to provide clear views and natural light. Spandrel glass often features coatings or back paints to match the building facade, whereas vision glass prioritizes clarity, solar control, and energy efficiency. Understanding these differences helps you select the right glass type for aesthetic and functional architectural needs.
Composition and Materials
Spandrel glass consists of a core material, such as insulation or metal, laminated between two or more sheets of glass to conceal building elements, whereas vision glass is composed of clear or tinted glass designed to provide transparency and natural light. Spandrel glass typically features ceramic frit or opaque coatings to block visibility, while vision glass uses low-emissivity coatings to enhance energy efficiency and reduce glare. Understanding the distinct composition of spandrel and vision glass helps optimize your building's facade for both aesthetics and functionality.
Functional Uses in Building Design
Spandrel glass serves as an opaque cladding element that conceals structural components and mechanical systems, enhancing a building's aesthetic while providing thermal insulation and weather resistance. Vision glass, by contrast, is transparent or translucent, allowing natural light into interiors and offering clear views to the outside, crucial for occupant comfort and energy efficiency. Your choice between spandrel and vision glass directly impacts both the functional performance and visual appeal of your building's facade.
Aesthetic Considerations
Spandrel glass offers a uniform, opaque finish that conceals structural elements and mechanical systems, enhancing the sleek aesthetics of modern facades. Vision glass provides transparency for natural light and exterior views, creating an inviting and open ambiance in interior spaces. Your choice between spandrel and vision glass significantly influences the building's visual rhythm and design coherence.
Thermal and Energy Performance
Spandrel glass enhances thermal and energy performance by concealing building elements while providing superior insulation compared to vision glass, which typically includes clear or tinted panels focused on daylight transmission. The opacity of spandrel glass reduces heat gain and loss, contributing to improved energy efficiency in building envelopes. Your choice between spandrel and vision glass impacts HVAC load and overall energy consumption, with spandrel glass offering significant advantages in thermal management.
Privacy and Transparency
Spandrel glass offers high privacy by obscuring vision and concealing structural elements, making it ideal for areas requiring limited visibility. Vision glass provides maximum transparency, allowing clear views and natural light penetration for enhanced interior visibility. Both types serve distinct architectural functions, balancing privacy and transparency based on design needs.
Installation Challenges and Solutions
Spandrel glass installation presents challenges such as alignment with vision glass and managing opaque coatings without compromising structural integrity. Solutions include precise framing systems and pre-fabrication techniques that ensure uniform fit and appearance when paired with vision glass. Your project benefits from comprehensive planning and collaboration with experienced installers to overcome these complexities efficiently.
Cost Comparison and Budget Impact
Spandrel glass typically costs less than vision glass due to its opaque nature and simpler manufacturing process, making it a budget-friendly option for covering structural elements and hiding mechanical systems. Vision glass, designed for transparency and often incorporating advanced coatings for energy efficiency, usually commands a higher price that can significantly impact your overall project budget. Choosing between spandrel and vision glass depends on balancing aesthetic desires with cost constraints to optimize financial resources.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Project
Spandrel glass provides opaque, decorative panels that conceal structural elements and mechanical systems, ideal for enhancing a building's exterior aesthetics while maintaining uniformity. Vision glass offers transparent or translucent properties, maximizing natural light and exterior views, which improves interior comfort and energy efficiency. Selecting between spandrel and vision glass depends on the project's design goals, desired daylighting levels, privacy needs, and thermal performance requirements.
spandrel glass vs vision glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com