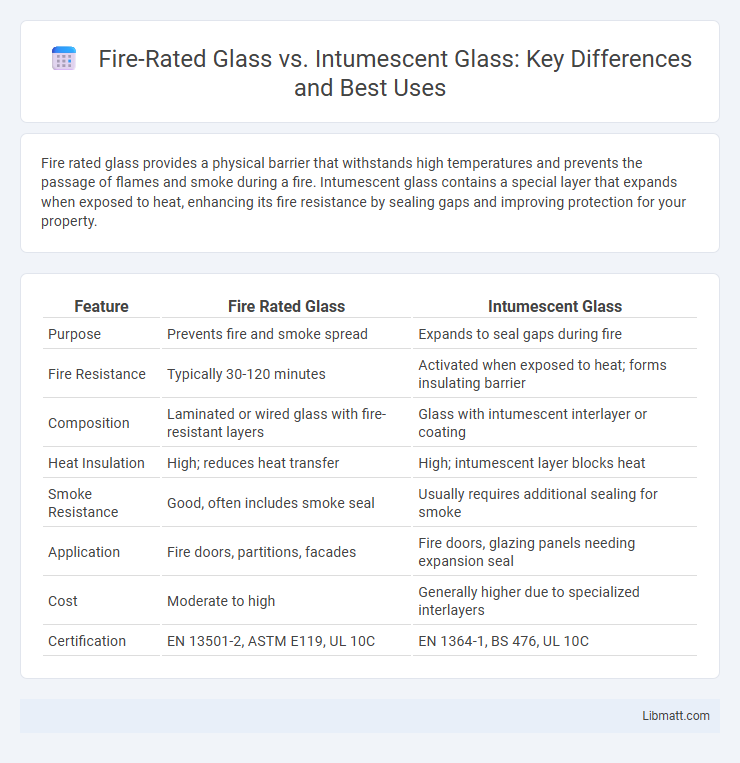
Fire rated glass provides a physical barrier that withstands high temperatures and prevents the passage of flames and smoke during a fire. Intumescent glass contains a special layer that expands when exposed to heat, enhancing its fire resistance by sealing gaps and improving protection for your property.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fire Rated Glass | Intumescent Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prevents fire and smoke spread | Expands to seal gaps during fire |
| Fire Resistance | Typically 30-120 minutes | Activated when exposed to heat; forms insulating barrier |
| Composition | Laminated or wired glass with fire-resistant layers | Glass with intumescent interlayer or coating |
| Heat Insulation | High; reduces heat transfer | High; intumescent layer blocks heat |
| Smoke Resistance | Good, often includes smoke seal | Usually requires additional sealing for smoke |
| Application | Fire doors, partitions, facades | Fire doors, glazing panels needing expansion seal |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Generally higher due to specialized interlayers |
| Certification | EN 13501-2, ASTM E119, UL 10C | EN 1364-1, BS 476, UL 10C |
Introduction to Fire Rated Glass and Intumescent Glass
Fire rated glass is designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of flames and smoke during a fire, ensuring safety and structural integrity. Intumescent glass incorporates a special interlayer that expands when exposed to heat, creating an insulating barrier that blocks heat transfer and maintains the glass's protective function. Both types are essential in fire safety design, with fire rated glass providing direct flame resistance and intumescent glass enhancing thermal protection.
Definition and Properties of Fire Rated Glass
Fire rated glass is specially engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of fire and smoke, offering both visibility and protection in emergency situations. Intumescent glass incorporates a heat-activated layer that expands when exposed to fire, enhancing its insulation and creating a barrier against heat and flames. Your choice between these two depends on the specific fire safety requirements and building regulations you need to comply with.
Understanding Intumescent Glass: Key Features
Intumescent glass is a specialized fire-rated glazing material that expands when exposed to high temperatures, forming an insulating char layer that blocks heat and flames. Its key features include the ability to maintain transparency under normal conditions while providing superior fire resistance compared to standard fire-rated glass. This technology enables enhanced safety in buildings by combining aesthetic appeal with effective fire containment.
Fire Resistance Mechanisms: How Each Glass Type Works
Fire rated glass resists heat and flames through a specially formulated laminate that maintains integrity, preventing fire and smoke from spreading while sustaining structural stability under high temperatures. Intumescent glass incorporates a heat-activated interlayer that swells and forms an insulating char barrier during fire exposure, reducing heat transfer and enhancing protection against radiant heat. Both technologies comply with fire safety standards but differ fundamentally in their mechanisms: fire rated glass relies on physical durability and thermal resistance, whereas intumescent glass offers active thermal insulation through chemical expansion.
Performance Ratings and Standards Comparison
Fire rated glass and intumescent glass are tested under distinct performance standards such as ASTM E119 for fire resistance and BS EN 13501-2 for classification, with fire rated glass typically offering fixed resistance times ranging from 30 to 120 minutes. Intumescent glass incorporates a special interlayer that expands when exposed to heat, providing enhanced smoke and fire containment aligned with EN 1634-1 standards while maintaining clarity and structural integrity. Both glasses must meet stringent criteria for thermal insulation, integrity, and radiation control, but intumescent glass often excels in limiting heat transfer, making it suitable for applications requiring visibility and high fire protection performance.
Applications: Where to Use Fire Rated vs Intumescent Glass
Fire rated glass is commonly used in commercial buildings, corridors, stairwells, and exits where it provides a barrier to flames and smoke, preventing fire spread for a specified period. Intumescent glass, with its thin, transparent intumescent layer, is ideal for high-visibility areas such as offices, retail stores, and hotels where aesthetics and fire protection are equally important. Your choice between fire rated and intumescent glass depends on the specific fire safety requirements and design considerations of the space.
Aesthetics and Design Flexibility
Fire rated glass offers clear, unobstructed views with high transparency, making it ideal for modern architectural designs where natural light and visibility are priorities. Intumescent glass incorporates a special interlayer that expands under heat to provide fire resistance without compromising on sleek, slim profiles, allowing versatile installation in both contemporary and traditional settings. Both options balance safety and aesthetics, but intumescent glass provides greater design flexibility with customizable thickness and finishes for seamless integration.
Installation Considerations for Both Glass Types
Fire rated glass requires precise installation within certified frames to ensure its fire resistance integrity, demanding skilled professionals for proper sealing and structural support. Intumescent glass involves applying a reactive coating that expands under heat, necessitating careful handling to avoid damage and ensuring compatibility with framing systems designed to accommodate the expanding material. Your choice between these glass types should consider installation complexity, frame compatibility, and adherence to fire safety codes for optimal protection.
Cost Analysis: Fire Rated Glass vs Intumescent Glass
Fire rated glass generally offers a lower upfront cost compared to intumescent glass, making it a budget-friendly option for standard fire protection requirements. Intumescent glass, infused with heat-activated materials, tends to be more expensive due to advanced manufacturing processes and enhanced fire-resistance properties. Long-term cost considerations favor intumescent glass when factoring in durability, maintenance, and higher fire-resistance ratings that may reduce insurance premiums and compliance risks.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Project
Fire rated glass offers transparent fire resistance by maintaining integrity and limiting heat transfer during a fire, making it ideal for safety-focused projects requiring clear visibility. Intumescent glass contains layers that expand under heat to form an insulating barrier, providing enhanced thermal protection and insulation in addition to fire resistance. Selecting between these depends on project needs for fire performance, visual clarity, thermal insulation, and compliance with local fire safety regulations.
fire rated glass vs intumescent glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com