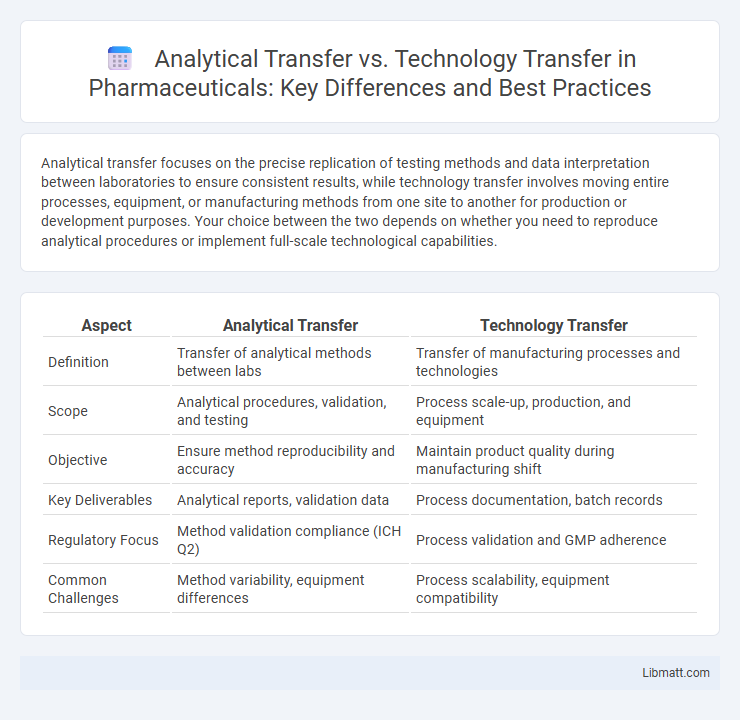
Analytical transfer focuses on the precise replication of testing methods and data interpretation between laboratories to ensure consistent results, while technology transfer involves moving entire processes, equipment, or manufacturing methods from one site to another for production or development purposes. Your choice between the two depends on whether you need to reproduce analytical procedures or implement full-scale technological capabilities.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Analytical Transfer | Technology Transfer |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Transfer of analytical methods between labs | Transfer of manufacturing processes and technologies |
| Scope | Analytical procedures, validation, and testing | Process scale-up, production, and equipment |
| Objective | Ensure method reproducibility and accuracy | Maintain product quality during manufacturing shift |
| Key Deliverables | Analytical reports, validation data | Process documentation, batch records |
| Regulatory Focus | Method validation compliance (ICH Q2) | Process validation and GMP adherence |
| Common Challenges | Method variability, equipment differences | Process scalability, equipment compatibility |
Introduction to Analytical Transfer and Technology Transfer
Analytical transfer involves the systematic migration of analytical methods between laboratories or organizations, ensuring consistency in testing accuracy and reliability. Technology transfer encompasses the broader process of conveying scientific knowledge, processes, or manufacturing technologies from research to production phases. Understanding these distinctions helps your organization maintain quality control while scaling operations efficiently.
Defining Analytical Transfer: Scope and Purpose
Analytical transfer involves the systematic replication of validated analytical methods from one laboratory to another to ensure consistent quality control and regulatory compliance. Unlike technology transfer, which encompasses the broader movement of processes, equipment, and knowledge across organizations, analytical transfer specifically focuses on the accuracy, precision, and reliability of analytical procedures. Your successful analytical transfer guarantees that testing methods yield equivalent results regardless of location, safeguarding product integrity throughout development and manufacturing.
Defining Technology Transfer: Scope and Applications
Technology transfer involves the systematic process of moving scientific findings, innovations, or inventions from research institutions to commercial enterprises for practical application and market development. Its scope includes the licensing of patents, collaboration agreements, and the establishment of startups to bring new technologies to industry sectors such as healthcare, energy, and manufacturing. Understanding this transfer helps you leverage innovations effectively by bridging the gap between laboratory research and real-world implementation.
Key Objectives of Analytical Transfer
Analytical transfer aims to ensure the accurate and reliable replication of analytical methods between laboratories, maintaining data integrity and compliance with regulatory standards. It focuses on demonstrating method equivalence, precision, accuracy, and robustness to support consistent product quality and safety. Your focus should be on validating parameters like specificity, sensitivity, and reproducibility during the analytical transfer process to minimize risks in technology development and commercialization.
Primary Goals of Technology Transfer
The primary goals of technology transfer focus on facilitating the movement of innovations, proprietary processes, and technical knowledge from research institutions to commercial entities, enabling practical application and market development. Analytical transfer primarily aims to ensure method reproducibility and validation when shifting analytical procedures between laboratories or production scales. Technology transfer prioritizes the efficient and secure handover of technology to support product development, scalability, and regulatory compliance in industrial contexts.
Regulatory Considerations for Analytical and Technology Transfer
Regulatory considerations for analytical and technology transfer emphasize strict compliance with guidelines from agencies such as the FDA, EMA, and ICH to ensure data integrity, method validation, and consistent product quality across manufacturing sites. Analytical transfer requires validation of testing procedures and analytical methods to maintain accuracy, precision, and robustness, while technology transfer focuses on demonstrating process equivalence, scalability, and control strategy adherence under GMP conditions. Both transfers demand comprehensive documentation, change control, and risk assessment to meet regulatory expectations and facilitate timely product approval.
Step-by-Step Process of Analytical Transfer
The step-by-step process of analytical transfer involves method validation, data comparison, and documentation to ensure consistent test results across different laboratories. Your role includes coordinating sample shipment, training personnel on analytical techniques, and verifying method performance through reproducibility studies. This meticulous process contrasts with technology transfer, which focuses on transferring manufacturing processes and equipment alongside analytical methods.
Critical Stages in Technology Transfer
Critical stages in technology transfer include invention disclosure, intellectual property protection, proof of concept, and scaling up production. Analytical transfer focuses on ensuring the reproducibility and consistency of analytical methods during technology transfer to maintain product quality and compliance with regulatory standards. Technology transfer encompasses a broader process involving knowledge, equipment, and process transfer from development to manufacturing, requiring coordinated cross-functional collaboration to ensure successful commercialization.
Challenges in Analytical Transfer vs. Technology Transfer
Challenges in analytical transfer center on ensuring precise method reproducibility, validation across different laboratories, and maintaining data integrity despite variations in equipment and analyst expertise. Technology transfer faces hurdles such as scaling processes from development to production, aligning cross-functional teams, and managing intellectual property and regulatory compliance. Your successful transfer strategy requires tailored solutions addressing these distinct obstacles for each transfer type.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Transfer Strategy
Selecting the appropriate transfer strategy depends on the specific goals and resources of your project, as analytical transfer focuses on knowledge and data accuracy, while technology transfer emphasizes the practical application and commercialization of innovations. Analytical transfer ensures precision in replicating processes through detailed data exchange, whereas technology transfer facilitates market readiness and intellectual property management. Understanding the balance between expertise dissemination and operational deployment helps you optimize outcomes and drive successful innovation adoption.
Analytical transfer vs Technology transfer Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com