Sterile APIs are pharmaceutical active ingredients manufactured in aseptic conditions to prevent contamination, making them suitable for injectable and ophthalmic products. Non-sterile APIs do not require aseptic processing and are typically used in oral, topical, or other formulations where sterilization is not critical for patient safety.
Table of Comparison
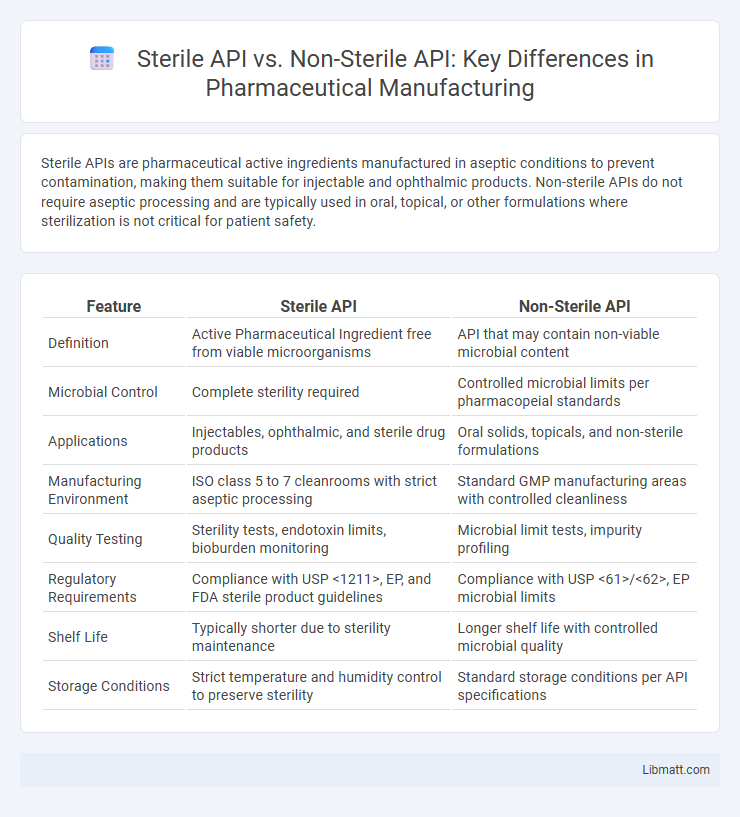
| Feature | Sterile API | Non-Sterile API |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient free from viable microorganisms | API that may contain non-viable microbial content |
| Microbial Control | Complete sterility required | Controlled microbial limits per pharmacopeial standards |
| Applications | Injectables, ophthalmic, and sterile drug products | Oral solids, topicals, and non-sterile formulations |
| Manufacturing Environment | ISO class 5 to 7 cleanrooms with strict aseptic processing | Standard GMP manufacturing areas with controlled cleanliness |
| Quality Testing | Sterility tests, endotoxin limits, bioburden monitoring | Microbial limit tests, impurity profiling |
| Regulatory Requirements | Compliance with USP <1211>, EP, and FDA sterile product guidelines | Compliance with USP <61>/<62>, EP microbial limits |
| Shelf Life | Typically shorter due to sterility maintenance | Longer shelf life with controlled microbial quality |
| Storage Conditions | Strict temperature and humidity control to preserve sterility | Standard storage conditions per API specifications |
Introduction to Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) represent the essential components responsible for the therapeutic effects in medications. Sterile APIs require stringent manufacturing processes to eliminate microbial contamination, ensuring safety for injectable or ophthalmic formulations. Non-sterile APIs are produced under controlled conditions suitable for oral, topical, or other non-injectable drug forms where sterility is not mandatory.
Defining Sterile API
Sterile Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) are substances that are free from viable microorganisms, ensuring they meet strict sterility standards crucial for injectable, ophthalmic, and inhalation products. These APIs undergo rigorous sterilization processes, such as filtration or terminal sterilization, to prevent contamination and ensure patient safety. Non-sterile APIs do not require microbial-free conditions and are typically used in solid oral dosage forms where sterility is not critical.
Defining Non-Sterile API
Non-sterile APIs refer to active pharmaceutical ingredients that are manufactured without aseptic processing or terminal sterilization and are intended for formulations where sterility is not required. These APIs are commonly used in solid dosage forms, topical products, or inhalers where microbial contamination risk is controlled through other means. Proper quality controls ensure non-sterile APIs meet regulatory standards for purity, potency, and safety despite not being sterile.
Key Differences Between Sterile and Non-Sterile APIs
Sterile APIs are produced under strict aseptic conditions to eliminate microbial contamination, essential for injectable drugs and ophthalmic products, whereas non-sterile APIs do not require such stringent controls and are used in oral or topical formulations. The primary distinction lies in the manufacturing environment, with sterile APIs undergoing terminal sterilization or aseptic processing to ensure sterility assurance levels, contrasting non-sterile APIs which focus on purity and potency without sterility requirements. Regulatory standards like USP <71> for sterility testing apply exclusively to sterile APIs, emphasizing their critical role in patient safety for parenteral administration.
Manufacturing Process for Sterile APIs
Sterile API manufacturing involves aseptic processing, strict environmental controls, and validated sterilization techniques such as filtration, heat, or irradiation to ensure the absence of viable microorganisms. This process requires specialized cleanroom facilities with controlled air quality, pressure differentials, and rigorous personnel hygiene protocols to maintain sterility throughout production. Your sterile API must comply with stringent regulatory standards like USP <1211> and FDA guidelines to guarantee safety and efficacy in injectable or implantable drug products.
Manufacturing Process for Non-Sterile APIs
The manufacturing process for non-sterile Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) involves chemical synthesis, purification, and quality control without the need for aseptic processing conditions required for sterile APIs. Non-sterile API production includes operations under controlled environments but does not mandate cleanrooms with ISO Class 5 standards, focusing instead on preventing contamination that affects chemical purity rather than microbial contamination. Process validation, in-process testing, and adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) ensure the consistency and quality of non-sterile APIs used in oral, topical, or other non-injectable drug formulations.
Regulatory Requirements for Sterile vs Non-Sterile API
Sterile API production must comply with stringent regulatory requirements including aseptic processing, environmental monitoring, and validation of sterilization methods as mandated by agencies like the FDA and EMA. Non-sterile API manufacturing follows less rigorous controls focusing on purity, potency, and contamination limits without the need for sterile conditions. Your compliance with these regulatory standards ensures product safety, efficacy, and market approval for both sterile and non-sterile APIs.
Quality Control and Testing Considerations
Sterile APIs require rigorous quality control with stringent microbial limits and endotoxin testing to ensure product safety for parenteral use, while non-sterile APIs focus primarily on controlling impurities and chemical stability. Validation of sterilization processes and environmental monitoring are critical for sterile API manufacturing but are not mandatory for non-sterile APIs. Your testing strategy should align with the intended use and regulatory requirements to maintain compliance and ensure product efficacy.
Applications and End-Uses of Sterile and Non-Sterile APIs
Sterile APIs are primarily used in injectable drugs, ophthalmic solutions, and other parenteral products where contamination control is critical, ensuring patient safety in sensitive medical treatments. Non-sterile APIs find applications in oral solid dosage forms, topical formulations, and inhalants, where sterility is less crucial but purity and potency remain vital. Your choice between sterile and non-sterile APIs directly impacts the formulation process, regulatory compliance, and therapeutic efficacy of the final pharmaceutical product.
Challenges and Future Trends in API Production
Sterile API production faces stringent contamination control and validation challenges, requiring specialized cleanroom environments and aseptic processing techniques to ensure product safety. Non-sterile API manufacturing struggles with maintaining consistent purity and managing impurities without the complexity of sterile conditions, yet still demands precise quality control to meet regulatory standards. Your choice between sterile and non-sterile API production will increasingly involve adopting advanced technologies like continuous manufacturing and real-time monitoring to enhance efficiency and compliance in the evolving pharmaceutical landscape.
Sterile API vs Non-sterile API Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com