Bulk biologic refers to the large-scale production of the active pharmaceutical ingredient before it undergoes purification and formulation, while fill finish involves aseptically filling the purified biologic into final containers such as vials or syringes. Your choice between bulk biologic and fill finish processes impacts manufacturing efficiency, product stability, and regulatory compliance in biologics production.
Table of Comparison
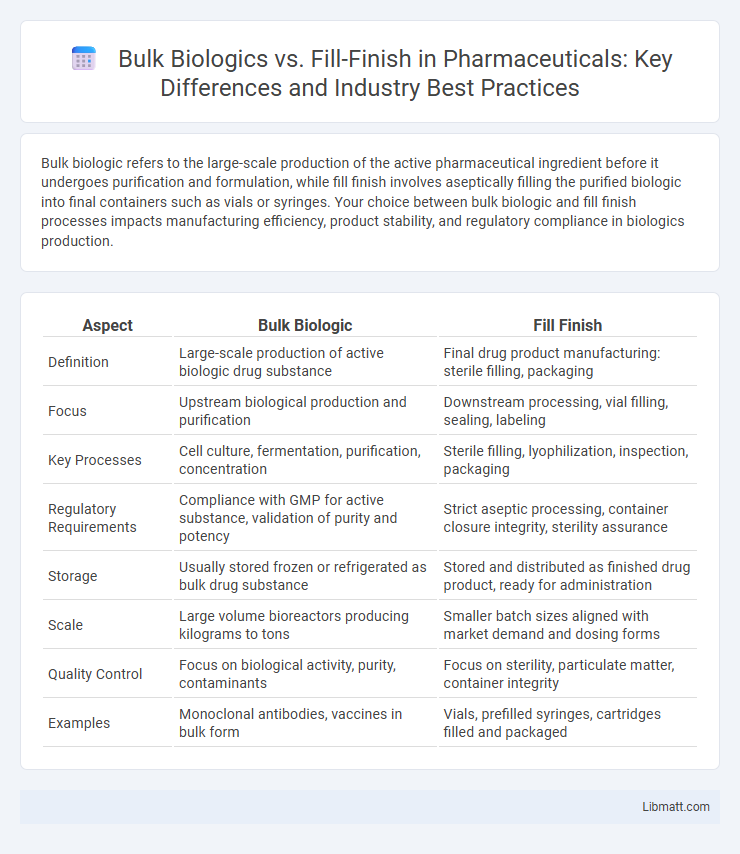
| Aspect | Bulk Biologic | Fill Finish |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Large-scale production of active biologic drug substance | Final drug product manufacturing: sterile filling, packaging |
| Focus | Upstream biological production and purification | Downstream processing, vial filling, sealing, labeling |
| Key Processes | Cell culture, fermentation, purification, concentration | Sterile filling, lyophilization, inspection, packaging |
| Regulatory Requirements | Compliance with GMP for active substance, validation of purity and potency | Strict aseptic processing, container closure integrity, sterility assurance |
| Storage | Usually stored frozen or refrigerated as bulk drug substance | Stored and distributed as finished drug product, ready for administration |
| Scale | Large volume bioreactors producing kilograms to tons | Smaller batch sizes aligned with market demand and dosing forms |
| Quality Control | Focus on biological activity, purity, contaminants | Focus on sterility, particulate matter, container integrity |
| Examples | Monoclonal antibodies, vaccines in bulk form | Vials, prefilled syringes, cartridges filled and packaged |
Introduction to Bulk Biologic and Fill Finish
Bulk biologic refers to the large-scale production of biologic drug substances before they undergo further processing, ensuring high purity and consistency in the initial manufacturing phase. Fill finish involves the precise aseptic filling of these bulk biologics into final containers, such as vials or syringes, while maintaining sterility and product integrity. Your choice in optimizing these processes impacts the overall efficiency and quality of biologic drug manufacturing.
Key Differences Between Bulk Biologic and Fill Finish
Bulk biologic refers to the large-scale production of a biological drug substance before it undergoes purification, while fill finish is the critical process of filling the purified biologic into final containers such as vials or syringes. Key differences include the stage of production, with bulk biologics involving upstream and downstream processing, and fill finish focusing on aseptic filling, packaging, and labeling to ensure product sterility and stability. Your choice between these services depends on whether you require large-scale production of the active substance or the final product preparation for patient administration.
The Bulk Biologic Manufacturing Process
The bulk biologic manufacturing process involves the large-scale production of a biologic drug substance using cell culture systems, typically employing bioreactors that maintain controlled environments for optimal cell growth and protein expression. Critical parameters such as temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen, and nutrient supply are monitored to ensure high yield and product quality. This stage concludes with primary recovery and purification steps that prepare the bulk drug substance for subsequent fill finish operations, where the product is formulated, filled, and packaged into final dosage forms.
Understanding Fill Finish in Biopharmaceuticals
Fill finish in biopharmaceuticals refers to the critical process of transferring bulk biologic products into final containers, such as vials or syringes, under sterile conditions to ensure product safety and efficacy. This step involves precise automation and stringent quality control to maintain the integrity of sensitive biologics while preparing them for distribution and administration. Understanding fill finish is essential for optimizing manufacturing workflows and meeting regulatory compliance in biopharmaceutical production.
Regulatory Considerations for Bulk Biologic vs Fill Finish
Regulatory considerations for bulk biologic manufacturing emphasize strict compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure product purity, safety, and consistency before final formulation. Fill finish processes require additional regulatory scrutiny for aseptic processing, container closure integrity, and sterility assurance to prevent contamination during vial filling or packaging. Your quality systems must address both stages separately to meet regulatory standards and enable successful product approval.
Quality Control in Bulk Biologic and Fill Finish Processes
Quality control in bulk biologic production involves rigorous testing at various stages to ensure the purity, potency, and consistency of the active pharmaceutical ingredient before filling. During fill finish processes, quality control prioritizes sterility, accurate dosage, and container integrity to maintain product safety and efficacy. Your pharmaceutical product's overall quality hinges on stringent monitoring and validation protocols implemented throughout both bulk biologic and fill finish stages.
Cost Implications: Bulk Biologic vs Fill Finish
Bulk biologic production typically incurs higher initial equipment and facility investment costs due to large-scale upstream processing requirements. Fill finish processes, involving aseptic filling and packaging, often present lower capital expenses but can significantly impact overall costs through stringent quality controls and specialized labor. Optimizing Your biomanufacturing strategy requires balancing the higher upstream bulk production expenses with downstream fill finish operational costs to achieve cost-effective biologic manufacturing.
Challenges in Scaling Production: Bulk Biologic vs Fill Finish
Scaling production of bulk biologics presents challenges such as maintaining consistent cell culture conditions, managing large bioreactor volumes, and ensuring quality control for high-yield protein expression. Fill finish processes face hurdles including aseptic processing, precise dosing, and minimizing contamination risks during vial or syringe filling. Your manufacturing strategy must address these distinct bottlenecks to optimize overall biopharmaceutical production efficiency.
Supply Chain Strategies for Bulk Biologic and Fill Finish
Supply chain strategies for Bulk Biologic emphasize temperature-controlled storage, streamlined raw material sourcing, and robust quality control to maintain product integrity during upstream processing. Fill Finish supply chains prioritize aseptic conditions, precise scheduling to optimize vial filling, and cold chain logistics to ensure sterility and timely delivery. Your coordinated supply chain integrating both processes reduces bottlenecks and enhances overall biologic drug production efficiency.
Future Trends in Biopharmaceutical Manufacturing
Future trends in biopharmaceutical manufacturing emphasize integration of Bulk Biologic production with advanced Fill Finish technologies to enhance efficiency and reduce contamination risks. Continuous manufacturing and automation innovations are driving higher scalability and consistency in both stages, enabling faster time-to-market for therapies. Your ability to adopt flexible, modular systems will be crucial for meeting evolving regulatory standards and patient demands in this dynamic landscape.
Bulk Biologic vs Fill Finish Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com