The LAL Test detects bacterial endotoxins by measuring the clotting reaction of horseshoe crab blood, ensuring your pharmaceuticals are free from harmful Gram-negative bacterial toxins. The Rabbit Pyrogen Test assesses fever-inducing pyrogens in medical products by monitoring temperature changes in rabbits, providing a broader safety evaluation including non-endotoxin pyrogens.
Table of Comparison
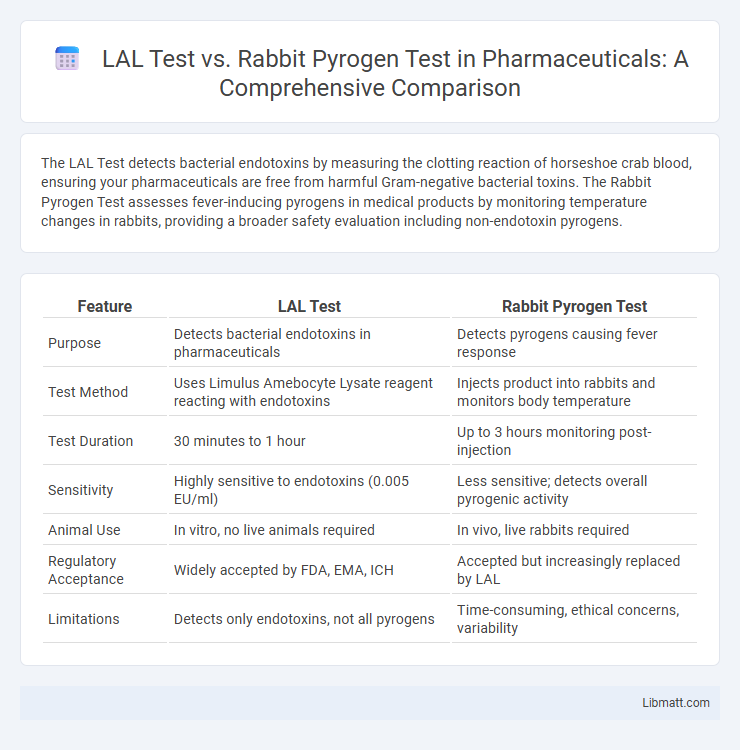
| Feature | LAL Test | Rabbit Pyrogen Test |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Detects bacterial endotoxins in pharmaceuticals | Detects pyrogens causing fever response |
| Test Method | Uses Limulus Amebocyte Lysate reagent reacting with endotoxins | Injects product into rabbits and monitors body temperature |
| Test Duration | 30 minutes to 1 hour | Up to 3 hours monitoring post-injection |
| Sensitivity | Highly sensitive to endotoxins (0.005 EU/ml) | Less sensitive; detects overall pyrogenic activity |
| Animal Use | In vitro, no live animals required | In vivo, live rabbits required |
| Regulatory Acceptance | Widely accepted by FDA, EMA, ICH | Accepted but increasingly replaced by LAL |
| Limitations | Detects only endotoxins, not all pyrogens | Time-consuming, ethical concerns, variability |
Introduction to Pyrogen Testing
Pyrogen testing is essential for detecting fever-causing substances in pharmaceuticals and medical devices, ensuring patient safety and regulatory compliance. The LAL Test specifically detects endotoxins from Gram-negative bacteria using Limulus amebocyte lysate, while the Rabbit Pyrogen Test identifies pyrogens through fever response in live rabbits. Understanding these methodologies helps you select the suitable test based on sensitivity, ethical considerations, and application requirements.
Overview of the LAL Test
The LAL (Limulus Amebocyte Lysate) Test detects bacterial endotoxins by using blood cells from the horseshoe crab, offering rapid and sensitive results essential for pharmaceutical and medical device safety. This test quantifies endotoxin levels to ensure your products meet regulatory standards and prevent adverse reactions in patients. Compared to the Rabbit Pyrogen Test, the LAL Test is more reproducible, ethical, and cost-effective for routine endotoxin screening.
Overview of the Rabbit Pyrogen Test
The Rabbit Pyrogen Test is a traditional biological assay used to detect pyrogens, substances that cause fever, by measuring the temperature response in rabbits after exposure to a test sample. This method evaluates the presence of endotoxins and other pyrogenic contaminants to ensure pharmaceutical safety and compliance with regulatory standards. Your understanding of this test is crucial for selecting reliable pyrogen detection methods in drug formulation and quality control processes.
Mechanism of Action: LAL Test vs Rabbit Pyrogen Test
The LAL Test detects bacterial endotoxins by using Limulus amebocyte lysate that coagulates in the presence of lipopolysaccharides from gram-negative bacteria. The Rabbit Pyrogen Test measures pyrogenic fever response by injecting test samples into rabbits and monitoring their body temperature elevation due to pyrogen-induced cytokine production. The LAL Test specifically targets endotoxins at a molecular level, while the Rabbit Pyrogen Test assesses a broader range of pyrogens including endotoxins and non-endotoxin substances causing febrile reactions.
Sensitivity and Specificity Comparison
The LAL Test demonstrates higher sensitivity in detecting endotoxins from Gram-negative bacteria compared to the Rabbit Pyrogen Test, which identifies a broader spectrum of pyrogens, including non-endotoxin substances. Specificity in the LAL Test is enhanced due to its targeted reaction to lipopolysaccharides, while the Rabbit Pyrogen Test may yield false positives from various fever-inducing agents. Understanding these differences ensures your selection aligns with the required precision and scope in pyrogen detection.
Regulatory Guidelines and Acceptance
The LAL Test is widely accepted by regulatory agencies such as the FDA and EMA for detecting endotoxins in pharmaceuticals and medical devices, while the Rabbit Pyrogen Test is mandated by some pharmacopeias for identifying pyrogens beyond endotoxins. Regulatory guidelines increasingly favor the LAL Test due to its sensitivity, reproducibility, and ethical advantages over animal-based methods. Your compliance strategy should prioritize the LAL Test for endotoxin assessment, reserving the Rabbit Pyrogen Test only when required by specific regional regulations or for complex samples.
Ethical Considerations in Pyrogen Testing
The LAL Test offers a more ethical alternative to the Rabbit Pyrogen Test by reducing the reliance on live animals, aligning with the principles of the 3Rs (Replacement, Reduction, Refinement) in scientific research. Your choice of the LAL Test supports animal welfare while providing rapid and sensitive detection of bacterial endotoxins, enhancing both ethical standards and efficiency in pyrogen testing. This shift towards in vitro methods reflects growing regulatory and societal demands for cruelty-free testing practices.
Practical Applications in Industry
The LAL Test is extensively used in the pharmaceutical and medical device industries for detecting endotoxins to ensure product safety and compliance with regulatory standards. The Rabbit Pyrogen Test remains relevant in validating pyrogenicity in biological products and vaccines, especially when animal-based testing is required. Both tests are critical in quality control processes, with LAL favored for its sensitivity and speed, while the Rabbit Pyrogen Test provides confirmatory results in pyrogenicity assessment.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Method
The LAL Test offers rapid detection of endotoxins with high sensitivity, making it ideal for pharmaceutical and medical device safety evaluations, but it cannot detect non-endotoxin pyrogens. The Rabbit Pyrogen Test detects a broader range of pyrogens, including both endotoxins and non-endotoxin pyrogens, providing a comprehensive safety assessment; however, it is time-consuming, ethically contentious, and less sensitive. Choosing between these tests depends on your specific application, balancing the need for speed, sensitivity, and the range of detectable pyrogens.
Future Trends in Pyrogen Detection
Advancements in pyrogen detection are shifting focus toward endotoxin-specific methods like the LAL test, which offers rapid and sensitive results for bacterial endotoxins compared to the broader, animal-based Rabbit Pyrogen Test. Emerging technologies such as recombinant factor C assays and biosensors aim to enhance specificity, reproducibility, and reduce reliance on animal testing. Integration of artificial intelligence and microfluidics is expected to further streamline pyrogen detection processes, meeting stringent regulatory demands and promoting ethical testing approaches in pharmaceutical and medical device industries.
LAL Test vs Rabbit Pyrogen Test Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com