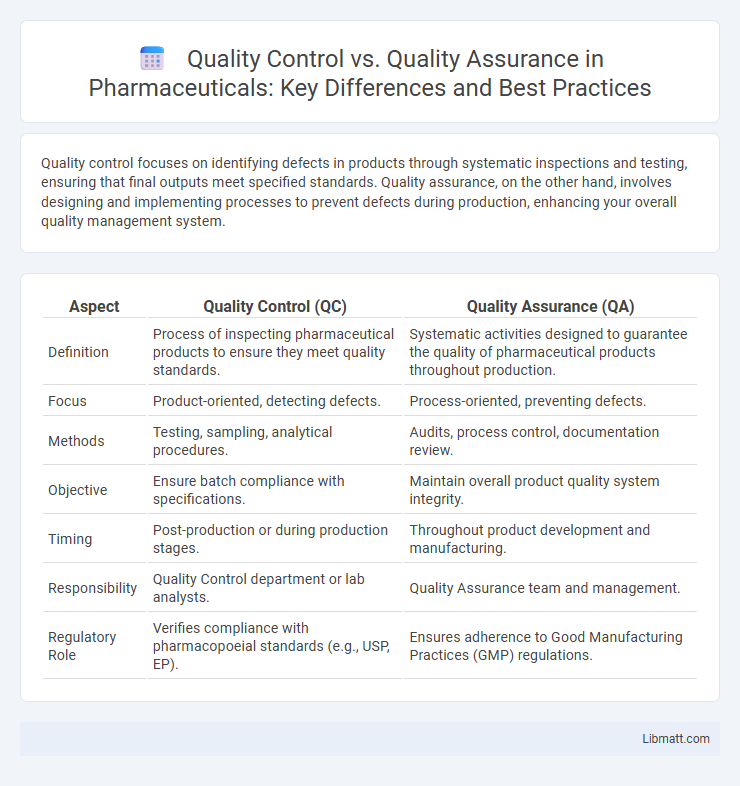
Quality control focuses on identifying defects in products through systematic inspections and testing, ensuring that final outputs meet specified standards. Quality assurance, on the other hand, involves designing and implementing processes to prevent defects during production, enhancing your overall quality management system.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Quality Control (QC) | Quality Assurance (QA) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of inspecting pharmaceutical products to ensure they meet quality standards. | Systematic activities designed to guarantee the quality of pharmaceutical products throughout production. |
| Focus | Product-oriented, detecting defects. | Process-oriented, preventing defects. |
| Methods | Testing, sampling, analytical procedures. | Audits, process control, documentation review. |
| Objective | Ensure batch compliance with specifications. | Maintain overall product quality system integrity. |
| Timing | Post-production or during production stages. | Throughout product development and manufacturing. |
| Responsibility | Quality Control department or lab analysts. | Quality Assurance team and management. |
| Regulatory Role | Verifies compliance with pharmacopoeial standards (e.g., USP, EP). | Ensures adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations. |
Introduction to Quality Control and Quality Assurance
Quality Control (QC) involves the systematic inspection and testing of products to identify defects and ensure they meet specified standards. Quality Assurance (QA) focuses on the process-oriented activities designed to prevent defects by improving and stabilizing production procedures. Both QC and QA are essential components in quality management systems, ensuring products consistently satisfy customer expectations and regulatory requirements.
Defining Quality Control
Quality Control (QC) involves the systematic process of inspecting and testing products or services to ensure they meet specified quality standards and identify defects before delivery. QC focuses on the operational techniques and activities used to fulfill requirements for quality, emphasizing product-oriented evaluation. You benefit from QC by receiving consistent, defect-free goods that adhere to established benchmarks.
Defining Quality Assurance
Quality Assurance (QA) is a systematic process designed to ensure that products and services meet specified requirements and standards throughout development and production. It emphasizes preventive measures and process-oriented activities to avoid defects, enhancing overall quality. QA involves continuous monitoring, documentation, and improvement of processes to guarantee consistent output and customer satisfaction.
Key Differences Between Quality Control and Quality Assurance
Quality Control (QC) involves the process of identifying defects in finished products through inspection and testing, ensuring compliance with specified standards. In contrast, Quality Assurance (QA) focuses on establishing and maintaining systematic processes to prevent defects by monitoring and improving production methodologies. QC is product-oriented and reactive, while QA is process-oriented and proactive, aiming to enhance overall quality management systems.
Objectives of Quality Control
Quality Control (QC) focuses on detecting defects in finished products to ensure they meet specified standards and customer requirements. The primary objectives of QC include identifying and correcting defects, maintaining product consistency, and preventing non-conforming products from reaching customers. QC employs inspection, testing, and measurement techniques to verify product quality throughout the production process.
Objectives of Quality Assurance
Quality assurance aims to prevent defects by focusing on process improvements and adherence to established standards throughout product development. Its objectives include ensuring consistent quality, compliance with regulatory requirements, and fostering continuous improvement in workflows. This systematic approach enhances customer satisfaction by delivering reliable and defect-free products.
Methods and Techniques Used in Quality Control
Quality control employs inspection, testing, and statistical process control methods to identify defects and ensure products meet specified standards. Techniques such as sampling, control charts, and cause-and-effect diagrams are commonly used to monitor production quality and detect deviations. By focusing on detecting and correcting defects, quality control supports maintaining consistent product reliability and performance.
Methods and Techniques Used in Quality Assurance
Quality assurance employs systematic methods such as process checklists, audits, and standards like ISO 9001 to ensure products meet predefined quality criteria. Techniques include statistical process control, root cause analysis, and continuous improvement models like Six Sigma and Total Quality Management (TQM). These approaches focus on preventing defects by optimizing development and production processes rather than solely inspecting the final output.
Industry Examples of Quality Control vs Quality Assurance
Quality control in the automotive industry involves rigorous inspection of parts to detect defects before assembly, ensuring each component meets safety standards. Quality assurance in pharmaceuticals emphasizes systematic process audits and validation to guarantee consistent drug efficacy and compliance with regulatory requirements. You can improve your manufacturing output by implementing quality control checks like testing products and quality assurance protocols such as standardized operating procedures to prevent issues.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Organization
Quality control (QC) focuses on identifying defects in finished products through systematic testing, while quality assurance (QA) emphasizes process improvements to prevent defects throughout production. Choosing the right approach depends on your organization's goals, industry standards, and resource allocation, balancing product inspection with proactive process management. Integrating both QC and QA ensures comprehensive quality management, enhancing customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Quality control vs Quality assurance Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com