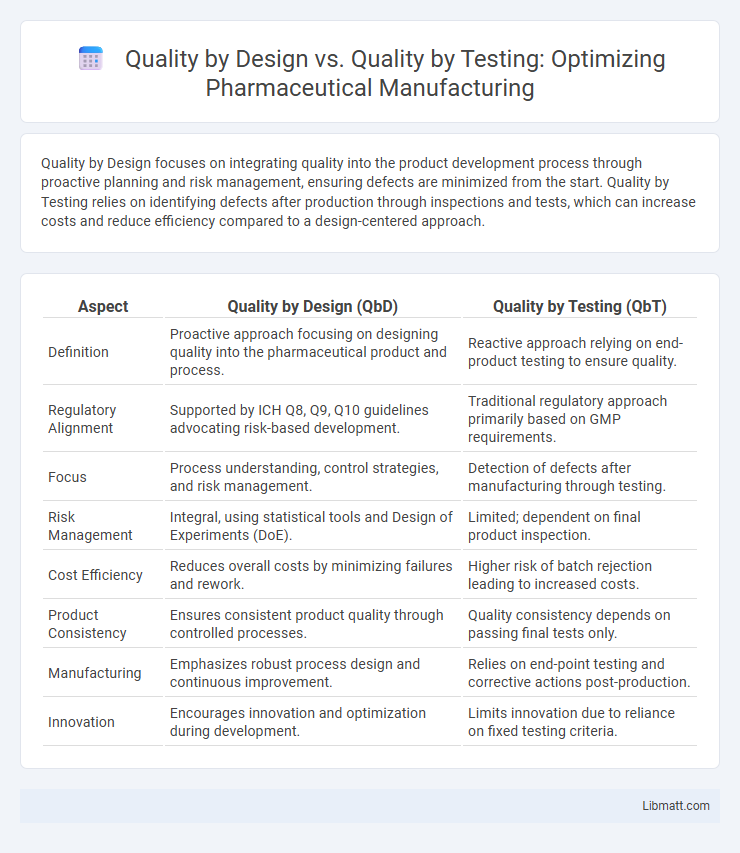
Quality by Design focuses on integrating quality into the product development process through proactive planning and risk management, ensuring defects are minimized from the start. Quality by Testing relies on identifying defects after production through inspections and tests, which can increase costs and reduce efficiency compared to a design-centered approach.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Quality by Design (QbD) | Quality by Testing (QbT) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Proactive approach focusing on designing quality into the pharmaceutical product and process. | Reactive approach relying on end-product testing to ensure quality. |
| Regulatory Alignment | Supported by ICH Q8, Q9, Q10 guidelines advocating risk-based development. | Traditional regulatory approach primarily based on GMP requirements. |
| Focus | Process understanding, control strategies, and risk management. | Detection of defects after manufacturing through testing. |
| Risk Management | Integral, using statistical tools and Design of Experiments (DoE). | Limited; dependent on final product inspection. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces overall costs by minimizing failures and rework. | Higher risk of batch rejection leading to increased costs. |
| Product Consistency | Ensures consistent product quality through controlled processes. | Quality consistency depends on passing final tests only. |
| Manufacturing | Emphasizes robust process design and continuous improvement. | Relies on end-point testing and corrective actions post-production. |
| Innovation | Encourages innovation and optimization during development. | Limits innovation due to reliance on fixed testing criteria. |
Understanding Quality by Design (QbD)
Quality by Design (QbD) is a systematic approach in pharmaceutical development that emphasizes designing processes to ensure predefined product quality. It involves identifying critical quality attributes (CQAs) and critical process parameters (CPPs) to build quality into the product from the outset, rather than relying solely on end-product testing. Understanding QbD enables you to improve product consistency, reduce variability, and enhance regulatory compliance by proactively managing quality risks throughout the development lifecycle.
Defining Quality by Testing (QbT)
Quality by Testing (QbT) focuses on assessing product quality through extensive post-production testing to identify defects and ensure compliance with specifications. This approach relies heavily on detecting issues after manufacturing, rather than embedding quality into the design process. Your product's reliability depends on rigorous testing protocols, which can increase costs and time-to-market compared to proactive quality strategies.
Historical Evolution: QbD vs QbT
Quality by Design (QbD) evolved from regulatory demands for more robust pharmaceutical manufacturing processes, emphasizing risk management and product understanding from development through commercialization. Quality by Testing (QbT) relies on end-product inspection to ensure quality, a method that emerged during earlier industrialization phases when process control technologies were limited. Your manufacturing strategy benefits by integrating QbD principles, which reduce reliance on post-production testing and enable proactive control of critical quality attributes.
Key Principles of Quality by Design
Quality by Design (QbD) emphasizes proactively building quality into products through systematic processes such as defining critical quality attributes (CQAs), identifying critical process parameters (CPPs), and establishing design space to ensure consistent manufacturing outcomes. It relies on risk management, process understanding, and scientific knowledge to optimize product development and manufacturing processes, thus minimizing variability and defects. This approach contrasts with Quality by Testing (QbT), which focuses on end-product inspection rather than integrating quality throughout the product lifecycle.
Core Methodologies of Quality by Testing
Quality by Testing centers on identifying defects through rigorous inspection, verification, and validation processes performed after product development. This methodology relies heavily on comprehensive test plans, functional tests, regression tests, and user acceptance testing to ensure product quality. Your product's reliability depends on these systematic tests designed to catch errors before market release, contrasting with Quality by Design's proactive approach.
Benefits of Implementing QbD
Implementing Quality by Design (QbD) ensures a thorough understanding of processes, leading to consistent product quality and reduced variability. This proactive approach minimizes reliance on end-product testing, saving time and costs while enhancing regulatory compliance. Your manufacturing efficiency and product robustness significantly improve when QbD principles are applied, fostering continuous improvement throughout the product lifecycle.
Limitations of Quality by Testing Approaches
Quality by Testing approaches often fail to detect every defect since testing can only evaluate a finite number of samples and scenarios, leaving potential risks unaddressed. Relying solely on testing can lead to costly rework and product recalls due to hidden issues that were not identified during the inspection phase. Your manufacturing process benefits more from Quality by Design, which integrates quality principles into every stage, minimizing reliance on end-product testing and enhancing overall product reliability.
Regulatory Perspectives on QbD and QbT
Regulatory agencies such as the FDA and EMA emphasize Quality by Design (QbD) for its proactive approach in ensuring product quality through predefined objectives and risk management, facilitating consistent manufacturing processes and reducing regulatory scrutiny. Quality by Testing (QbT), often seen as a retrospective method, relies on end-product testing to detect defects but may lead to variability and increased risk of non-compliance due to the absence of process understanding. Regulatory guidance increasingly advocates for QbD integration to enhance product robustness, accelerate approval timelines, and support lifecycle management more effectively than QbT.
Case Studies: QbD Success Stories
Case studies of Quality by Design (QbD) demonstrate significant improvements in product consistency and regulatory compliance compared to traditional Quality by Testing (QbT) methods. Companies implementing QbD frameworks report reduced batch failures and streamlined manufacturing processes, as seen in pharmaceutical giants like Pfizer and Novartis. You can leverage these success stories to understand how proactive design and risk assessment lead to superior product quality and cost savings.
Future Trends in Quality Management
Future trends in quality management emphasize a shift from traditional Quality by Testing towards Quality by Design (QbD), integrating predictive analytics and AI-driven process optimization. QbD ensures product quality is built into development stages, reducing reliance on end-product inspections and enhancing overall efficiency. Your organization can achieve sustainable compliance and innovation by adopting QbD frameworks supported by digital twins and real-time data monitoring.
Quality by Design vs Quality by Testing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com