Electric propulsion offers quieter operation, reduced emissions, and lower maintenance costs compared to diesel propulsion, making it an eco-friendly and efficient choice. Your decision between the two should consider factors like range, power requirements, and upfront investment.
Table of Comparison
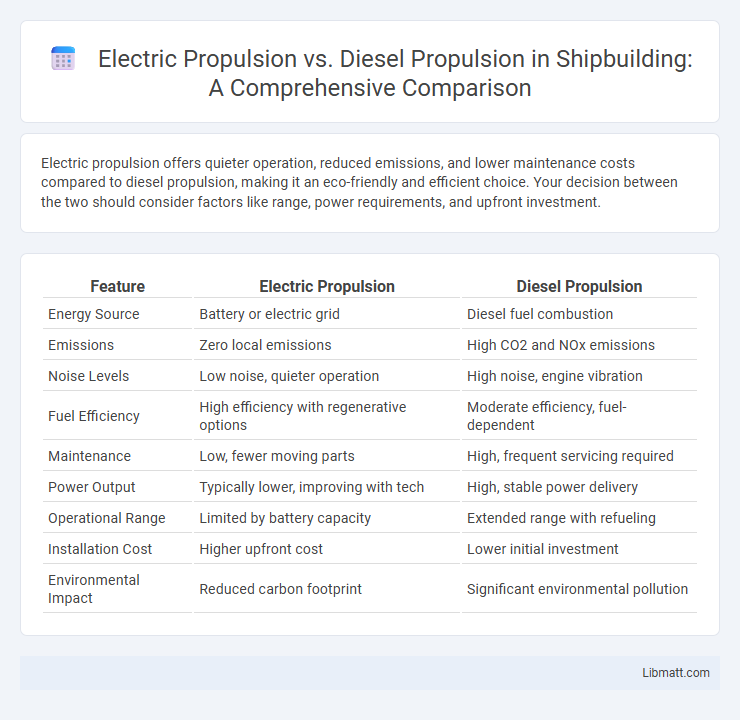
| Feature | Electric Propulsion | Diesel Propulsion |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Battery or electric grid | Diesel fuel combustion |
| Emissions | Zero local emissions | High CO2 and NOx emissions |
| Noise Levels | Low noise, quieter operation | High noise, engine vibration |
| Fuel Efficiency | High efficiency with regenerative options | Moderate efficiency, fuel-dependent |
| Maintenance | Low, fewer moving parts | High, frequent servicing required |
| Power Output | Typically lower, improving with tech | High, stable power delivery |
| Operational Range | Limited by battery capacity | Extended range with refueling |
| Installation Cost | Higher upfront cost | Lower initial investment |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced carbon footprint | Significant environmental pollution |
Introduction to Electric and Diesel Propulsion
Electric propulsion systems use electric motors powered by batteries or fuel cells, offering quiet operation and zero local emissions, ideal for environmentally conscious applications. Diesel propulsion relies on internal combustion engines burning diesel fuel, providing high power density and established refueling infrastructure suitable for long-range and heavy-duty uses. Your choice between electric and diesel propulsion depends on factors like operational range, environmental regulations, and maintenance requirements.
How Electric Propulsion Works
Electric propulsion systems utilize electric motors powered by batteries or fuel cells to generate thrust, converting electrical energy directly into mechanical energy with high efficiency. Unlike diesel propulsion, which relies on combustion engines burning fossil fuels, electric propulsion produces zero direct emissions and operates silently with minimal vibration. Advancements in lithium-ion battery technology and power management have enhanced the range and performance of electric propulsion in marine and aerospace applications.
How Diesel Propulsion Works
Diesel propulsion operates through an internal combustion engine that ignites diesel fuel to generate mechanical energy, driving the vessel's propeller shaft. The engine converts the chemical energy from diesel fuel into rotational power, allowing for efficient and robust performance in marine environments. Diesel engines are favored for their high torque output, fuel efficiency, and reliability in long-distance maritime operations.
Efficiency Comparison: Electric vs Diesel
Electric propulsion systems convert energy with up to 90% efficiency, significantly outperforming diesel engines, which typically operate around 30-40% efficiency. This higher efficiency means electric propulsion reduces energy waste and operating costs, making it a sustainable choice for modern maritime and automotive applications. You can expect lower emissions and a smaller environmental footprint by choosing electric over diesel propulsion.
Environmental Impact of Propulsion Systems
Electric propulsion systems produce zero tailpipe emissions, significantly reducing air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions compared to diesel propulsion. Diesel engines emit nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and carbon dioxide (CO2), contributing to climate change and respiratory health issues. Transitioning to electric propulsion supports compliance with stricter environmental regulations and promotes sustainable maritime and automotive industries.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-Term Expenses
Electric propulsion systems typically have higher initial costs due to expensive batteries and advanced technology but benefit from lower long-term expenses thanks to reduced fuel consumption and maintenance requirements. Diesel propulsion involves lower upfront investment but incurs higher ongoing costs driven by fuel prices, regular engine servicing, and emissions compliance. Your choice impacts total cost of ownership, with electric options offering cost efficiency over time despite significant starting investment.
Maintenance Requirements and Lifespan
Electric propulsion systems feature fewer moving parts than diesel engines, significantly reducing maintenance frequency and associated costs. Their lifespan often exceeds diesel counterparts due to minimal mechanical wear, as electric motors avoid combustion-related degradation. Diesel propulsion demands regular oil changes, fuel system upkeep, and periodic engine overhauls, which cumulatively shorten overall operational longevity.
Performance and Power Output Differences
Electric propulsion systems offer instant torque and smooth acceleration, delivering consistent power output ideal for variable speed applications, whereas diesel propulsion provides higher peak power and long-range endurance suitable for heavy-duty and extended operations. Electric motors operate with greater efficiency and lower noise levels but may have limitations in continuous power output due to battery capacity and thermal management. Diesel engines excel in sustained high-power scenarios but generate higher emissions and require more maintenance.
Applications in Various Industries
Electric propulsion systems are increasingly favored in industries such as marine transport, aviation, and automotive manufacturing due to their efficiency, lower emissions, and reduced noise levels. Diesel propulsion remains dominant in heavy-duty applications like freight shipping, construction equipment, and long-haul trucking because of superior fuel energy density and established infrastructure. Your choice between electric and diesel propulsion should consider operational requirements, environmental impact, and total cost of ownership in the specific industrial context.
Future Trends in Marine and Vehicle Propulsion
Electric propulsion systems are rapidly advancing with improvements in battery energy density and efficiency, driving significant growth in marine and vehicle sectors. Diesel propulsion, while still dominant for heavy-duty and long-range applications, faces stricter emissions regulations that encourage hybrid and alternative fuel integrations. Emerging trends highlight a shift towards fully electric and fuel cell technologies, supported by expanding charging infrastructure and government incentives promoting sustainable transportation.
Electric propulsion vs diesel propulsion Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com