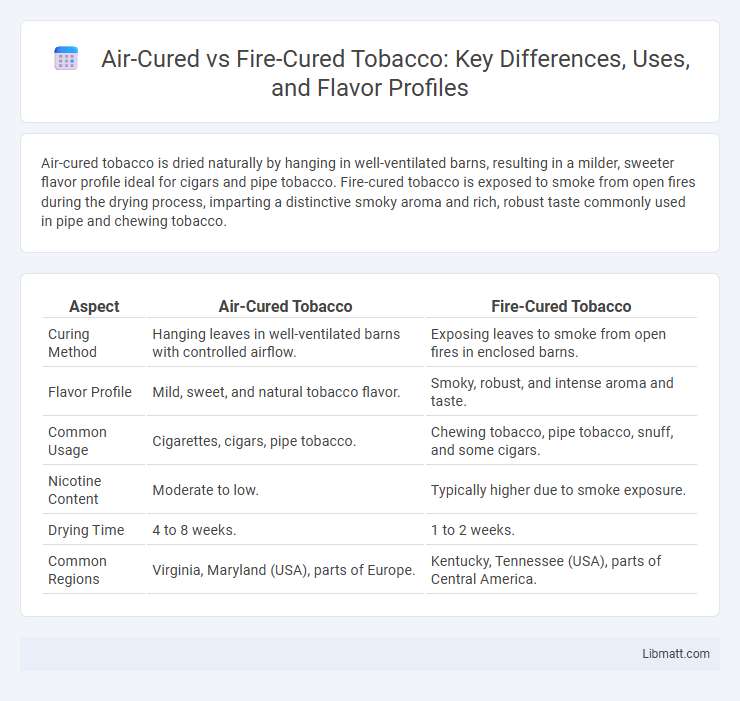
Air-cured tobacco is dried naturally by hanging in well-ventilated barns, resulting in a milder, sweeter flavor profile ideal for cigars and pipe tobacco. Fire-cured tobacco is exposed to smoke from open fires during the drying process, imparting a distinctive smoky aroma and rich, robust taste commonly used in pipe and chewing tobacco.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Air-Cured Tobacco | Fire-Cured Tobacco |
|---|---|---|
| Curing Method | Hanging leaves in well-ventilated barns with controlled airflow. | Exposing leaves to smoke from open fires in enclosed barns. |
| Flavor Profile | Mild, sweet, and natural tobacco flavor. | Smoky, robust, and intense aroma and taste. |
| Common Usage | Cigarettes, cigars, pipe tobacco. | Chewing tobacco, pipe tobacco, snuff, and some cigars. |
| Nicotine Content | Moderate to low. | Typically higher due to smoke exposure. |
| Drying Time | 4 to 8 weeks. | 1 to 2 weeks. |
| Common Regions | Virginia, Maryland (USA), parts of Europe. | Kentucky, Tennessee (USA), parts of Central America. |
Understanding Air-Cured and Fire-Cured Processes
Air-cured tobacco undergoes a natural drying process where leaves hang in well-ventilated barns for several weeks, allowing gradual moisture evaporation that preserves smooth, mild flavors ideal for cigars and pipe tobacco. Fire-cured tobacco is exposed to controlled smoke from hardwood fires inside curing barns, imparting a distinct smoky aroma and robust taste popular in certain pipe tobaccos and chewing tobacco. The choice between air-cured and fire-cured methods significantly influences the chemical composition and flavor profile of the final tobacco product.
Historical Background of Tobacco Curing Methods
Air-curing and fire-curing represent two traditional tobacco curing methods developed over centuries. Air-curing originated in Europe during the early cultivation of tobacco, relying on natural airflow to slowly dry leaves, preserving mild flavors and reducing sugar content. Fire-curing, with roots in Native American practices, uses controlled smoke from hardwood fires to impart distinctive smoky aromas and increase nicotine levels, shaping regional tobacco varieties like those in Kentucky and Tennessee.
Key Differences Between Air-Cured and Fire-Cured Tobacco
Air-cured tobacco undergoes a drying process in well-ventilated barns, where leaves slowly lose moisture over several weeks, resulting in a milder flavor with lower sugar and nicotine content. Fire-cured tobacco uses controlled smoke from wood fires to dry and flavor the leaves, producing a stronger, smoky taste with higher nicotine levels ideal for pipe and chewing tobacco. The primary distinction lies in the curing method, moisture removal, and resultant flavor profiles tailored to different tobacco products.
Temperature and Environment in Curing
Air-cured tobacco is dried at ambient temperatures ranging between 20degC to 30degC (68degF to 86degF) in well-ventilated barns, allowing slow moisture evaporation in a controlled, low-temperature environment. Fire-cured tobacco involves exposing leaves to smoke from smoldering hardwood fires, with temperatures typically maintained between 35degC and 55degC (95degF to 131degF), creating a smoky environment that imparts distinct flavors. The temperature and environment differences significantly influence the chemical composition and aroma profile of the cured tobacco.
Flavor Profiles: Contrasting Air-Cured and Fire-Cured Products
Air-cured products develop mild, smooth flavor profiles with natural, earthy undertones due to the slow drying process in well-ventilated environments. Fire-cured products exhibit robust, smoky, and intense flavors created by exposing the material to wood smoke and heat during curing. Your choice between these methods greatly influences the taste experience, with air-cured offering subtle complexity and fire-cured providing a bold, smoky character.
Impact on Tobacco Color and Texture
Air-cured tobacco typically develops a lighter, golden to light brown color with a smooth and pliable texture due to the slow drying process in a well-ventilated environment. Fire-cured tobacco, exposed to smoke from open fires, acquires a darker, reddish-brown to almost black hue and a drier, coarser texture with a distinctive smoky aroma. These curing methods directly influence the final appearance and mouthfeel of tobacco, affecting both the visual appeal and the smoking experience.
Health Implications of Different Curing Methods
Air-cured tobacco tends to have lower levels of carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) compared to fire-cured tobacco, which is exposed to smoke from burning wood or charcoal. Fire-curing introduces higher concentrations of PAHs and other harmful chemicals that increase the risk of respiratory diseases and cancer among users. Choosing air-cured tobacco may reduce exposure to these toxic compounds, potentially lowering adverse health effects associated with smoking.
Uses in Cigars, Pipes, and Chewing Tobacco
Air-cured tobacco, dried slowly in well-ventilated barns, is commonly used in cigars and chewing tobacco for its mild, natural flavor and smooth burn. Fire-cured tobacco, exposed to open flames or smoke during drying, imparts a robust, smoky taste ideal for pipe tobacco and distinctive chewing tobacco blends. Understanding these curing methods helps you choose the perfect tobacco type based on your preferred flavor profile and smoking experience.
Market Demand and Consumer Preferences
Air-cured tobacco appeals to consumers seeking mild, smooth flavor profiles and is frequently used in products like cigars and pipe tobacco, contributing to a steady market demand in traditional and premium tobacco segments. Fire-cured tobacco, valued for its rich, smoky taste, dominates in products such as chewing tobacco and certain cigarette blends, attracting consumers who prefer bold, robust flavors, driving higher demand in niche markets. Shifts in consumer preferences towards natural and artisanal products have increased interest in air-cured tobacco, while fire-cured tobacco retains a strong following among enthusiasts of classic and intense tobacco experiences.
Future Trends in Tobacco Curing Techniques
Future trends in tobacco curing techniques emphasize sustainability and efficiency, with air-cured methods evolving to reduce environmental impact through controlled humidity and temperature systems. Fire-cured tobacco is being enhanced by cleaner-burning fuels and automated monitoring to lower emissions and improve consistency. Your opportunity lies in adopting innovative curing technologies that balance traditional flavor profiles with eco-friendly processes.
air-cured vs fire-cured Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com