A curing barn is designed to control temperature and humidity to preserve crops like tobacco and certain fruits by slowly reducing moisture, ensuring quality and flavor retention. A drying barn primarily focuses on rapidly removing moisture from crops such as hay or grains to prevent spoilage and mold growth, preserving Your harvest efficiently.
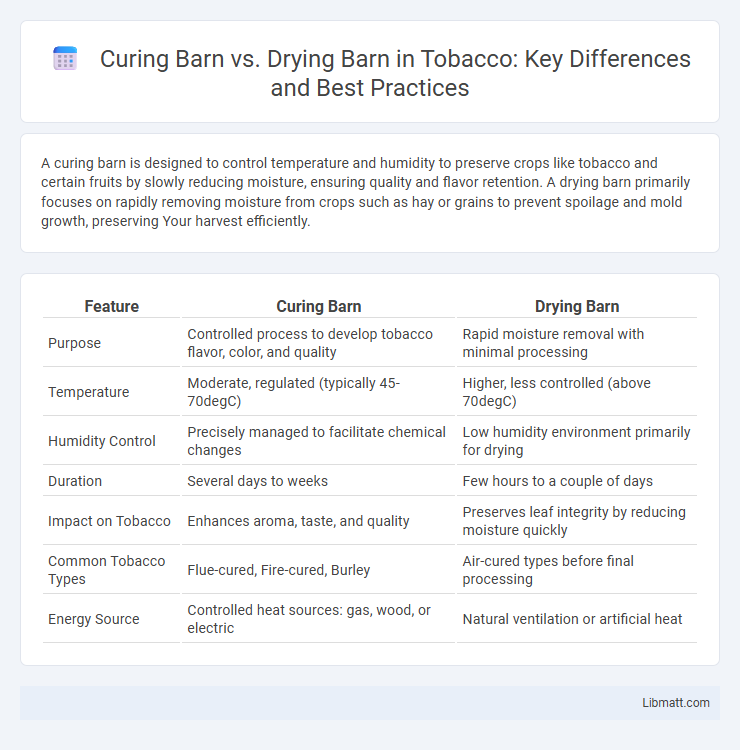
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Curing Barn | Drying Barn |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Controlled process to develop tobacco flavor, color, and quality | Rapid moisture removal with minimal processing |
| Temperature | Moderate, regulated (typically 45-70degC) | Higher, less controlled (above 70degC) |
| Humidity Control | Precisely managed to facilitate chemical changes | Low humidity environment primarily for drying |
| Duration | Several days to weeks | Few hours to a couple of days |
| Impact on Tobacco | Enhances aroma, taste, and quality | Preserves leaf integrity by reducing moisture quickly |
| Common Tobacco Types | Flue-cured, Fire-cured, Burley | Air-cured types before final processing |
| Energy Source | Controlled heat sources: gas, wood, or electric | Natural ventilation or artificial heat |
Introduction to Curing Barns and Drying Barns
Curing barns and drying barns are specialized facilities essential for preserving agricultural products like tobacco, herbs, and certain crops. A curing barn focuses on controlled humidity and temperature to enhance flavor and texture through processes such as fermentation and aging. Your choice between a curing barn and a drying barn depends on the specific post-harvest requirements to optimize product quality and shelf life.
Purpose and Functionality of Curing Barns
Curing barns are designed to optimize the drying process by controlling temperature, humidity, and airflow to ensure proper curing of crops like tobacco or hemp, enhancing flavor and quality. Unlike drying barns that primarily focus on removing moisture quickly, curing barns maintain specific environmental conditions to enable biochemical changes and prevent spoilage. This controlled environment is essential for developing the desired aroma, texture, and chemical composition in the final product.
Purpose and Functionality of Drying Barns
Drying barns are specifically designed to reduce the moisture content of harvested crops, such as hay, grains, or tobacco, through controlled ventilation and airflow systems that prevent mold and spoilage. Unlike curing barns, which focus on the chemical changes during the aging process to enhance flavor or quality, drying barns emphasize maintaining optimal temperature and humidity levels to ensure preservation and storage readiness. Proper functionality of drying barns ensures crops retain nutritional value and resist microbial growth, improving overall yield quality.
Key Differences Between Curing and Drying Barns
Curing barns and drying barns serve distinct functions in agricultural processing, with curing barns primarily designed to facilitate the slow, controlled aging of crops like tobacco or hops, enhancing flavor and quality through regulated temperature and humidity. Drying barns, on the other hand, focus on rapid moisture removal from crops such as grains or herbs to prevent spoilage and prepare them for storage or sale. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the appropriate barn type for optimal post-harvest handling and product preservation.
Structural Design Features: Curing Barns vs Drying Barns
Curing barns feature airtight, temperature-controlled environments with adjustable ventilation systems designed to maintain consistent humidity and prevent mold, essential for preserving tobacco leaves. Drying barns emphasize open or semi-open structures with ample airflow facilitated by slatted walls or removable panels, promoting natural drying processes by maximizing air circulation. Your choice between these structural designs depends on whether precise environmental control or natural airflow optimization is critical for your agricultural product.
Environmental Control and Ventilation
Curing barns feature precise environmental control systems designed to maintain optimal temperature and humidity levels critical for preventing mold and ensuring uniform drying of harvested crops. Drying barns emphasize robust ventilation mechanisms that maximize airflow to rapidly reduce moisture content while minimizing exposure to contaminants. Both barn types utilize adjustable vents and fans, but curing barns prioritize stable, gradual drying environments, whereas drying barns focus on accelerated moisture removal through continuous air circulation.
Types of Materials Best Suited for Each Barn
Curing barns are ideal for materials that require controlled temperature and humidity to enhance flavor and prevent spoilage, such as tobacco leaves, aged meats, and certain fruits. Drying barns suit bulky agricultural products like grains, hay, and herbs that need effective air circulation to reduce moisture content quickly and avoid mold growth. Your choice depends on whether the goal is flavor development and preservation (curing barn) or rapid moisture removal and storage readiness (drying barn).
Advantages and Limitations of Curing Barns
Curing barns offer controlled environments that enhance the flavor and quality of tobacco by maintaining optimal temperature and humidity levels, which prevents mold and ensures even drying. These barns, however, require substantial initial investment and ongoing energy costs to regulate conditions, making them less suitable for small-scale farmers or regions with limited resources. Your choice between curing and drying barns should consider these trade-offs to maximize product quality and economic efficiency.
Advantages and Limitations of Drying Barns
Drying barns offer the advantage of controlled airflow and reduced moisture buildup, which helps prevent mold growth and preserves the quality of crops such as tobacco or hay. However, their limitations include dependence on consistent weather conditions and higher energy costs for maintaining optimal drying environments. You should consider these factors when choosing between curing and drying barns for your agricultural needs.
Choosing the Right Barn for Optimal Crop Processing
Selecting the right barn for optimal crop processing depends on your specific agricultural needs, with curing barns designed to gently reduce moisture in crops like tobacco or hops, preserving quality through controlled humidity and temperature. Drying barns provide faster moisture removal, ideal for grains and other crops requiring rapid drying to prevent spoilage and maintain structural integrity. Your choice impacts crop longevity, flavor, and value, making understanding the differences between curing and drying barns essential for efficient post-harvest management.
Curing barn vs Drying barn Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com