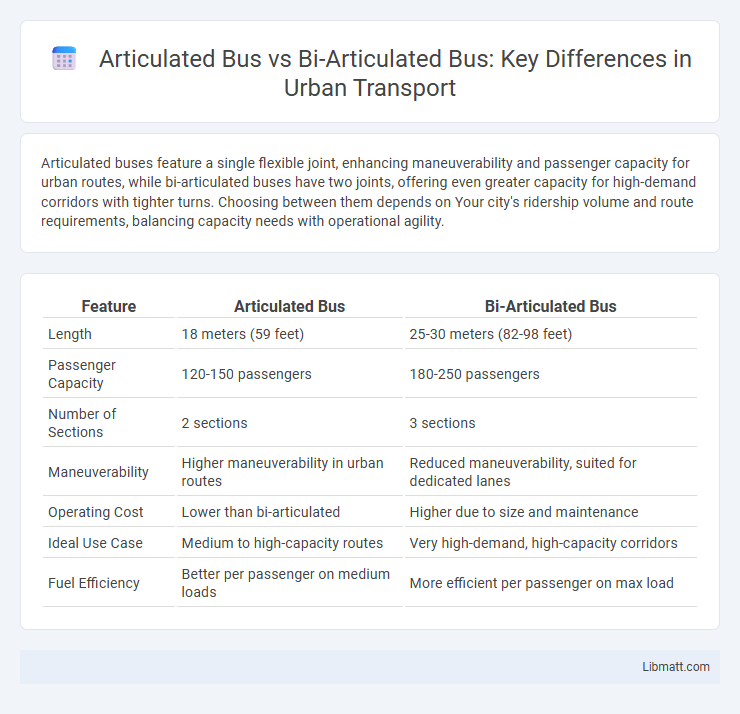
Articulated buses feature a single flexible joint, enhancing maneuverability and passenger capacity for urban routes, while bi-articulated buses have two joints, offering even greater capacity for high-demand corridors with tighter turns. Choosing between them depends on Your city's ridership volume and route requirements, balancing capacity needs with operational agility.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Articulated Bus | Bi-Articulated Bus |
|---|---|---|
| Length | 18 meters (59 feet) | 25-30 meters (82-98 feet) |
| Passenger Capacity | 120-150 passengers | 180-250 passengers |
| Number of Sections | 2 sections | 3 sections |
| Maneuverability | Higher maneuverability in urban routes | Reduced maneuverability, suited for dedicated lanes |
| Operating Cost | Lower than bi-articulated | Higher due to size and maintenance |
| Ideal Use Case | Medium to high-capacity routes | Very high-demand, high-capacity corridors |
| Fuel Efficiency | Better per passenger on medium loads | More efficient per passenger on max load |
Introduction to Articulated and Bi-Articulated Buses
Articulated buses feature a single flexible joint that connects two sections, increasing passenger capacity and maneuverability on urban routes. Bi-articulated buses extend this concept with two flexible joints and three passenger sections, significantly boosting capacity for high-demand transit corridors. Both designs optimize space and efficiency, with bi-articulated models serving as a solution for dense metropolitan areas requiring mass transit solutions beyond traditional bus sizes.
Design and Structure Comparison
An articulated bus features a single flexible joint connecting two rigid sections, optimizing maneuverability and passenger capacity in urban environments. In contrast, a bi-articulated bus incorporates two joints linking three sections, significantly increasing passenger space and length but requiring wider turning radii and enhanced structural support. Your choice between these designs depends on route demand and city infrastructure compatibility, balancing capacity and navigability.
Passenger Capacity Differences
Articulated buses typically accommodate around 120 passengers, offering a balance between length and maneuverability for urban transit routes. Bi-articulated buses extend this capacity significantly, often carrying up to 200 passengers due to their additional flexible joint and longer chassis. When considering Your transit system's demand for high passenger volume, bi-articulated buses provide a decisive advantage in maximizing capacity during peak hours.
Operational Efficiency and Route Suitability
Articulated buses offer improved operational efficiency by balancing passenger capacity with maneuverability, making them ideal for urban routes with moderate traffic and frequent stops. Bi-articulated buses provide even greater capacity for high-demand corridors but require wider turning radii and longer stops, limiting their suitability to dedicated or high-capacity transit lanes. Your choice depends on route characteristics and passenger volume, ensuring optimized service without compromising efficiency.
Maneuverability in Urban Environments
Articulated buses offer improved maneuverability in urban environments compared to standard buses by featuring a single pivot joint that allows easier navigation through tight city streets and sharp turns. Bi-articulated buses, with two pivot joints and longer lengths, provide higher passenger capacity but have reduced agility, making them less suited for narrow or congested routes. Transit agencies often choose articulated buses for routes requiring frequent stops and complex turns, while bi-articulated buses are deployed on high-demand corridors with broader roadways.
Cost Analysis: Purchase and Maintenance
Articulated buses typically have lower purchase prices and maintenance costs compared to bi-articulated buses due to their simpler design and shorter length. Bi-articulated buses, while more expensive initially, offer increased passenger capacity that can lead to reduced operational costs per traveler in high-demand routes. Maintenance expenses for bi-articulated buses are higher because of additional articulation joints and more complex mechanical systems requiring specialized parts and servicing.
Environmental Impact and Fuel Consumption
Articulated buses typically consume less fuel per passenger compared to standard buses but are less efficient environmentally than bi-articulated buses, which accommodate higher passenger capacity and reduce overall emissions per capita. Bi-articulated buses optimize fuel consumption by transporting more passengers in a single trip, significantly lowering greenhouse gas emissions and urban air pollution. When comparing both, bi-articulated buses present a more sustainable option for high-demand transit corridors due to their enhanced fuel economy and reduced environmental footprint.
Accessibility and Passenger Comfort
Articulated buses offer improved accessibility with lower floors and multiple wide doors designed for faster boarding, while bi-articulated buses provide extended capacity, which can sometimes compromise ease of movement within the vehicle. Passenger comfort in articulated buses benefits from smoother maneuverability and better ride quality due to shorter length, whereas bi-articulated buses may experience slightly reduced comfort during turns or in congested areas. Your choice should balance the need for accessibility features against the higher passenger volume capacity of bi-articulated models.
Safety Considerations and Challenges
Articulated buses, typically around 18 meters long, offer enhanced maneuverability and easier navigation in urban environments compared to bi-articulated buses, which can extend up to 25 meters and pose increased challenges in turning radius and lane changes. Safety considerations for bi-articulated buses include managing the increased risk of jackknifing and ensuring effective communication between multiple articulation joints to maintain stability. Both types require specialized driver training and advanced braking systems to mitigate the risks associated with their extended lengths and passenger capacities.
Future Trends in High-Capacity Bus Transit
Bi-articulated buses are emerging as the future trend in high-capacity bus transit due to their ability to carry up to 270 passengers, significantly more than standard articulated buses. Your city's transit system can benefit from these buses' enhanced capacity, reducing congestion and improving efficiency on busy urban routes. Innovations such as electric and autonomous bi-articulated models are expected to further revolutionize sustainable mass transit solutions.
articulated bus vs bi-articulated bus Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com