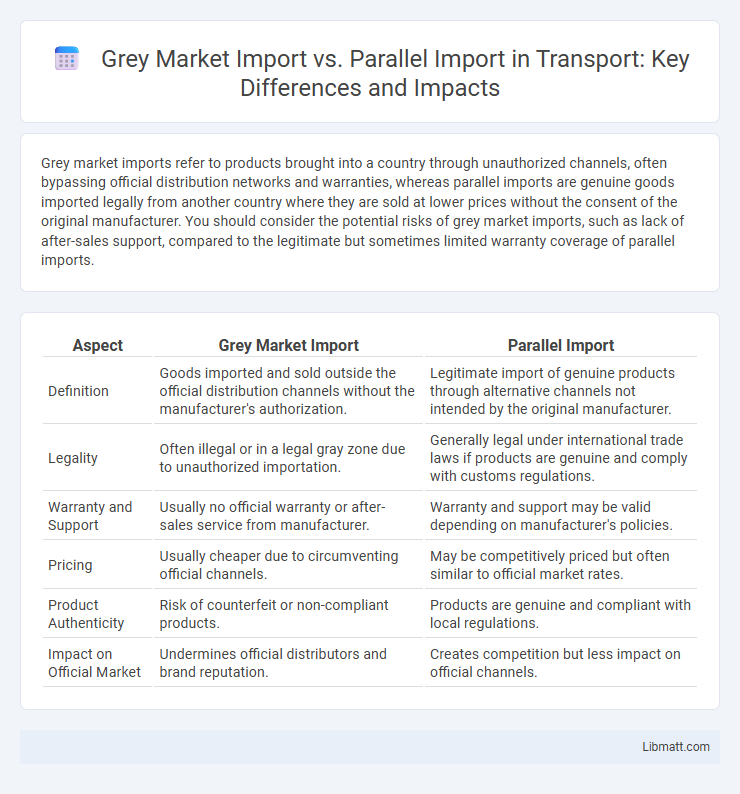
Grey market imports refer to products brought into a country through unauthorized channels, often bypassing official distribution networks and warranties, whereas parallel imports are genuine goods imported legally from another country where they are sold at lower prices without the consent of the original manufacturer. You should consider the potential risks of grey market imports, such as lack of after-sales support, compared to the legitimate but sometimes limited warranty coverage of parallel imports.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Grey Market Import | Parallel Import |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Goods imported and sold outside the official distribution channels without the manufacturer's authorization. | Legitimate import of genuine products through alternative channels not intended by the original manufacturer. |
| Legality | Often illegal or in a legal gray zone due to unauthorized importation. | Generally legal under international trade laws if products are genuine and comply with customs regulations. |
| Warranty and Support | Usually no official warranty or after-sales service from manufacturer. | Warranty and support may be valid depending on manufacturer's policies. |
| Pricing | Usually cheaper due to circumventing official channels. | May be competitively priced but often similar to official market rates. |
| Product Authenticity | Risk of counterfeit or non-compliant products. | Products are genuine and compliant with local regulations. |
| Impact on Official Market | Undermines official distributors and brand reputation. | Creates competition but less impact on official channels. |
Understanding Grey Market Imports
Grey market imports refer to genuine products brought into a country without the authorization of the original manufacturer, often bypassing official distribution channels. These imports are typically sold at lower prices but may lack manufacturer warranties or after-sales support, creating risks for consumers. Parallel imports, a subset of grey market goods, involve genuine products imported from another country through unauthorized but legal means, differing primarily in regional pricing or packaging.
Defining Parallel Imports
Parallel imports refer to genuine products imported through unauthorized channels without the trademark owner's permission, often bypassing official distribution networks. These imports are legally produced goods but sold outside the intended market, typically resulting in lower prices or varied availability. Understanding parallel imports helps you assess risks related to warranty, quality, and support compared to authorized products.
Key Differences Between Grey Market and Parallel Imports
Grey market imports refer to genuine products imported and sold through unauthorized channels without the manufacturer's consent, often lacking official warranties and after-sales support. Parallel imports involve legally imported genuine goods purchased from foreign markets and resold domestically, typically with the manufacturer's approval or compliance with local regulations. The key differences lie in authorization levels, warranty validity, and the legality of distribution channels.
Legal Perspectives on Grey and Parallel Imports
Legal perspectives on grey market imports vary by country but generally distinguish them from parallel imports based on authorization status and product sourcing. Grey market imports involve unauthorized sales of genuine goods, often violating trademark or distribution rights, whereas parallel imports are legitimate products imported without the manufacturer's consent but typically comply with national import laws. Understanding these legal distinctions helps you navigate intellectual property regulations and avoid infringement risks in cross-border trade.
Impact on Manufacturers and Official Distributors
Grey market imports bypass authorized channels, leading to significant revenue loss and weakened brand control for manufacturers and official distributors. These imports often undermine pricing strategies and warranty protections, resulting in diminished customer trust and reduced dealer loyalty. Your preferred brand's market stability depends on stringent measures against unauthorized parallel imports to protect official distribution networks and maintain product integrity.
Consumer Risks and Benefits
Grey market imports often present lower prices and early access to products, but carry risks such as lack of manufacturer warranty and potential difficulties in after-sales service. Parallel imports are genuine products imported through unauthorized channels, offering competitive pricing and product authenticity, yet consumers may face challenges with warranty enforcement and compatibility with local standards. Understanding these differences helps you make informed purchasing decisions balancing cost savings against possible service limitations.
Price Variations: What Drives the Market?
Price variations in grey market imports often stem from bypassing authorized distribution channels, enabling sellers to offer products at lower costs due to reduced overhead and tax evasion. Parallel imports maintain product authenticity but exploit price differentials between countries, capitalizing on favorable exchange rates and regional pricing strategies set by manufacturers. Both markets are driven by consumers seeking cost savings, but the lack of manufacturer control in grey markets can lead to warranty and service discrepancies.
Warranty and After-Sales Service Concerns
Grey market imports often lack official manufacturer warranties, resulting in limited or no after-sales service support, which can lead to costly repairs and customer dissatisfaction. Parallel imports, while sometimes carrying valid warranties, may face restrictions on warranty claims depending on regional policies and authorized service centers. Consumers should carefully verify warranty terms and after-sales service availability before purchasing products through either grey market or parallel import channels.
Regulatory Actions and Enforcement
Regulatory actions against grey market imports involve stricter customs inspections and seizure of unauthorized goods to protect intellectual property rights and maintain market integrity. Enforcement agencies target parallel imports by verifying compliance with trademark laws and authorized distribution channels to prevent consumer deception and support local distributors. Both import types face increasing scrutiny through international cooperation and legal frameworks aimed at upholding brand protection and regulatory standards.
Future Trends in Grey and Parallel Import Markets
Future trends in grey market import and parallel import markets indicate increasing consumer demand for diverse product options and competitive pricing across global regions. Advances in e-commerce platforms and cross-border logistics are expected to facilitate smoother access to parallel imports while regulatory scrutiny and brand protection efforts might impact grey market operations. Your ability to navigate these evolving market dynamics will determine success in leveraging opportunities from both import channels.
grey market import vs parallel import Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com