Axle load refers to the weight supported by a single axle of a vehicle, while gross vehicle weight (GVW) is the total weight of the vehicle including its load. Understanding your vehicle's axle load is crucial for safe operation and compliance with road regulations that govern GVW limits.
Table of Comparison
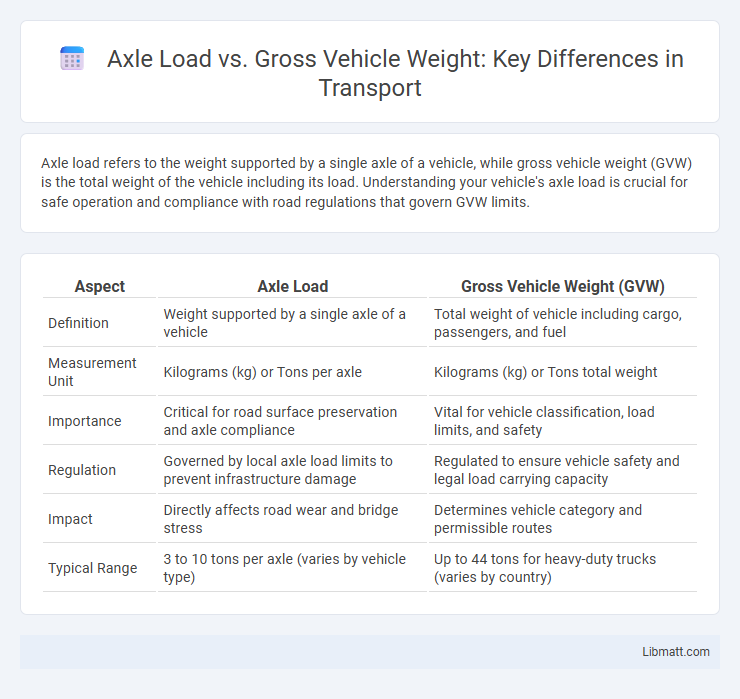
| Aspect | Axle Load | Gross Vehicle Weight (GVW) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Weight supported by a single axle of a vehicle | Total weight of vehicle including cargo, passengers, and fuel |
| Measurement Unit | Kilograms (kg) or Tons per axle | Kilograms (kg) or Tons total weight |
| Importance | Critical for road surface preservation and axle compliance | Vital for vehicle classification, load limits, and safety |
| Regulation | Governed by local axle load limits to prevent infrastructure damage | Regulated to ensure vehicle safety and legal load carrying capacity |
| Impact | Directly affects road wear and bridge stress | Determines vehicle category and permissible routes |
| Typical Range | 3 to 10 tons per axle (varies by vehicle type) | Up to 44 tons for heavy-duty trucks (varies by country) |
Introduction to Axle Load and Gross Vehicle Weight
Axle load refers to the weight supported by a single axle of a vehicle, crucial for maintaining road safety and structural integrity. Gross vehicle weight (GVW) is the total weight of your vehicle including cargo, passengers, and the vehicle itself, influencing fuel efficiency and legal compliance. Understanding the balance between axle load and GVW ensures optimal vehicle performance and prevents road damage.
Definitions: Axle Load vs Gross Vehicle Weight
Axle load refers to the weight supported by a single axle of a vehicle, which directly impacts road wear and vehicle stability. Gross vehicle weight (GVW) is the total weight of the vehicle including its chassis, body, engine, passengers, cargo, and fuel. Understanding the difference between axle load and GVW helps you ensure compliance with transportation regulations and maintain safe, efficient vehicle operation.
Key Differences Between Axle Load and Gross Vehicle Weight
Axle load refers to the weight supported by a single axle of a vehicle, while gross vehicle weight (GVW) is the total weight of the vehicle including cargo, passengers, and fuel. Axle load is critical for determining road wear and compliance with bridge load limits, whereas GVW affects overall vehicle performance and legal weight limits for transportation. Understanding the distinction ensures proper vehicle loading, safety adherence, and infrastructure protection.
Importance of Understanding Vehicle Weight Limits
Understanding axle load and gross vehicle weight limits is crucial for ensuring road safety, preventing vehicle damage, and complying with legal regulations. Exceeding axle load can lead to increased tire wear, suspension failure, and compromised braking performance, while surpassing gross vehicle weight limits can cause structural road damage and significant fines. Accurate knowledge of these weight restrictions helps optimize vehicle performance, maintain regulatory compliance, and extend infrastructure lifespan.
Calculation Methods for Axle Load and Gross Vehicle Weight
Axle load is calculated by measuring the weight transmitted by each axle to the ground, typically using weighbridges or load sensors, ensuring compliance with road safety standards. Gross Vehicle Weight (GVW) represents the total weight of the vehicle including its own mass, cargo, passengers, and fuel, determined by summing the individual axle loads or using certified vehicle scales. Your accurate assessment of axle load and GVW is crucial for preventing overloading, maintaining vehicle stability, and adhering to legal weight limits.
Impact on Road Safety and Infrastructure
Axle load directly influences the wear and tear on road surfaces, with excessive loads accelerating pavement damage and increasing maintenance costs, while gross vehicle weight ensures overall vehicle balance and compliance with safety regulations. Overloading axles beyond legal limits can compromise vehicle handling, raise accident risks, and strain bridges and road networks, reducing infrastructure lifespan. Understanding the relationship between axle load and gross vehicle weight is crucial for protecting your safety and preserving road infrastructure integrity.
Legal Regulations and Compliance Standards
Legal regulations on axle load and gross vehicle weight (GVW) ensure road safety and infrastructure preservation, with limits varying by country and vehicle type. Compliance standards typically require that axle loads do not exceed specified maximums to prevent excessive road wear and avoid penalties, while GVW caps are enforced through weigh stations and onboard monitoring systems. Adhering to these regulations is crucial for transport operators to maintain lawful operations and avoid fines or vehicle restrictions.
Effects on Vehicle Performance and Maintenance
Higher axle load increases stress on suspension and tires, accelerating wear and reducing vehicle durability. Gross vehicle weight impacts overall fuel efficiency and braking performance, with heavier loads requiring more power and longer stopping distances. Proper load distribution optimizes vehicle handling, minimizing maintenance costs and enhancing safety.
Commercial Transport Considerations
Axle load directly impacts the gross vehicle weight (GVW) limits imposed on commercial transport to ensure road safety and infrastructure longevity. Regulatory agencies set maximum axle load limits to prevent excessive wear on highways and bridges while optimizing payload capacity for efficient logistics. Properly managing axle load distribution enhances vehicle stability, reduces maintenance costs, and complies with transportation laws critical to commercial fleet operations.
Best Practices for Managing Axle Load and Gross Vehicle Weight
Effective management of axle load and gross vehicle weight ensures vehicle safety, prolongs infrastructure lifespan, and complies with legal weight limits. Utilizing advanced weighing technology and regular inspections helps maintain optimal load distribution, preventing overloading of individual axles. Implementing strict adherence to weight regulations and driver training programs reduces road wear and enhances overall fleet efficiency.
axle load vs gross vehicle weight Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com