Autonomous trucks operate independently, using advanced sensors and AI to navigate and make decisions without human intervention, enhancing efficiency and safety. Platooning trucks rely on vehicle-to-vehicle communication to closely follow a lead truck, reducing fuel consumption and improving road capacity while still requiring human drivers in each vehicle.
Table of Comparison
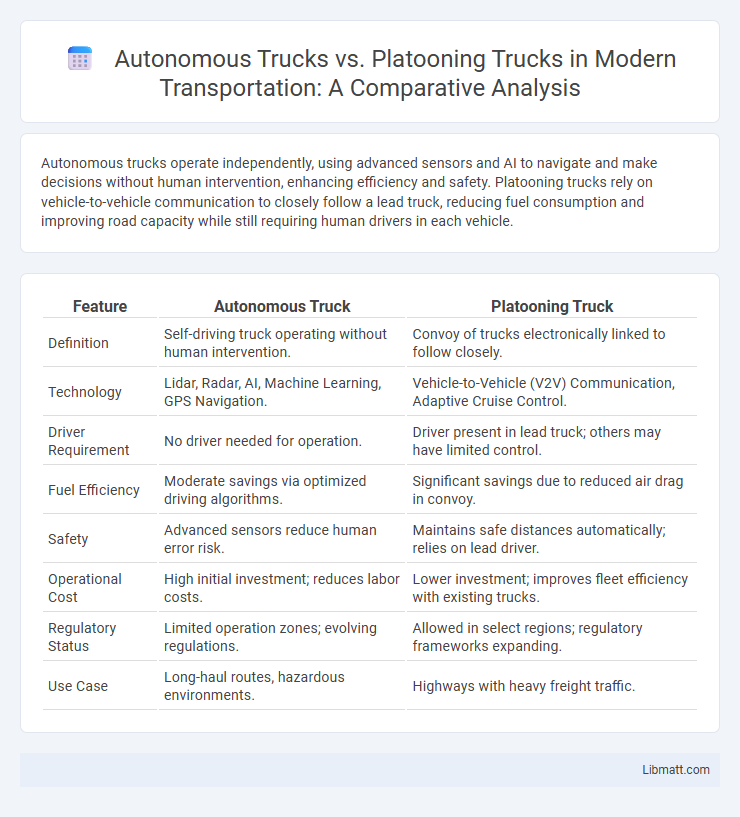
| Feature | Autonomous Truck | Platooning Truck |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Self-driving truck operating without human intervention. | Convoy of trucks electronically linked to follow closely. |
| Technology | Lidar, Radar, AI, Machine Learning, GPS Navigation. | Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) Communication, Adaptive Cruise Control. |
| Driver Requirement | No driver needed for operation. | Driver present in lead truck; others may have limited control. |
| Fuel Efficiency | Moderate savings via optimized driving algorithms. | Significant savings due to reduced air drag in convoy. |
| Safety | Advanced sensors reduce human error risk. | Maintains safe distances automatically; relies on lead driver. |
| Operational Cost | High initial investment; reduces labor costs. | Lower investment; improves fleet efficiency with existing trucks. |
| Regulatory Status | Limited operation zones; evolving regulations. | Allowed in select regions; regulatory frameworks expanding. |
| Use Case | Long-haul routes, hazardous environments. | Highways with heavy freight traffic. |
Introduction to Autonomous Trucks and Platooning Trucks
Autonomous trucks utilize advanced sensors, AI, and machine learning to navigate and operate independently without human intervention, enhancing safety and efficiency in freight transportation. Platooning trucks connect multiple vehicles via vehicle-to-vehicle communication technology, allowing them to travel closely together with synchronized acceleration and braking, reducing fuel consumption and traffic congestion. Both technologies aim to revolutionize logistics by improving operational efficiency, though autonomous trucks focus on full self-driving capabilities, while platooning emphasizes collaborative driving within a convoy.
Core Technologies Behind Autonomous and Platooning Trucks
Autonomous trucks rely heavily on advanced sensors such as LiDAR, radar, and computer vision systems to enable real-time environment perception and decision-making without human intervention. Platooning trucks utilize vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication and adaptive cruise control technology to maintain close, synchronized convoy formations, reducing drag and improving fuel efficiency. Your choice between these technologies will depend on how much automation and connectivity you need for optimized logistics performance.
Operational Principles: Autonomy vs. Connectivity
Autonomous trucks rely on advanced sensors, AI, and real-time data processing to independently navigate and make driving decisions without human intervention. Platooning trucks utilize vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) connectivity, where a lead truck controls the convoy's speed and braking, allowing following trucks to react instantaneously via wireless communication. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize full independence for each truck or enhanced coordination and fuel efficiency through connected driving.
Safety Features and Risk Management
Autonomous trucks utilize advanced sensors, machine learning algorithms, and real-time data processing to enhance safety by detecting obstacles, predicting road conditions, and executing precise maneuvers, thereby reducing human error-related accidents. Platooning trucks rely on vehicle-to-vehicle communication and synchronized braking systems to maintain tight gaps, improving fuel efficiency while mitigating rear-end collision risks through cooperative control mechanisms. Both technologies implement rigorous risk management protocols, including fail-safe redundancies and continuous monitoring, but autonomous trucks offer superior adaptability to diverse traffic scenarios compared to the coordinated yet dependent nature of platooned convoys.
Fuel Efficiency and Environmental Impact
Autonomous trucks use advanced sensors and AI to optimize routes and maintain steady speeds, reducing fuel consumption by up to 15%. Platooning trucks, which drive closely together using connected technology, cut air drag by approximately 10-20%, significantly improving fuel efficiency and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. Both technologies contribute to reducing the carbon footprint of freight transport but platooning delivers immediate aerodynamic benefits while autonomous trucks enable broader efficiency improvements through intelligent navigation.
Cost Comparison and Economic Viability
Autonomous trucks typically involve higher upfront costs due to advanced AI systems and sensor integration, while platooning trucks leverage existing vehicles connected via wireless communication, reducing initial investment. Over time, platooning offers economic viability by improving fuel efficiency through reduced aerodynamic drag and enabling synchronized driving, lowering operational expenses. Your choice depends on balancing long-term savings from platooning against the transformative capabilities and maintenance costs of fully autonomous trucks.
Infrastructure Requirements and Challenges
Autonomous trucks demand advanced infrastructure with extensive sensor networks, high-definition mapping, and reliable 5G connectivity to ensure real-time data processing and safe navigation. Platooning trucks require dedicated V2V (vehicle-to-vehicle) communication systems, synchronized control algorithms, and supportive roadways equipped with clear lane markings for maintaining close distances. Both technologies face challenges such as the high cost of infrastructure upgrades, interoperability standards, and ensuring cybersecurity against potential hacking threats.
Regulatory Landscape and Legal Considerations
The regulatory landscape for autonomous trucks is evolving rapidly, with ongoing efforts to establish federal and state-level frameworks addressing safety standards, liability, and operational guidelines. Platooning trucks benefit from existing regulations that allow for connected vehicle technologies, yet require clear legal definitions on following distances and vehicle control responsibilities between lead and following trucks. Legal considerations for both systems emphasize cybersecurity, data privacy, and cross-jurisdictional compliance to enable safe deployment on public highways.
Industry Adoption and Real-World Case Studies
Industry adoption of autonomous trucks is rapidly expanding, with companies like Waymo and TuSimple leading deployments that showcase enhanced safety and efficiency in logistics. Platooning trucks, utilized by fleets such as Volvo and Peloton Technology, demonstrate significant fuel savings and reduced emissions through synchronized driving on highways. Your business can benefit from these technologies by analyzing case studies that highlight improved operational costs and scalability in real-world transportation scenarios.
Future Outlook: Integration and Coexistence
Autonomous trucks and platooning trucks are expected to integrate seamlessly, combining individual vehicle autonomy with cooperative convoy technology to enhance efficiency and safety. Industry forecasts predict widespread adoption of mixed fleets where autonomous trucks operate independently or in platoons depending on route and traffic conditions. Strategic investments in V2X communication and AI-driven logistics will drive the coexistence of these technologies, optimizing fuel consumption and reducing emissions across freight transport networks.
autonomous truck vs platooning truck Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com