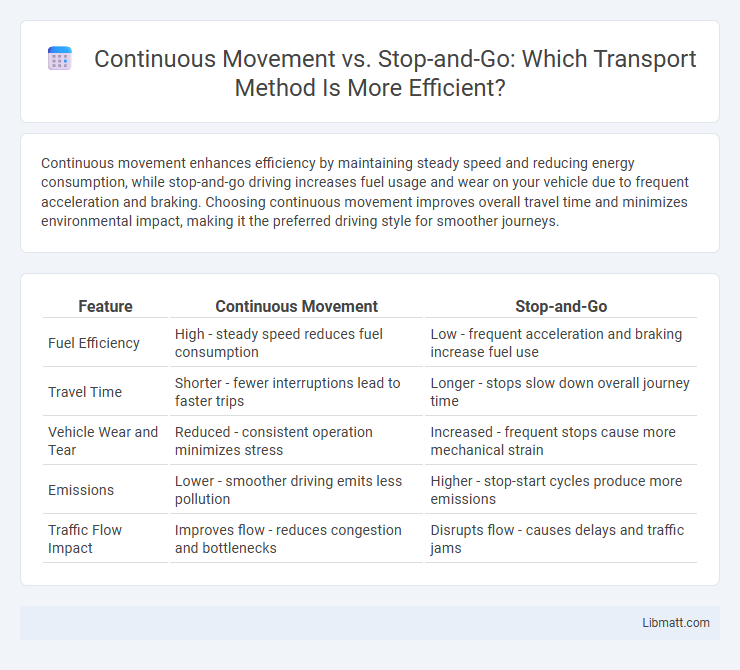
Continuous movement enhances efficiency by maintaining steady speed and reducing energy consumption, while stop-and-go driving increases fuel usage and wear on your vehicle due to frequent acceleration and braking. Choosing continuous movement improves overall travel time and minimizes environmental impact, making it the preferred driving style for smoother journeys.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Continuous Movement | Stop-and-Go |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Efficiency | High - steady speed reduces fuel consumption | Low - frequent acceleration and braking increase fuel use |
| Travel Time | Shorter - fewer interruptions lead to faster trips | Longer - stops slow down overall journey time |
| Vehicle Wear and Tear | Reduced - consistent operation minimizes stress | Increased - frequent stops cause more mechanical strain |
| Emissions | Lower - smoother driving emits less pollution | Higher - stop-start cycles produce more emissions |
| Traffic Flow Impact | Improves flow - reduces congestion and bottlenecks | Disrupts flow - causes delays and traffic jams |
Introduction to Continuous Movement vs Stop-and-Go
Continuous movement promotes efficient energy use and smoother traffic flow by maintaining steady speeds, reducing fuel consumption and emissions. Stop-and-go driving increases wear on brakes and engines, leading to higher maintenance costs and increased environmental impact. Your choice between these driving styles significantly affects vehicle performance and overall travel time.
Defining Continuous Movement
Continuous movement refers to uninterrupted motion where an object or person maintains steady velocity without pauses or abrupt changes in speed. This type of movement optimizes energy efficiency and reduces mechanical strain compared to stop-and-go patterns characterized by frequent halts and accelerations. In transportation and robotics, continuous movement enhances fluidity and operational performance, minimizing wear and improving overall system reliability.
Understanding Stop-and-Go Techniques
Stop-and-go techniques involve alternating periods of movement and complete stops to optimize traffic flow, reduce fuel consumption, and enhance safety in congested areas. Continuous movement strategies prioritize steady, uninterrupted motion to minimize acceleration and deceleration, improving fuel efficiency and reducing wear on your vehicle. Mastering stop-and-go methods helps drivers adapt to urban driving conditions, balancing time efficiency and energy savings.
Key Differences Between the Two Approaches
Continuous movement promotes steady energy flow and higher efficiency by maintaining momentum without interruption. Stop-and-go involves frequent starts and stops, which increase energy consumption, mechanical wear, and travel time. Understanding how your workflow benefits from continuous movement can optimize productivity and reduce operational costs.
Benefits of Continuous Movement
Continuous movement improves cardiovascular health by maintaining a steady heart rate and enhancing blood circulation. It boosts metabolic efficiency, helping your body burn calories more effectively compared to stop-and-go patterns. Sustained motion also reduces joint stiffness and minimizes the risk of injury by promoting consistent muscle engagement.
Advantages of Stop-and-Go Methods
Stop-and-go methods offer precise control and flexibility, making them ideal for tasks requiring frequent adjustments or pauses. These techniques enhance safety by allowing operators to assess conditions at each stop, reducing the risk of errors or accidents. Your efficiency improves in environments where intermittent movement is necessary to navigate obstacles or perform detailed work.
Common Applications in Real-World Scenarios
Continuous movement systems dominate in conveyor belts and assembly lines where steady, uninterrupted flow maximizes efficiency and reduces wear. Stop-and-go mechanisms are prevalent in traffic lights and automated packaging, allowing precise control and timing critical for safety and accuracy. Both methods optimize operational performance in manufacturing, logistics, and transportation industries by addressing specific task requirements.
Impact on Efficiency and Performance
Continuous movement enhances efficiency by minimizing energy loss and reducing wear on machinery, resulting in smoother operations and higher performance levels. Stop-and-go patterns cause frequent acceleration and deceleration, increasing fuel consumption and mechanical strain, which negatively affects overall productivity. Your system's efficiency improves significantly with consistent movement, optimizing resource use and extending equipment lifespan.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Needs
Continuous movement enhances efficiency and reduces wear by maintaining steady momentum, ideal for long-distance travel or sustained tasks. Stop-and-go offers better control and precision, beneficial in dynamic environments requiring frequent adjustments. Evaluating your specific operational demands ensures the approach aligns with your performance and safety goals.
Conclusion: Making Informed Movement Decisions
Continuous movement enhances energy efficiency and reduces wear on joints compared to stop-and-go patterns, promoting overall physical health. Stop-and-go movement often increases cardiovascular strain and can lead to higher fatigue levels, impacting endurance and performance negatively. Informed movement decisions should prioritize consistent momentum to optimize physiological benefits and minimize injury risks.
continuous movement vs stop-and-go Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com