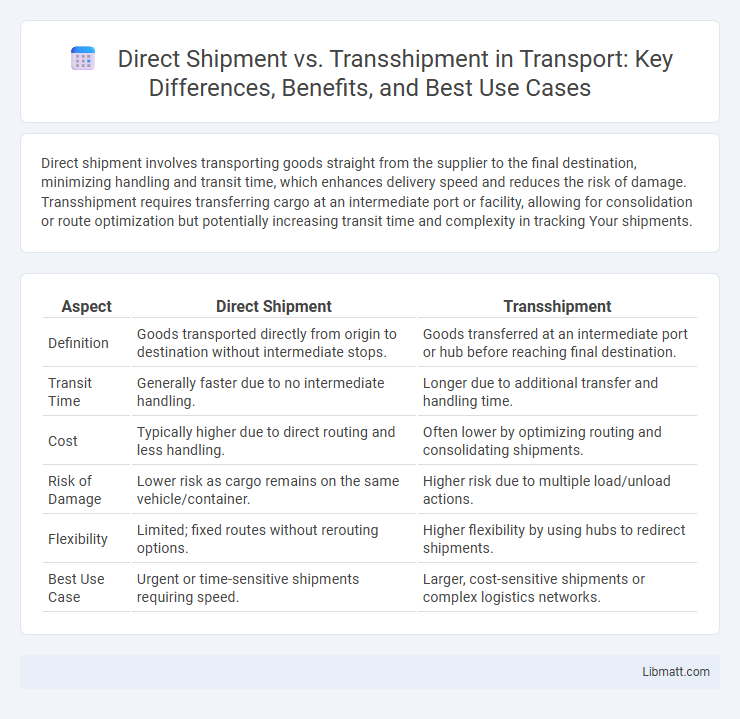
Direct shipment involves transporting goods straight from the supplier to the final destination, minimizing handling and transit time, which enhances delivery speed and reduces the risk of damage. Transshipment requires transferring cargo at an intermediate port or facility, allowing for consolidation or route optimization but potentially increasing transit time and complexity in tracking Your shipments.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Direct Shipment | Transshipment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Goods transported directly from origin to destination without intermediate stops. | Goods transferred at an intermediate port or hub before reaching final destination. |
| Transit Time | Generally faster due to no intermediate handling. | Longer due to additional transfer and handling time. |
| Cost | Typically higher due to direct routing and less handling. | Often lower by optimizing routing and consolidating shipments. |
| Risk of Damage | Lower risk as cargo remains on the same vehicle/container. | Higher risk due to multiple load/unload actions. |
| Flexibility | Limited; fixed routes without rerouting options. | Higher flexibility by using hubs to redirect shipments. |
| Best Use Case | Urgent or time-sensitive shipments requiring speed. | Larger, cost-sensitive shipments or complex logistics networks. |
Introduction to Direct Shipment and Transshipment
Direct shipment involves transporting goods from the supplier directly to the final destination without intermediate stops, ensuring faster delivery and reduced handling risks. Transshipment requires transferring cargo between different vessels or transport modes at an intermediate port or hub before reaching the ultimate destination, which can increase transit time and complexity. Understanding these methods helps optimize your supply chain strategy based on cost, speed, and reliability requirements.
Key Differences Between Direct Shipment and Transshipment
Direct shipment involves transporting goods straight from the supplier to the final destination, reducing transit time and minimizing handling risks. Transshipment requires transferring cargo at an intermediate port or hub, which can increase flexibility in routing but may lead to longer delivery times and higher risk of damage. Understanding these key differences helps you optimize logistics strategies based on cost, speed, and reliability.
How Direct Shipment Works
Direct shipment involves sending goods straight from the supplier to the customer without intermediate handling or storage, ensuring faster delivery and reduced risk of damage. This method streamlines logistics by eliminating the need for unloading, repacking, or reloading at transit points, resulting in lower transportation costs and enhanced supply chain efficiency. Direct shipment is commonly used in industries with time-sensitive or high-value products requiring secure and prompt delivery.
How Transshipment Operates
Transshipment involves transferring goods from one vessel to another at an intermediate port before reaching the final destination, enabling flexible routing and consolidation of shipments. This process helps optimize shipping schedules and reduces overall transportation costs, especially when direct routes are unavailable or inefficient. Your cargo undergoes handling at a transshipment hub, requiring careful coordination to minimize delays and maintain shipment integrity.
Advantages of Direct Shipment
Direct shipment offers faster delivery times by eliminating intermediate handling points, reducing the risk of delays caused by transshipment hubs. It minimizes potential damage or loss of goods since cargo is transported directly from origin to destination without transfers. Your supply chain benefits from streamlined logistics and increased transparency, enhancing overall efficiency and reliability.
Benefits of Transshipment
Transshipment offers significant logistical flexibility by allowing shipments to be efficiently consolidated or redirected at intermediate ports, reducing shipping costs and optimizing routes. It enables access to markets that lack direct shipping connections, improving supply chain reach and reliability. Your supply chain benefits from enhanced inventory management and faster response times to demand fluctuations thanks to transshipment hubs.
Disadvantages of Direct Shipment
Direct shipment can lead to higher transportation costs due to limited consolidation opportunities and less flexibility in routing. It increases the risk of delays or disruptions since there are fewer handling points for correcting shipment issues. Inventory management becomes more challenging as direct shipments often require precise scheduling and minimal buffer stock.
Drawbacks of Transshipment
Transshipment often results in longer delivery times due to the need for cargo handling at intermediate ports, increasing the risk of delays. The process can lead to higher operational costs because of additional handling fees, storage charges, and increased complexity in logistics management. Moreover, transshipment raises the likelihood of cargo damage or loss, as goods are transferred multiple times between vessels or modes of transport.
Choosing the Right Method: Factors to Consider
Choosing between direct shipment and transshipment depends on factors like delivery speed, cost efficiency, and route reliability. Direct shipment offers faster delivery and reduced handling, ideal for time-sensitive goods, while transshipment can lower costs by consolidating cargo but may increase transit time due to multiple transfers. Your decision should balance urgency, budget constraints, and the complexity of shipping routes to optimize supply chain performance.
Conclusion: Direct Shipment vs Transshipment
Direct shipment reduces transit time and minimizes risks of damage or loss by moving goods straight from origin to destination, ideal for time-sensitive cargos. Transshipment offers flexibility and cost savings by consolidating shipments at intermediate hubs, beneficial for complex supply chains with multiple routes. Your choice between direct shipment and transshipment should balance speed, cost, and logistical complexity to optimize delivery efficiency.
direct shipment vs transshipment Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com