A Transportation Management System (TMS) focuses on optimizing the planning, execution, and tracking of shipments to improve logistics efficiency, while a Warehouse Management System (WMS) manages day-to-day operations within a warehouse, including inventory control, order fulfillment, and storage optimization. Your business can enhance supply chain performance by integrating both systems to ensure seamless coordination between transportation and warehouse activities.
Table of Comparison
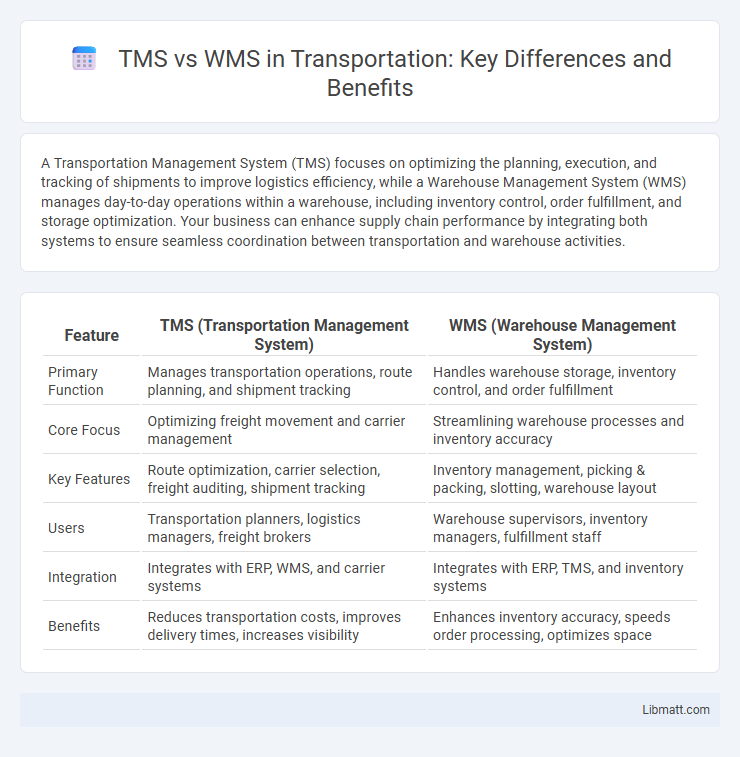
| Feature | TMS (Transportation Management System) | WMS (Warehouse Management System) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Manages transportation operations, route planning, and shipment tracking | Handles warehouse storage, inventory control, and order fulfillment |
| Core Focus | Optimizing freight movement and carrier management | Streamlining warehouse processes and inventory accuracy |
| Key Features | Route optimization, carrier selection, freight auditing, shipment tracking | Inventory management, picking & packing, slotting, warehouse layout |
| Users | Transportation planners, logistics managers, freight brokers | Warehouse supervisors, inventory managers, fulfillment staff |
| Integration | Integrates with ERP, WMS, and carrier systems | Integrates with ERP, TMS, and inventory systems |
| Benefits | Reduces transportation costs, improves delivery times, increases visibility | Enhances inventory accuracy, speeds order processing, optimizes space |
Introduction to TMS and WMS
Transportation Management Systems (TMS) optimize the planning, execution, and tracking of shipments to improve supply chain efficiency. Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) focus on managing inventory, storage, and order fulfillment within warehouses to enhance operational accuracy. Your business can benefit from integrating both systems to streamline logistics and warehouse processes effectively.
Core Functions of TMS
Transportation Management Systems (TMS) primarily optimize the planning, execution, and tracking of freight shipments, focusing on route optimization, carrier selection, and load consolidation. These systems manage shipping documents, track freight status in real-time, and analyze transportation costs to improve efficiency and reduce expenses. TMS integrates with carrier networks and ERP systems to enhance visibility and streamline logistics workflows.
Core Functions of WMS
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) primarily focus on optimizing inventory control, order fulfillment, and warehouse operations through real-time tracking of stock levels and locations. Core functions include receiving, put-away, picking, packing, and shipping processes, ensuring accuracy and efficiency within the warehouse environment. These systems also support labor management and space utilization, driving cost reduction and increased productivity in supply chain management.
Key Differences Between TMS and WMS
Transportation Management Systems (TMS) primarily focus on the planning, execution, and optimization of the physical movement of goods, including carrier selection, route optimization, and freight payment. Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) concentrate on inventory tracking, storage management, and warehouse operations like picking, packing, and shipping within the facility. The key difference lies in TMS managing outbound transportation logistics, while WMS handles in-facility inventory control and workflow optimizations.
Benefits of Integrating TMS and WMS
Integrating Transportation Management Systems (TMS) with Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) enhances supply chain visibility, enabling real-time tracking of inventory and shipments. This integration optimizes route planning and inventory allocation, reducing delivery times and transportation costs. Your business gains improved operational efficiency and customer satisfaction through streamlined coordination between transportation and warehousing functions.
Industry Use Cases: TMS vs WMS
TMS (Transportation Management Systems) are essential for industries focused on optimizing freight movement, such as retail, manufacturing, and third-party logistics providers, enabling efficient route planning and shipment tracking. WMS (Warehouse Management Systems) are critical in industries with complex inventory and storage needs, like e-commerce, pharmaceuticals, and food distribution, ensuring accurate stock control and streamlined warehouse operations. Your choice depends on whether transportation optimization or inventory management is the primary challenge in your supply chain operations.
Cost Implications: TMS vs WMS
Transportation Management Systems (TMS) typically involve lower upfront costs compared to Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) due to simpler implementation and fewer hardware requirements. WMS often requires significant investment in infrastructure, including barcode scanners and RFID technology, which increases total cost of ownership. Long-term, TMS can reduce transportation expenses by optimizing routes and freight, while WMS drives cost savings through improved inventory accuracy and warehouse efficiency.
Implementation Challenges
Implementing a Transportation Management System (TMS) often involves integrating complex logistics data and coordinating with multiple carriers, which can lead to significant technical and operational challenges. In contrast, Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) require extensive customization to accommodate unique inventory workflows and real-time accuracy, demanding thorough staff training and change management. Understanding your organization's specific needs and preparing for data migration or system integration issues is crucial to overcoming these implementation hurdles effectively.
Choosing the Right System for Your Business
Selecting the right system for your business depends on specific operational needs: a Transportation Management System (TMS) optimizes freight planning, carrier selection, and shipment tracking, ideal for companies focusing on logistics and distribution efficiency. A Warehouse Management System (WMS) enhances inventory management, order fulfillment, and storage optimization, benefiting businesses with complex warehousing operations. Evaluating factors like order volume, inventory complexity, and transportation requirements ensures the chosen solution aligns with your supply chain goals.
Future Trends in TMS and WMS Technologies
Future trends in Transportation Management Systems (TMS) and Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) emphasize increased integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning for enhanced predictive analytics and automation. Both systems are evolving to support real-time data visibility through IoT and blockchain technologies, improving supply chain transparency and security. Cloud-based solutions and advanced robotics further drive scalability and operational efficiency in TMS and WMS, meeting growing demands for agility in logistics management.
TMS vs WMS Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com