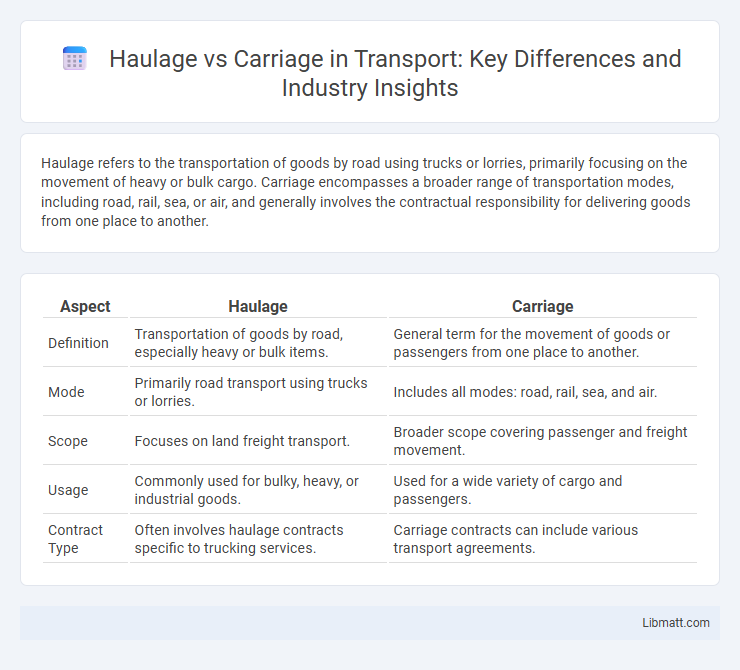
Haulage refers to the transportation of goods by road using trucks or lorries, primarily focusing on the movement of heavy or bulk cargo. Carriage encompasses a broader range of transportation modes, including road, rail, sea, or air, and generally involves the contractual responsibility for delivering goods from one place to another.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Haulage | Carriage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Transportation of goods by road, especially heavy or bulk items. | General term for the movement of goods or passengers from one place to another. |
| Mode | Primarily road transport using trucks or lorries. | Includes all modes: road, rail, sea, and air. |
| Scope | Focuses on land freight transport. | Broader scope covering passenger and freight movement. |
| Usage | Commonly used for bulky, heavy, or industrial goods. | Used for a wide variety of cargo and passengers. |
| Contract Type | Often involves haulage contracts specific to trucking services. | Carriage contracts can include various transport agreements. |
Introduction to Haulage and Carriage
Haulage refers to the transportation of goods overland, typically by road, involving the movement of freight using trucks or lorries. Carriage encompasses a broader scope of transporting goods by various modes, including road, rail, air, or sea, under contractual terms defining liability and responsibilities. Understanding the distinction helps you choose the appropriate logistics solution tailored to your transportation needs.
Defining Haulage: Key Concepts
Haulage refers to the transport of goods by road using large vehicles such as trucks or lorries, emphasizing the movement of heavy or bulk cargo over varied distances. It involves specialized logistics services including loading, route planning, and compliance with transport regulations to ensure safe and efficient delivery. In contrast to general carriage, haulage typically denotes commercial freight transport, often under contracts specifying terms, liability, and scope of service.
Understanding Carriage: Scope and Meaning
Carriage encompasses the transportation of goods or passengers by various modes, including road, rail, sea, and air, highlighting its broad and versatile scope. It refers not only to the physical movement but also to the contractual relationship governing the responsibilities and liabilities between the carrier and consignee. Understanding carriage means recognizing these legal and logistical dimensions that differentiate it from specialized haulage services focused primarily on road freight.
Key Differences Between Haulage and Carriage
Haulage primarily involves the transportation of goods using road vehicles, typically trucks or lorries, focusing on the actual movement within land routes. Carriage encompasses a broader scope, including the transport of goods or passengers by various modes such as road, rail, sea, or air, often involving contractual obligations and legal responsibilities. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the appropriate service based on the mode of transport and legal framework required for your shipment.
Types of Haulage Services
Haulage services encompass various types, including full truckload (FTL), less-than-truckload (LTL), and container haulage, each designed to meet specific freight requirements. FTL haulage involves the transportation of goods occupying an entire truck, optimizing delivery speed and reducing handling risks, while LTL haulage consolidates multiple shipments to lower costs for smaller consignments. Choosing the appropriate haulage service ensures your cargo is transported efficiently, balancing cost, speed, and load size.
Types of Carriage Services
Carriage services encompass various types including road haulage, rail freight, sea freight, and air cargo, each tailored to specific cargo types and delivery timelines. Road haulage dominates short to medium distances, offering flexibility and door-to-door service, while rail freight is cost-effective for bulk goods over long distances. Sea freight specializes in large volume international shipments, and air cargo ensures rapid delivery for high-value or perishable items.
Legal Implications in Haulage and Carriage
Legal implications in haulage and carriage center on the distinction between possession and ownership, where haulage contracts transfer possession of goods for transport without transferring ownership, influencing liability and risk allocation. In carriage contracts governed by international conventions like the CMR or Hague-Visby Rules, carriers bear stricter responsibilities and liabilities for loss or damage during transit. Understanding these differences is crucial for businesses to determine contractual terms, insurance requirements, and dispute resolution mechanisms in freight transport operations.
Cost Factors: Haulage vs Carriage
Cost factors in haulage typically depend on distance, cargo weight, and fuel prices, with added expenses for specialized equipment or permits. Carriage costs often reflect the type of goods transported, the mode of transport (road, rail, sea), and handling requirements, which can increase fees for fragile or hazardous items. Understanding these variables helps you optimize budgeting for logistics by choosing the most cost-effective option between haulage and carriage.
Choosing the Right Service: Haulage or Carriage
Choosing the right service depends on your specific logistics needs, as haulage refers to the transportation of goods by road using trucks, while carriage typically involves broader methods including rail, sea, or air. Haulage is ideal for short to medium distances requiring flexible and direct delivery, whereas carriage suits long-distance or multimodal transport options. Understanding your cargo type, destination, and timelines will help you determine whether haulage or carriage best supports your supply chain efficiency.
Future Trends in Haulage and Carriage
Future trends in haulage and carriage emphasize the integration of advanced telematics and autonomous vehicles, enhancing efficiency and safety in freight transport. The adoption of electric and hydrogen-powered trucks is accelerating, aiming to reduce carbon emissions and meet stringent environmental regulations. Digital platforms and blockchain technology are increasingly used to optimize logistics, improve transparency, and streamline supply chain management.
haulage vs carriage Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com