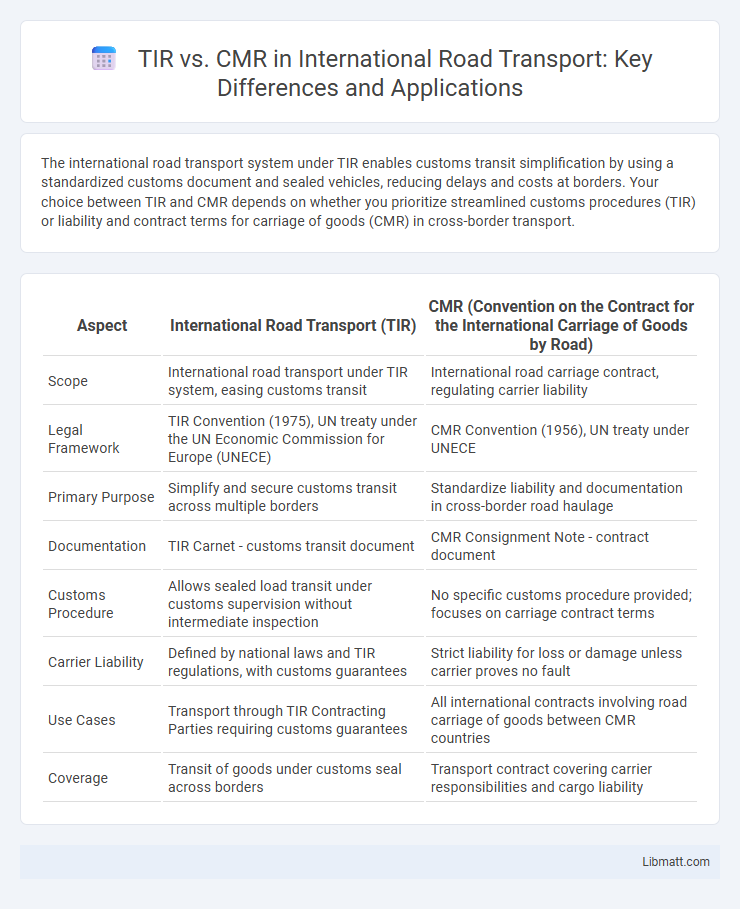
The international road transport system under TIR enables customs transit simplification by using a standardized customs document and sealed vehicles, reducing delays and costs at borders. Your choice between TIR and CMR depends on whether you prioritize streamlined customs procedures (TIR) or liability and contract terms for carriage of goods (CMR) in cross-border transport.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | International Road Transport (TIR) | CMR (Convention on the Contract for the International Carriage of Goods by Road) |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | International road transport under TIR system, easing customs transit | International road carriage contract, regulating carrier liability |
| Legal Framework | TIR Convention (1975), UN treaty under the UN Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) | CMR Convention (1956), UN treaty under UNECE |
| Primary Purpose | Simplify and secure customs transit across multiple borders | Standardize liability and documentation in cross-border road haulage |
| Documentation | TIR Carnet - customs transit document | CMR Consignment Note - contract document |
| Customs Procedure | Allows sealed load transit under customs supervision without intermediate inspection | No specific customs procedure provided; focuses on carriage contract terms |
| Carrier Liability | Defined by national laws and TIR regulations, with customs guarantees | Strict liability for loss or damage unless carrier proves no fault |
| Use Cases | Transport through TIR Contracting Parties requiring customs guarantees | All international contracts involving road carriage of goods between CMR countries |
| Coverage | Transit of goods under customs seal across borders | Transport contract covering carrier responsibilities and cargo liability |
Overview of International Road Transport Systems
The TIR (Transports Internationaux Routiers) system streamlines customs procedures by allowing goods to transit multiple countries under a single customs seal, significantly reducing border delays in international road transport. The CMR (Convention on the Contract for the International Carriage of Goods by Road) governs the contractual obligations between carriers and consignors, standardizing liability and documentation across cross-border road freight within Europe and beyond. Both TIR and CMR systems are crucial for efficient international road transport, with TIR emphasizing customs facilitation and CMR focusing on contractual liability and transport documentation.
Understanding TIR: The Transports Internationaux Routiers Convention
The Transports Internationaux Routiers (TIR) Convention facilitates international road transport by simplifying customs procedures through a standardized carnet system, ensuring goods move seamlessly across borders under customs control without multiple inspections. The TIR system significantly reduces transit times and costs for carriers by providing a secure and efficient customs guarantee recognized by over 70 contracting parties worldwide. Compared to the CMR (Convention on the Contract for the International Carriage of Goods by Road), which primarily regulates contractual obligations and liabilities between carrier and consignor, the TIR focuses on customs-related processes, making it essential for transit across multiple customs territories.
The CMR Convention: Key Features and Purpose
The CMR Convention standardizes contracts for international road transport of goods, ensuring legal clarity and uniformity across signatory countries in Europe and beyond. It defines carrier responsibilities, liabilities, and documentation requirements, facilitating smoother cross-border shipments under consistent regulations. Your shipments benefit from clearer claims processes and enhanced legal protection under the CMR framework.
TIR vs CMR: Scope and Applicability
The TIR Convention governs international road transport by simplifying customs procedures for goods crossing multiple countries, primarily outside the EU, under a single customs transit system. The CMR Convention applies mainly to international road carriage contracts by road within Europe and some non-EU countries, defining carrier liability and transport documents. Understanding the scope and applicability of TIR versus CMR regulations ensures your shipments comply with respective customs or contractual obligations efficiently.
Customs Procedures under TIR and CMR
Customs procedures under the TIR system streamline international road transport by allowing goods to transit through multiple countries with a single carnet, minimizing border checks and reducing delays. The CMR Convention governs the contractual aspect of carriage but does not provide standardized customs procedures, requiring individual customs documentation per country. Your shipments benefit from TIR's customs efficiency when transporting goods across multiple borders compared to the more document-intensive CMR process.
Documentation Requirements: TIR Carnet vs CMR Consignment Note
The TIR Carnet is an internationally recognized customs document that simplifies border crossings by allowing goods to transit under customs control without intermediate inspections, requiring strict adherence to the TIR Convention. The CMR Consignment Note, governed by the CMR Convention, serves as a transport document and evidence of the contract of carriage for international road shipments, detailing consignment specifics, consignor and consignee information, and conditions of transport. Your choice between TIR and CMR documentation depends on whether customs procedures or contractual proof of carriage is the primary concern in your international road transport operation.
Liability and Insurance in TIR and CMR
TIR (Transports Internationaux Routiers) and CMR (Convention on the Contract for the International Carriage of Goods by Road) both regulate liability and insurance for international road transport but differ significantly. Under the TIR system, carriers benefit from a customs transit procedure that limits liability through a financial guarantee covering customs duties and taxes, while insurance primarily protects against customs-related obligations. In contrast, CMR sets carrier liability based on strict rules for loss, damage, or delay of goods, requiring carriers to maintain liability insurance, which directly safeguards your cargo during international road transport.
Advantages and Limitations of TIR
The TIR system offers significant advantages in international road transport, including simplified customs procedures, reduced transit times, and cost savings through a carnet guaranteeing customs duties and taxes. Its limitations include the requirement for authorized vehicles and operators, potential complexity in administrative paperwork, and limited acceptance compared to the widely recognized CMR convention. Your shipments benefit from TIR's streamlined border crossing but must comply with strict regulations to avoid delays.
Benefits and Challenges of the CMR Convention
The CMR Convention facilitates international road transport by standardizing consignment notes and liability rules, enhancing legal certainty and simplifying cross-border trade across Europe and adjacent regions. Benefits include streamlined claims processing and reduced disputes, improving efficiency for carriers, consignors, and consignees involved in consignments transported by road. Challenges encompass inconsistent national interpretations, limited applicability outside contracting states, and difficulties in enforcement which can hinder seamless transport and limit global harmonization compared to the broader TIR system.
Choosing Between TIR and CMR for International Road Transport
Choosing between TIR (Transport Internationaux Routiers) and CMR (Convention on the Contract for the International Carriage of Goods by Road) depends on your specific logistic needs and regulatory environment. TIR offers a customs transit system that simplifies border crossings with a standardized carnet, reducing delays and costs during international road transport. CMR provides a uniform contract framework ensuring legal clarity and liability protection for cargo transport across multiple countries, making it essential for defining responsibilities in your shipping agreements.
international road transport (TIR) vs CMR Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com