Portage refers to carrying boats or cargo over land between waterways, while towage involves pulling a vessel through water using another boat or tug. Understanding these distinct processes helps ensure Your maritime operations are efficient and safe.
Table of Comparison
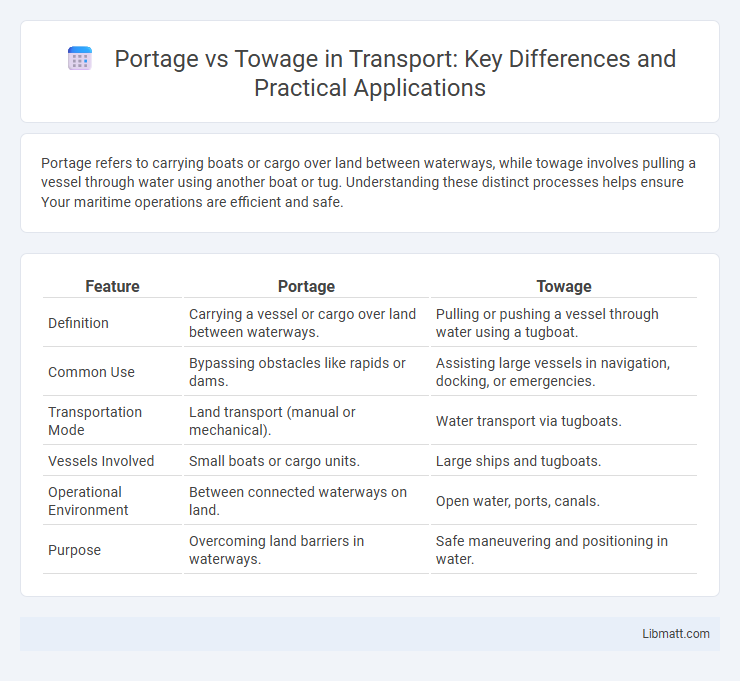
| Feature | Portage | Towage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Carrying a vessel or cargo over land between waterways. | Pulling or pushing a vessel through water using a tugboat. |
| Common Use | Bypassing obstacles like rapids or dams. | Assisting large vessels in navigation, docking, or emergencies. |
| Transportation Mode | Land transport (manual or mechanical). | Water transport via tugboats. |
| Vessels Involved | Small boats or cargo units. | Large ships and tugboats. |
| Operational Environment | Between connected waterways on land. | Open water, ports, canals. |
| Purpose | Overcoming land barriers in waterways. | Safe maneuvering and positioning in water. |
Introduction to Portage and Towage
Portage involves carrying boats over land between navigable waters, essential for bypassing obstacles like rapids or waterfalls. Towage refers to pulling vessels using tugboats or towboats, often critical for moving large ships through narrow or busy waterways. Your understanding of both processes ensures efficient and safe vessel transportation in varied maritime environments.
Definition of Portage
Portage refers to the practice of carrying watercraft or cargo overland between navigable waters to bypass obstacles such as rapids or waterfalls. This traditional method is essential in regions where waterways are interrupted, ensuring continuous transport routes. Understanding portage helps you appreciate how early traders and explorers managed logistics in challenging terrains.
Definition of Towage
Towage refers to the act of pulling or hauling a vessel using another boat or tug, typically in harbors, rivers, or confined waterways to assist maneuvering and navigation. It involves the use of towlines or cables to connect the assisting vessel to the ship being towed. Unlike portage, which generally relates to carrying boats or cargo over land, towage specifically denotes maritime assistance for moving or positioning vessels in the water.
Key Differences Between Portage and Towage
Portage involves carrying boats or cargo overland between water bodies, whereas towage refers to pulling or pushing vessels through water using tugboats or other powered craft. Key differences include the mode of transportation, with portage utilizing land routes and towage operating exclusively in maritime environments. Portage is primarily manual or mechanical movement over terrain, while towage depends on mechanical propulsion to assist navigation and docking of ships.
Legal Framework Governing Portage and Towage
The legal framework governing portage and towage is primarily defined by international conventions such as the Hamburg Rules and the Brussels Convention, alongside national maritime laws that regulate contractual obligations and liabilities. Towage agreements typically fall under maritime law addressing salvage and assistance at sea, emphasizing the duties and liabilities of towage service providers, whereas portage involves onshore cargo handling under port authority regulations and local transportation statutes. Clear distinctions in liability, risk allocation, and operational scope are established within these legal frameworks to mitigate disputes in port operations and vessel assistance.
Common Uses of Portage in Maritime Industry
Portage in the maritime industry primarily involves the overland transportation of vessels or cargo between waterways, often used to bypass navigational hazards or connect separate bodies of water. Your cargo may benefit when portage is employed to overcome natural obstructions such as rapids, locks, or dams that make continuous water transport impossible. This method is common in regions with extensive inland waterways where seamless navigation is interrupted, ensuring efficient and secure movement of goods.
Applications and Importance of Towage
Towage plays a critical role in assisting larger vessels in navigating confined or congested waterways, ensuring safe docking, undocking, and maneuvering within ports and harbors. Specialized towboats exert controlled power and precision, preventing accidents and minimizing delays, which is essential for maintaining efficient maritime operations and protecting valuable cargo. Your shipping operations benefit significantly from professional towage services, especially in crowded or challenging port environments where precise vessel control is paramount.
Safety Considerations in Portage and Towage
Safety considerations in portage and towage center on risk management, equipment reliability, and crew training specific to each operation. Portage requires attention to land and water interface hazards, requiring specialized gear and careful coordination to prevent cargo damage and operator injury. Towage demands rigorous inspections of towlines and vessels, adherence to navigation rules, and constant communication between tug and assisted vessel crews to mitigate collision or grounding risks.
Cost Comparison: Portage vs Towage
Portage typically incurs lower costs than towage due to shorter distances and less specialized equipment, making it an economical choice for moving vessels or cargo within confined waterways or between nearby locations. Towage involves higher expenses from using powerful tugboats, fuel consumption, and skilled crews necessary for navigating open waters or handling larger vessels, increasing your overall operational budget. Evaluating your specific transportation needs and comparing service quotes will help determine the most cost-effective solution between portage and towage.
Choosing the Best Method: Portage or Towage
Choosing the best method between portage and towage depends on factors like vessel size, distance, and environmental conditions. Portage is ideal for short, land-based transfers to bypass obstacles, while towage suits longer waterborne journeys requiring powerful vessels to pull or push ships safely. Your decision should balance efficiency, safety, and cost to optimize maritime operations.
portage vs towage Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com