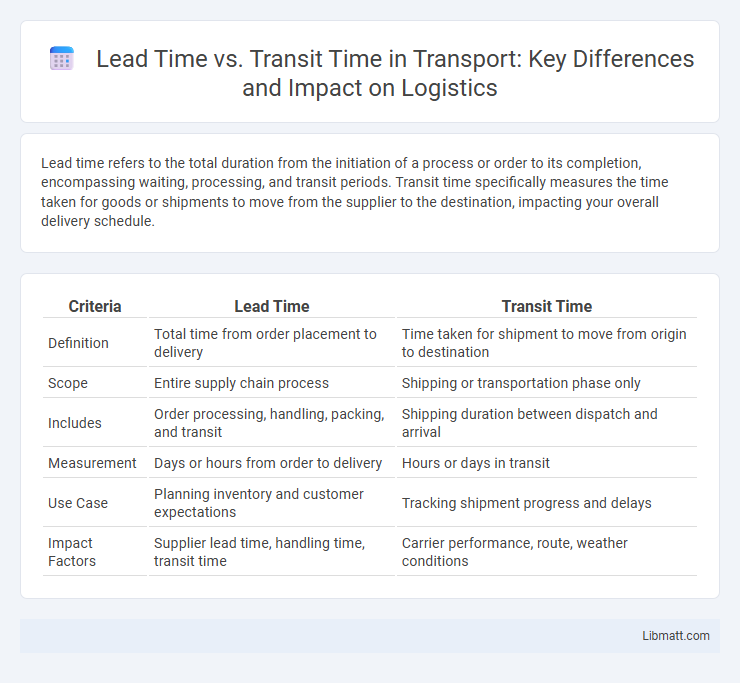
Lead time refers to the total duration from the initiation of a process or order to its completion, encompassing waiting, processing, and transit periods. Transit time specifically measures the time taken for goods or shipments to move from the supplier to the destination, impacting your overall delivery schedule.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Lead Time | Transit Time |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Total time from order placement to delivery | Time taken for shipment to move from origin to destination |
| Scope | Entire supply chain process | Shipping or transportation phase only |
| Includes | Order processing, handling, packing, and transit | Shipping duration between dispatch and arrival |
| Measurement | Days or hours from order to delivery | Hours or days in transit |
| Use Case | Planning inventory and customer expectations | Tracking shipment progress and delays |
| Impact Factors | Supplier lead time, handling time, transit time | Carrier performance, route, weather conditions |
Understanding Lead Time: Definition and Importance
Lead time refers to the total duration from order placement to product delivery, encompassing order processing, manufacturing, and shipping phases. It is crucial for accurate production planning, inventory management, and meeting customer expectations. Understanding lead time helps you optimize supply chain efficiency and improve overall delivery performance.
What is Transit Time? A Clear Explanation
Transit time refers to the duration required for a shipment to move from the point of origin to the final destination during transportation. It specifically measures the time spent in transit, excluding processing, loading, or waiting periods. Understanding transit time helps you accurately estimate delivery schedules and manage logistics efficiently.
Key Differences Between Lead Time and Transit Time
Lead time encompasses the total duration from order placement to delivery, including processing, handling, and shipping, while transit time specifically refers to the period goods spend moving between locations during shipment. Understanding the distinction helps you optimize supply chain efficiency by managing production schedules and delivery expectations accurately. Lead time impacts overall project timelines, whereas transit time affects only the transportation segment within that timeframe.
The Role of Lead Time in Supply Chain Management
Lead time plays a critical role in supply chain management by determining the total time required to fulfill customer orders, from order receipt to delivery. It encompasses procurement, production, and transit durations, directly impacting inventory levels, production scheduling, and customer satisfaction. Optimizing lead time enhances Your ability to respond swiftly to market demands and maintain a competitive edge.
How Transit Time Impacts Logistics Efficiency
Transit time directly influences logistics efficiency by determining the speed at which goods move from origin to destination, affecting inventory management and customer satisfaction. Shorter transit times reduce warehousing costs and minimize stockouts, enabling more responsive supply chains. Accurate transit time predictions enhance route planning and resource allocation, leading to optimized delivery schedules and overall cost savings.
Factors Affecting Lead Time in Modern Businesses
Factors affecting lead time in modern businesses include supplier reliability, production efficiency, and inventory management. Transportation modes and customs processing also impact transit time, influencing overall lead time. Optimizing these elements helps streamline your supply chain for faster delivery and improved customer satisfaction.
Influences on Transit Time Across Transportation Modes
Transit time varies significantly across transportation modes due to factors such as distance, carrier efficiency, and route complexity. Ocean freight often experiences longer transit times because of slower speeds and port handling delays, while air freight provides faster transit despite higher costs and susceptibility to weather disruptions. Understanding these influences helps you optimize delivery schedules and manage expectations for supply chain logistics.
Strategies to Reduce Lead Time for Competitive Advantage
Reducing lead time enhances customer satisfaction and boosts your competitive advantage by accelerating order fulfillment and minimizing delays. Implement strategies such as optimizing supply chain coordination, leveraging real-time inventory management, and adopting just-in-time production techniques to streamline processes. Prioritizing efficient communication with suppliers and investing in automation technology can also significantly cut down lead time while maintaining product quality.
Optimizing Transit Time: Best Practices
Optimizing transit time involves strategically selecting shipping routes, carriers, and modes of transportation to minimize delays and ensure timely delivery. Monitoring real-time tracking data and collaborating closely with logistics partners enhance efficiency and prevent bottlenecks during transit. You can significantly improve supply chain reliability by aligning lead time management with optimized transit schedules.
Lead Time vs Transit Time: Choosing the Right Metrics for Performance
Lead time measures the total duration from order placement to delivery, encompassing production, processing, and transit phases, while transit time specifically tracks the period goods spend in shipping. Analyzing lead time provides a comprehensive view of supply chain efficiency, critical for optimizing inventory and customer satisfaction, whereas transit time focuses on logistics performance, essential for carrier evaluation and route planning. Selecting the right metric depends on business goals: lead time supports end-to-end process improvements, and transit time enhances transportation management and cost control.
lead time vs transit time Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com