Alburnum, also known as sapwood, is the younger, outer part of the tree that actively conducts water and nutrients, while duramen, or heartwood, is the older, central wood that provides structural support and is typically darker and more resistant to decay. Understanding the differences between alburnum and duramen helps you select the right type of wood for durability and aesthetic purposes in woodworking projects.
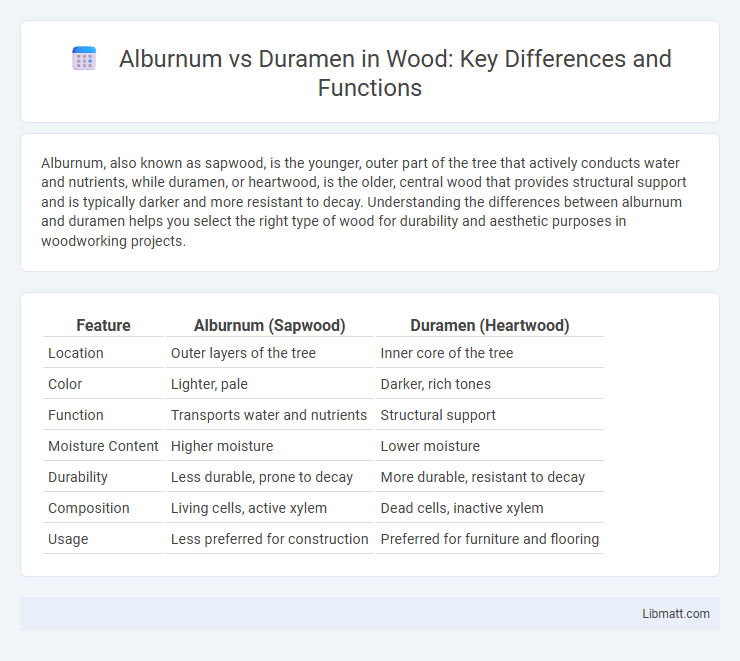
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Alburnum (Sapwood) | Duramen (Heartwood) |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Outer layers of the tree | Inner core of the tree |
| Color | Lighter, pale | Darker, rich tones |
| Function | Transports water and nutrients | Structural support |
| Moisture Content | Higher moisture | Lower moisture |
| Durability | Less durable, prone to decay | More durable, resistant to decay |
| Composition | Living cells, active xylem | Dead cells, inactive xylem |
| Usage | Less preferred for construction | Preferred for furniture and flooring |
Introduction to Alburnum and Duramen
Alburnum, or sapwood, is the younger, outer layer of wood that actively conducts water and nutrients, characterized by its lighter color and higher moisture content. Duramen, or heartwood, is the older, inner core of the tree, consisting of dead cells that provide structural support and exhibit darker pigmentation due to accumulated resins and extractives. Understanding the distinct properties of alburnum and duramen is crucial for applications in woodworking, construction, and tree health assessment.
Definition of Alburnum
Alburnum, also known as sapwood, is the outer layer of a tree trunk that consists of living, actively functioning xylem cells responsible for water and nutrient conduction. It contrasts with duramen, or heartwood, which is the inner, non-living wood that provides structural support and is often darker due to the deposition of chemical substances. The distinction between alburnum and duramen is crucial in forestry and wood processing, affecting wood durability, color, and resistance to decay.
Definition of Duramen
Duramen, also known as heartwood, is the dense, inner part of a tree trunk that provides structural support and is typically darker and more resistant to decay compared to the surrounding alburnum or sapwood. Alburnum, the outer, lighter-colored layer, conducts water and nutrients but gradually converts to duramen as the tree matures. Understanding the distinction between duramen and alburnum helps you select wood types for durability and specific applications in construction or woodworking.
Anatomical Differences
Alburnum, or sapwood, consists of younger, outer layers of wood that transport water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves, characterized by lighter color and higher moisture content. Duramen, or heartwood, forms the older, central core of the tree, composed of dead cells that provide structural support and exhibit darker coloration due to deposited resins and tannins. The anatomical distinction lies in vascular activity, as alburnum remains active in conduction, while duramen serves primarily as a protective, supportive tissue.
Functional Roles in the Tree
Alburnum, or sapwood, functions primarily in the conduction of water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves and serves as a storage area for vital nutrients. Duramen, or heartwood, provides structural support and strength to the tree, as it is composed of dead cells filled with resins and tannins that enhance durability and resistance to decay. The distinction between alburnum and duramen is crucial in forestry and wood science for understanding tree health, growth patterns, and timber quality.
Color and Texture Comparison
Alburnum, or sapwood, typically exhibits a lighter color with a uniform, softer texture compared to the darker, denser duramen or heartwood, which often shows a richer hue and tighter grain pattern. The contrast between alburnum's pale, sometimes creamy appearance and the duramen's deep brown or reddish tones highlights the distinction in aging and chemical composition. Understanding these differences helps you select the right wood type for aesthetic and structural purposes in woodworking or construction.
Importance in Wood Industry
Alburnum and duramen represent the two primary layers of a tree's wood, with duramen being the heartwood that provides strength, durability, and resistance to decay, making it highly valued in the wood industry for construction and furniture. Alburnum, or sapwood, while less durable, plays a crucial role in nutrient transport and is often easier to work with for products requiring flexibility or quick processing. Your choice between alburnum and duramen significantly impacts the performance, longevity, and application of wood products in various industrial settings.
Durability and Resistance to Decay
Duramen, the heartwood of a tree, exhibits significantly higher durability and resistance to decay compared to alburnum, or sapwood, due to its dense cellular structure and natural accumulation of extractives such as tannins and resins. Alburnum is more susceptible to fungal attack, insect infestation, and moisture absorption because it primarily functions in nutrient transport and lacks these protective compounds. Consequently, duramen is preferred for construction, furniture, and outdoor applications where long-lasting performance and decay resistance are critical.
Applications and Uses
Alburnum, or sapwood, is primarily used in applications requiring quick growth and natural moisture transport, making it ideal for new construction, furniture, and paper production. Duramen, or heartwood, offers greater durability and resistance to decay, making it preferred for outdoor structures, flooring, and heavy-duty timber products. Understanding the specific properties of your wood can optimize its application for longevity and performance.
Conclusion: Alburnum vs Duramen
Alburnum, or sapwood, is the outer, living part of the tree that transports water and nutrients, making it lighter and more susceptible to decay. Duramen, or heartwood, forms the dense, inner core of the tree, providing structural strength and natural resistance to pests and environmental damage. Your choice between alburnum and duramen will impact the durability and longevity of wood products based on these distinct properties.
Alburnum vs duramen Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com