Banak wood is prized for its smooth texture and light color, making it ideal for furniture and carvings that require fine detail, while Ayous wood is softer, lighter, and more affordable, commonly used in plywood, veneer, and lightweight construction. You should choose Banak for durability and aesthetic appeal, whereas Ayous offers versatility and cost-effectiveness for larger-scale or less demanding applications.
Table of Comparison
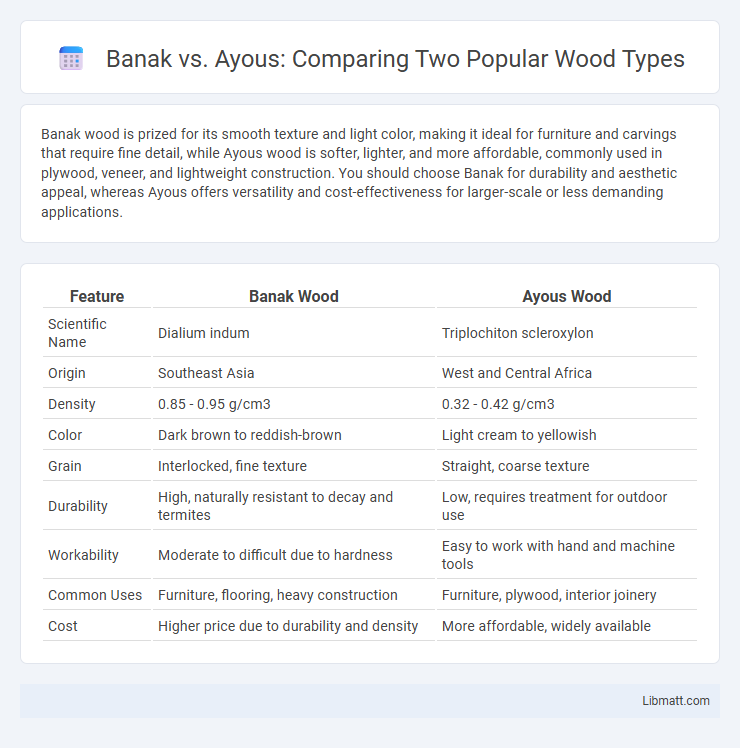
| Feature | Banak Wood | Ayous Wood |
|---|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Dialium indum | Triplochiton scleroxylon |
| Origin | Southeast Asia | West and Central Africa |
| Density | 0.85 - 0.95 g/cm3 | 0.32 - 0.42 g/cm3 |
| Color | Dark brown to reddish-brown | Light cream to yellowish |
| Grain | Interlocked, fine texture | Straight, coarse texture |
| Durability | High, naturally resistant to decay and termites | Low, requires treatment for outdoor use |
| Workability | Moderate to difficult due to hardness | Easy to work with hand and machine tools |
| Common Uses | Furniture, flooring, heavy construction | Furniture, plywood, interior joinery |
| Cost | Higher price due to durability and density | More affordable, widely available |
Introduction to Banak and Ayous
Banak, a dense hardwood primarily found in West Africa, is prized for its durability and resistance to decay, making it ideal for furniture and construction. Ayous, also known as obeche, is a softer wood native to tropical Africa, valued for its light weight and ease of machining, commonly used in veneers and plywood. Both species play crucial roles in the timber industry due to their distinct physical properties and applications.
Botanical Origins and Sources
Banak wood originates from the species *Millettia laurentii*, predominantly found in Central and West African rainforests, prized for its dense, durable hardwood. Ayous, derived from *Triplochiton scleroxylon*, commonly grows in West African regions with faster growth rates and lighter, softer timber suitable for furniture and construction. Both species contribute significantly to the forestry economy but differ botanically, with Banak classified under the Fabaceae family and Ayous within the Malvaceae family.
Physical Appearance and Color Differences
Banak wood features a dark brown to reddish hue with a dense, coarse texture, while Ayous wood exhibits a lighter, creamy yellow to pale brown color with a smooth, even grain. Banak typically has more pronounced natural variations and darker streaks, contrasting with Ayous's uniform and softer appearance. Understanding these physical and color distinctions helps you select the ideal wood for specific aesthetic or structural needs.
Density and Weight Comparison
Banak wood has a higher density, typically ranging from 550 to 650 kg/m3, making it noticeably heavier than Ayous, which has a lower density of about 320 to 400 kg/m3. The increased density of Banak results in a sturdier and more durable material, suitable for heavy-duty applications, whereas Ayous is lighter and easier to handle, ideal for furniture and interior paneling. Your choice between these woods should consider the balance between Banak's robustness and Ayous's lightweight convenience.
Durability and Resistance
Banak wood is renowned for its exceptional durability and high resistance to wear, moisture, and insect attacks, making it ideal for outdoor furniture and flooring. Ayous wood, while lighter and easier to work with, offers moderate durability and is less resistant to termites and fungal decay compared to Banak. The superior density and natural oils in Banak contribute significantly to its enhanced longevity and structural integrity in harsh environmental conditions.
Workability and Machining
Banak wood exhibits excellent workability and machining properties due to its fine, even texture and moderate hardness, enabling smooth cutting, shaping, and finishing. Ayous wood, while softer and lighter, offers good machinability but may be more prone to dents and requires careful handling to avoid splintering during machining processes. Your choice between Banak and Ayous should consider the balance between durability and ease of machining based on project demands.
Typical Applications and Uses
Banak wood is highly valued for its durability and resistance to decay, making it ideal for flooring, furniture, and marine construction. Ayous wood, known for its light weight and fine texture, is commonly used in interior paneling, plywood, and lightweight furniture. Both woods serve distinct purposes, with Banak preferred for heavy-duty applications and Ayous favored for aesthetic and indoor uses.
Price and Market Availability
Banak wood typically commands a higher price due to its durability and rarity, making it less accessible in many global markets. Ayous, being more abundant and softer, offers a more affordable alternative widely available across furniture and construction suppliers. Your choice depends on balancing cost with quality needs, as Banak is often preferred for premium applications while Ayous suits budget-conscious projects.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Banak, a hardwood native to West Africa, faces significant environmental challenges due to extensive logging, leading to habitat loss and biodiversity decline in tropical rainforests. Ayous, also known as obeche, grows faster and is considered more sustainable for timber production, with better regeneration rates and lesser ecosystem disruption. Sustainable management practices for Ayous can help reduce deforestation rates, whereas Banak requires stricter conservation efforts to mitigate long-term ecological damage.
Choosing Between Banak and Ayous
Choosing between Banak and Ayous depends on the intended use and desired wood characteristics. Banak, known for its durability and resistance to decay, is ideal for outdoor furniture and construction requiring longevity. Ayous offers a lighter, more workable texture suited for indoor applications like veneer, plywood, and lightweight furniture.
Banak vs Ayous Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com