A carpenter typically focuses on constructing and installing structural elements like framing, roofing, and staircases, while a joiner specializes in crafting detailed wooden components such as doors, windows, and cabinetry. Your choice depends on whether you need large-scale construction or finely finished woodwork.
Table of Comparison
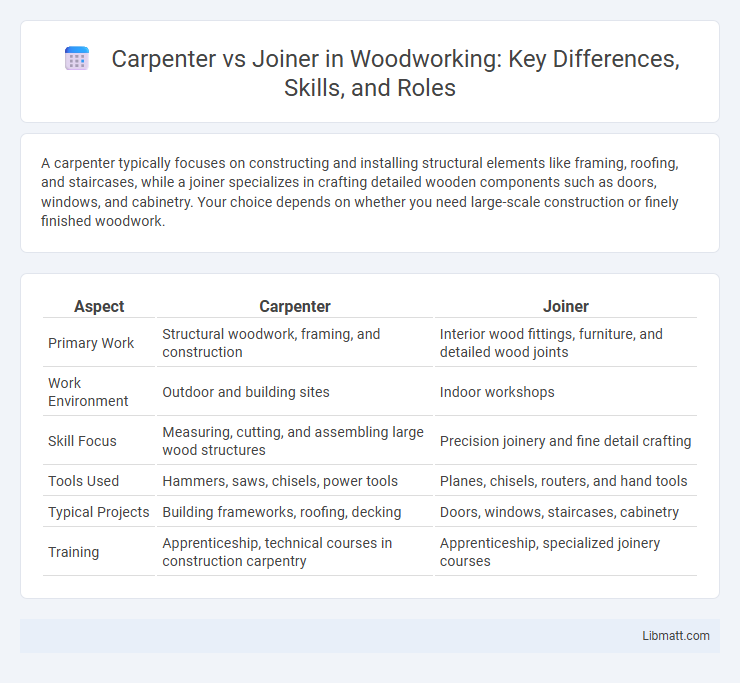
| Aspect | Carpenter | Joiner |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Work | Structural woodwork, framing, and construction | Interior wood fittings, furniture, and detailed wood joints |
| Work Environment | Outdoor and building sites | Indoor workshops |
| Skill Focus | Measuring, cutting, and assembling large wood structures | Precision joinery and fine detail crafting |
| Tools Used | Hammers, saws, chisels, power tools | Planes, chisels, routers, and hand tools |
| Typical Projects | Building frameworks, roofing, decking | Doors, windows, staircases, cabinetry |
| Training | Apprenticeship, technical courses in construction carpentry | Apprenticeship, specialized joinery courses |
Understanding the Roles: What is a Carpenter vs a Joiner?
A carpenter primarily works on constructing and installing structural elements such as frameworks, roofing, and staircases, focusing on building and repairing buildings. A joiner specializes in crafting and assembling detailed wooden components like doors, windows, and furniture, often working in workshops to create precise joints and finishes. The key difference lies in carpenters handling on-site construction tasks, while joiners concentrate on fine woodworking and detailed joinery.
Key Skills of Carpenters and Joiners
Carpenters excel in structural framing, installing large wooden frameworks, and working with heavy materials using saws, hammers, and nail guns. Joiners specialize in precision woodwork such as crafting doors, windows, and furniture by employing fine joinery techniques and hand tools like chisels and planes. Your choice between a carpenter and joiner depends on whether the project requires robust construction or detailed finishing work.
Tools of the Trade: Carpenter vs Joiner Equipment
Carpenters use heavy-duty tools like circular saws, nail guns, and framing hammers suited for large-scale construction and structural work. Joiners rely on precision instruments such as chisels, hand planes, and finely tuned routers to create detailed wood joints and fine furniture pieces. Understanding these distinct tools of the trade can help you choose the right professional for your woodworking or building project.
Typical Projects: Where Carpenters and Joiners Excel
Carpenters excel in structural projects such as framing houses, building stairs, and installing roof trusses, where precision and load-bearing skills are crucial. Joiners specialize in detailed woodworking tasks like crafting furniture, cabinetry, and window frames, focusing on fine joinery techniques and artisanal finishes. Your project choice determines whether a carpenter's strength or a joiner's finesse best meets your construction or woodwork needs.
Training and Qualifications Required
Carpenters typically complete formal apprenticeships lasting 3 to 4 years, involving both on-the-job training and classroom instruction in areas like framing, roofing, and blueprint reading. Joiners often undergo specialized apprenticeships focused on fine woodworking, cabinetry, and furniture construction, emphasizing precision and detailed craftsmanship. Both professions require knowledge of hand and power tools, safety standards, and building codes to ensure quality and compliance in their respective trades.
Work Environments Compared
Carpenters typically work on large construction sites or residential projects, handling structural elements such as framing and roofing, while joiners often operate in workshops or indoor settings, specializing in crafting furniture, doors, and cabinetry. The carpenter's environment involves heavy machinery and outdoor conditions, requiring physical endurance and safety awareness, whereas joiners benefit from controlled climates that allow precision work with hand tools and specialized equipment. Both trades demand distinct skill sets adapted to their unique work environments, influencing workflow, material handling, and project timelines.
Craftsmanship and Specialization Differences
Carpenters specialize in structural work like framing, roofing, and installing beams, showcasing skills in building the framework of buildings with precision and strength. Joiners focus on detailed woodworking tasks such as creating cabinets, doors, and window frames, emphasizing fine craftsmanship and intricate joinery techniques. Your choice between a carpenter and a joiner should depend on whether your project requires robust structural construction or detailed finishing work.
Costs and Hiring Considerations
Costs for hiring a carpenter typically vary depending on project complexity, ranging from $45 to $80 per hour, while joiners may charge between $50 and $90 hourly due to their specialized woodworking skills. Your decision should consider the type of work required: carpenters handle structural frameworks, often making their services essential for framing and general construction, whereas joiners focus on precision woodwork like cabinetry and furniture. Hiring a professional with relevant expertise ensures cost efficiency and project quality, preventing potential expenses from errors or rework.
How to Choose: Carpenter or Joiner for Your Project?
Choosing between a carpenter and a joiner depends on the scope and detail of your project. Carpenters specialize in structural work like framing, roofing, and larger construction tasks, while joiners focus on precision woodwork such as cabinetry, window frames, and furniture making. Assessing whether your project requires robust construction or intricate wood joinery helps determine which expert suits your needs best.
Frequently Asked Questions: Carpenter vs Joiner
Carpenters primarily work on structural frameworks and large-scale construction projects, while joiners specialize in crafting detailed wood components such as doors, stairs, and windows. Common questions include whether the skills overlap, with carpenters needing broader knowledge of building structures and joiners requiring precision in woodworking techniques. Both trades demand proficiency in tools and materials, but joiners focus on fine joinery techniques, whereas carpenters emphasize structural integrity and framing.
Carpenter vs joiner Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com