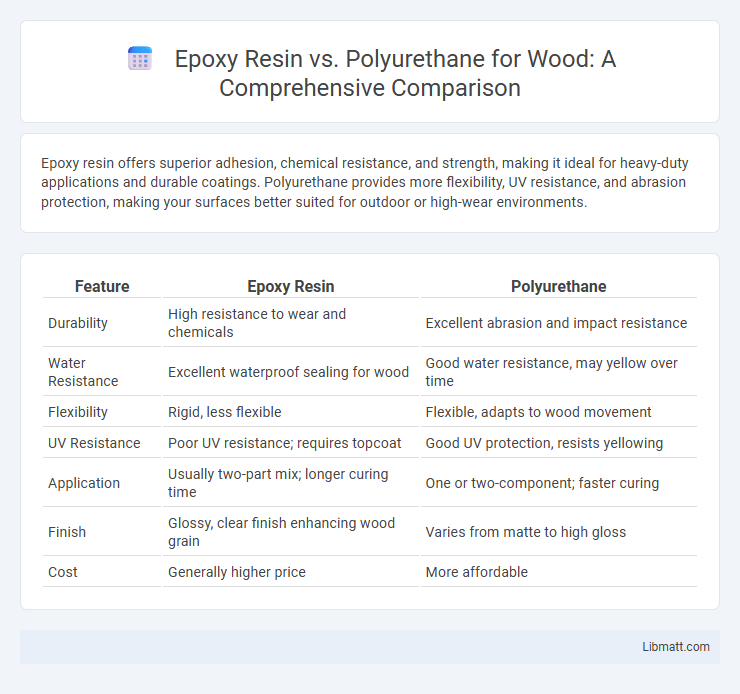
Epoxy resin offers superior adhesion, chemical resistance, and strength, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications and durable coatings. Polyurethane provides more flexibility, UV resistance, and abrasion protection, making your surfaces better suited for outdoor or high-wear environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Epoxy Resin | Polyurethane |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High resistance to wear and chemicals | Excellent abrasion and impact resistance |
| Water Resistance | Excellent waterproof sealing for wood | Good water resistance, may yellow over time |
| Flexibility | Rigid, less flexible | Flexible, adapts to wood movement |
| UV Resistance | Poor UV resistance; requires topcoat | Good UV protection, resists yellowing |
| Application | Usually two-part mix; longer curing time | One or two-component; faster curing |
| Finish | Glossy, clear finish enhancing wood grain | Varies from matte to high gloss |
| Cost | Generally higher price | More affordable |
Introduction to Epoxy Resin and Polyurethane
Epoxy resin is a thermosetting polymer known for its excellent adhesion, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, commonly used in coatings, adhesives, and composite materials. Polyurethane, a versatile polymer available as both thermoplastic and thermoset, provides superior flexibility, abrasion resistance, and impact strength, making it ideal for foams, elastomers, and sealants. Understanding the distinct properties of epoxy resin and polyurethane helps you select the right material for applications requiring durability, flexibility, or chemical stability.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Epoxy resin is composed of epoxide groups that form a tightly cross-linked thermosetting polymer upon curing, resulting in high mechanical strength and excellent chemical resistance. Polyurethane consists of urethane linkages formed by the reaction between polyols and isocyanates, offering a flexible, versatile polymer structure with varying degrees of hardness and elasticity. The rigid, three-dimensional network of epoxy contrasts with the segmented, polymer chain structure of polyurethane, influencing their distinct physical properties and application suitability.
Key Physical Properties
Epoxy resin exhibits superior adhesion, high tensile strength, and excellent chemical resistance, making it ideal for structural applications and coatings that require durability. Polyurethane offers greater flexibility, abrasion resistance, and UV stability, which suits it well for surfaces exposed to dynamic stresses and outdoor environments. Understanding these key physical properties helps you select the right material based on the specific demands of your project.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Epoxy resin offers superior durability with high resistance to chemicals, moisture, and mechanical wear, making it ideal for long-lasting applications. Polyurethane excels in flexibility and impact resistance but may degrade faster under UV exposure and harsh environmental conditions. Choosing epoxy resin enhances your project's longevity when durability is a critical factor.
Application Areas and Suitability
Epoxy resin excels in applications requiring strong adhesive properties, chemical resistance, and durability, making it ideal for marine coatings, flooring, and electronics encapsulation. Polyurethane is better suited for flexible coatings, automotive finishes, and foam insulation due to its elasticity and abrasion resistance. Your choice depends on whether rigidity and chemical stability or flexibility and impact resistance are prioritized in the specific application area.
Ease of Use and Installation
Epoxy resin offers a straightforward application process with a simple two-part mixing system, curing relatively quickly and providing strong adhesion for diverse surfaces. Polyurethane requires more precise mixing ratios and often a more controlled environment for application but excels in flexibility and resistance to weathering. Both materials demand surface preparation for optimal bonding, yet epoxy's user-friendly curing and straightforward installation make it a preferred choice for DIY projects and industrial coatings.
Adhesion and Bonding Strength
Epoxy resin offers superior adhesion and bonding strength on a wide variety of surfaces, including metals, concrete, and wood, due to its strong chemical bonds and excellent mechanical properties. Polyurethane provides good flexibility and impact resistance but generally exhibits lower adhesion compared to epoxy, especially on smooth or non-porous substrates. Your choice should consider epoxy resin for applications demanding maximum bond durability and polyurethane when elasticity and resistance to deformation are critical.
Resistance to Chemicals and Moisture
Epoxy resin exhibits superior resistance to chemicals and moisture due to its dense cross-linked structure, making it ideal for environments exposed to harsh solvents, acids, and water. Polyurethane offers good chemical resistance but can degrade faster when exposed to certain aggressive chemicals, particularly strong acids and alkalis. Moisture resistance in epoxy is generally higher, as polyurethane may absorb water over time, leading to potential swelling or loss of mechanical properties.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Epoxy resin generally offers a lower initial cost compared to polyurethane, making it a more economical choice for budget-sensitive projects. Polyurethane, while often more expensive upfront, can provide superior durability and flexibility, potentially reducing long-term maintenance and replacement expenses. You should evaluate both materials' lifecycle costs and performance requirements to determine the best investment for your application.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Epoxy resin offers superior adhesion, chemical resistance, and structural strength, making it ideal for high-load or waterproof applications such as countertops and boat repairs. Polyurethane provides greater flexibility, abrasion resistance, and UV stability, perfect for projects requiring impact absorption or outdoor durability like flooring and coatings. Your choice depends on desired hardness, environmental exposure, and longevity requirements to ensure optimal performance and finish.
Epoxy resin vs Polyurethane Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com