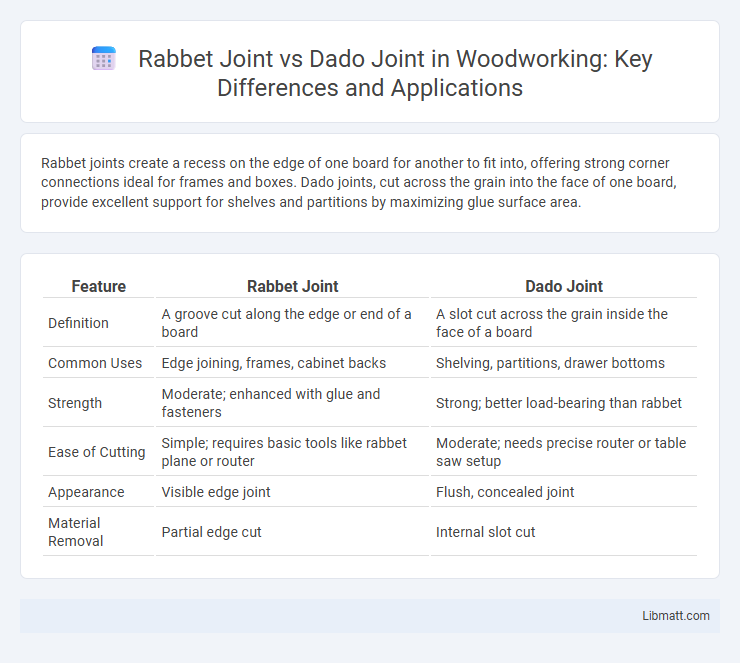
Rabbet joints create a recess on the edge of one board for another to fit into, offering strong corner connections ideal for frames and boxes. Dado joints, cut across the grain into the face of one board, provide excellent support for shelves and partitions by maximizing glue surface area.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rabbet Joint | Dado Joint |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A groove cut along the edge or end of a board | A slot cut across the grain inside the face of a board |
| Common Uses | Edge joining, frames, cabinet backs | Shelving, partitions, drawer bottoms |
| Strength | Moderate; enhanced with glue and fasteners | Strong; better load-bearing than rabbet |
| Ease of Cutting | Simple; requires basic tools like rabbet plane or router | Moderate; needs precise router or table saw setup |
| Appearance | Visible edge joint | Flush, concealed joint |
| Material Removal | Partial edge cut | Internal slot cut |
Introduction to Rabbet and Dado Joints
Rabbet joints feature a recess cut along the edge or end of a board, allowing it to fit snugly with another piece, commonly used in box and cabinet construction for strong corner joints. Dado joints consist of a groove cut across the grain of one board, designed to house the edge of another board, providing enhanced surface contact and strength in shelving and drawer assemblies. Both joints improve woodwork stability but differ in application and where the cuts are made, with rabbets typically on board edges and dadoes on board faces.
Understanding the Rabbet Joint
The rabbet joint features a recessed edge cut along the face or end of a board, allowing another piece to fit snugly into the groove and create a strong corner or edge connection. This joint is commonly used in cabinetry and framing for its ease of assembly and enhanced stability compared to simple butt joints. Understanding the rabbet joint helps you achieve precise alignment and increased surface area for gluing, improving the overall durability of your woodworking projects.
Exploring the Dado Joint
The dado joint features a rectangular groove cut into one piece of wood, allowing another piece to fit snugly within it for enhanced structural support. This joint is ideal for shelving and cabinetry, providing a strong connection without the need for additional fasteners. Understanding the dado joint's precise alignment and load distribution can help you create durable and professional woodworking projects.
Key Differences Between Rabbet and Dado Joints
Rabbet joints feature a single recess along the edge of a board, allowing another piece to fit flush against it, while dado joints have a groove cut across the grain or width of the board to receive another board. Rabbet joints are typically used for joining back panels to cabinet sides, offering simple edge alignment, whereas dado joints provide enhanced strength and stability by increasing the glue surface area, commonly used in shelving or drawer construction. The primary difference lies in rabbet joints being open notches along the edge, versus dado joints being internal grooves, impacting their application and load-bearing capabilities in woodworking projects.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Rabbet joints provide moderate strength and durability, suitable for frame construction where edge alignment is crucial but less load-bearing capacity is required. Dado joints exhibit higher strength and durability due to their increased surface area for glue application and mechanical interlocking, making them ideal for shelving and cabinetry that demands robust support. Both joints benefit from reinforcement techniques such as screws or dowels, but dado joints generally outperform rabbets in resisting shear and tensile forces.
Common Applications of Rabbet Joints
Rabbet joints are commonly used in cabinet and drawer construction due to their strong corner reinforcement and ease of assembly. They provide a reliable edge joint for attaching back panels to furniture frames, ensuring a flush fit and increased stability. These joints are also widely employed in window and door casings for precise alignment and enhanced durability.
Typical Uses for Dado Joints
Dado joints are commonly used in cabinetry and shelving to securely join shelves to side panels by fitting a slot (dado) into which the shelf fits snugly. These joints are ideal for creating strong, right-angle connections that support substantial weight and resist lateral movement. Their precision fitting makes dado joints essential in constructing bookcases, drawers, and other furniture pieces requiring durability and clean, flush surfaces.
Ease of Construction: Rabbet vs Dado
Rabbet joints are generally easier to construct than dado joints because they involve cutting a single recess along the edge of one board, requiring less precision and simpler tools. Dado joints require a groove cut across the grain or width of a board, demanding more accuracy and often specialized equipment like a router or table saw with a dado blade. This difference in complexity makes rabbet joints a preferred choice for quick assembly or beginner woodworking projects.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Joint
Rabbet joints offer a simple design that provides increased surface area for gluing, enhancing joint strength and alignment in woodworking projects, but they can be less visually appealing due to exposed edges and may require precise cutting for a snug fit. Dado joints excel in creating strong, load-bearing connections by fitting one piece into a groove cut in another, making them ideal for shelving and cabinetry; however, they demand accurate depth and width measurements and can weaken the grooves if overcut. Each joint's suitability depends on project requirements, balancing ease of assembly, structural integrity, and aesthetic considerations.
Choosing the Right Joint for Your Woodworking Project
Choosing between a rabbet joint and a dado joint depends on the strength and appearance requirements of your woodworking project. Rabbet joints create a strong, simple corner connection ideal for frames and cabinet backs, while dado joints provide a robust slot for shelving and drawer bottoms, enhancing load-bearing capacity. Your project's structural needs and aesthetic preferences will guide the decision to ensure durability and professional finish.
Rabbet joint vs Dado joint Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com