Reclaimed wood offers unique character and sustainability benefits by repurposing aged materials with rich textures and history, while new wood provides uniformity, consistency, and fresher structural integrity for modern construction needs. Your choice depends on balancing environmental impact, aesthetic preference, and project requirements.
Table of Comparison
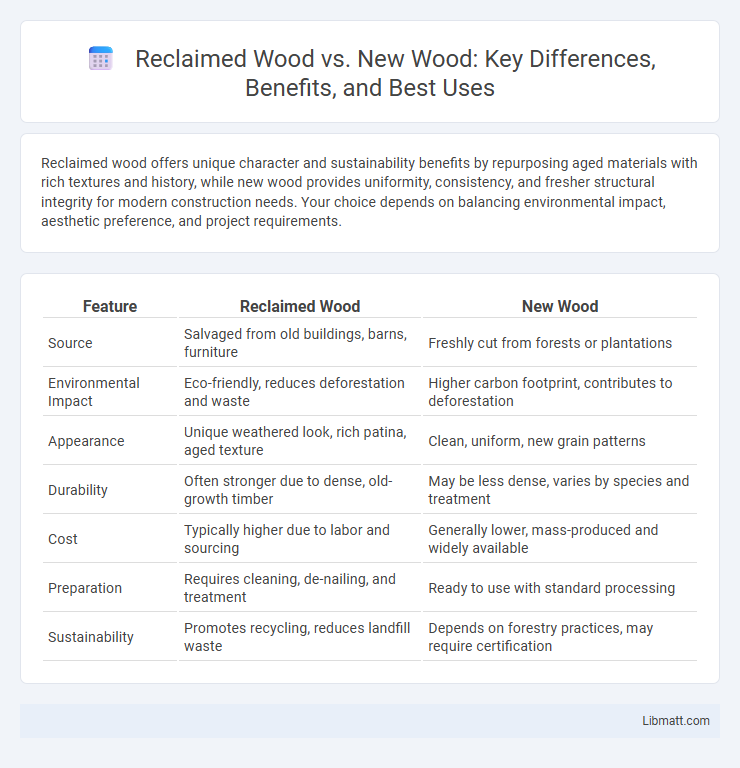
| Feature | Reclaimed Wood | New Wood |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Salvaged from old buildings, barns, furniture | Freshly cut from forests or plantations |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, reduces deforestation and waste | Higher carbon footprint, contributes to deforestation |
| Appearance | Unique weathered look, rich patina, aged texture | Clean, uniform, new grain patterns |
| Durability | Often stronger due to dense, old-growth timber | May be less dense, varies by species and treatment |
| Cost | Typically higher due to labor and sourcing | Generally lower, mass-produced and widely available |
| Preparation | Requires cleaning, de-nailing, and treatment | Ready to use with standard processing |
| Sustainability | Promotes recycling, reduces landfill waste | Depends on forestry practices, may require certification |
Introduction to Reclaimed Wood vs New Wood
Reclaimed wood offers unique character and environmental benefits by repurposing aged materials, while new wood provides consistent quality and availability for construction or furniture. Your choice depends on factors like sustainability, aesthetic preferences, durability, and project requirements. Reclaimed wood often features weathered textures and history, whereas new wood ensures uniformity and fewer imperfections.
Sourcing and Availability of Materials
Reclaimed wood is sourced primarily from old buildings, barns, and furniture, offering limited and variable availability influenced by regional demolition activities. New wood comes directly from sustainably managed forests, ensuring a steady and predictable supply aligned with market demand and environmental certifications. The choice between reclaimed and new wood hinges on project timelines and the desire for unique aged character versus consistent quality and dimensions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Reclaimed wood significantly reduces environmental impact by diverting waste from landfills and minimizing the need for deforestation, preserving natural forests and biodiversity. New wood production often involves harvesting mature trees, contributing to habitat loss and increased carbon emissions from logging and processing. Using reclaimed wood for your projects promotes sustainability by recycling materials and lowering your carbon footprint compared to choosing newly sourced timber.
Cost Comparison: Reclaimed vs New Wood
Reclaimed wood generally costs more upfront due to the labor-intensive process of sourcing, cleaning, and preparing the material, while new wood typically has lower initial prices because of mass production and widespread availability. However, reclaimed wood offers long-term value through its durability, unique character, and environmental benefits, which can justify the higher initial investment. New wood may require more frequent replacement or maintenance, potentially increasing overall costs over time compared to the resilience of reclaimed wood.
Aesthetic Differences and Visual Appeal
Reclaimed wood offers a unique, weathered patina with natural imperfections, knots, and a rich texture that enhances rustic and vintage interior designs. New wood provides a cleaner, uniform appearance with consistent grain patterns and a smoother finish, ideal for modern and minimalist aesthetics. The choice between reclaimed and new wood depends on the desired visual character, where reclaimed wood emphasizes authenticity and history, while new wood highlights freshness and precision.
Durability and Performance Over Time
Reclaimed wood often benefits from years of natural aging and weathering, which can enhance its durability and stability compared to new wood. Your choice of reclaimed wood typically involves denser, older growth timber, resulting in superior strength and resistance to warping or shrinking over time. New wood may require treatments to achieve similar performance, making reclaimed wood a lasting, environmentally-friendly option for long-term projects.
Installation and Workability Considerations
Reclaimed wood often presents challenges during installation due to its variable thickness, prior nail or screw holes, and potential warping, requiring specialized tools and additional preparation. New wood offers uniform dimensions and consistency, making it easier to cut, fasten, and fit precisely during construction or remodeling projects. Workability of new wood generally results in faster installation times and less need for adjustments compared to the unpredictable nature of reclaimed materials.
Common Applications in Design and Construction
Reclaimed wood is widely used in flooring, furniture, and accent walls due to its unique character and sustainability benefits, making it ideal for rustic and vintage-inspired designs. New wood, preferred for structural framing, cabinetry, and custom millwork, offers consistent quality and uniform dimensions necessary for precise construction projects. Both materials find specialized applications depending on aesthetic goals and environmental considerations in architectural and interior design.
Maintenance and Longevity
Reclaimed wood typically requires more maintenance due to its aged condition, often needing treatments to prevent pests and decay, whereas new wood benefits from modern treatments that enhance durability and reduce upkeep. However, reclaimed wood can offer exceptional longevity if properly maintained because it has already aged and acclimated, making it less prone to warping and shrinking compared to new wood. Investing in sealants and regular inspections extends the lifespan of both wood types, but reclaimed wood's unique character often justifies the additional care.
Choosing the Right Wood for Your Project
Choosing the right wood for your project depends on factors such as durability, cost, and environmental impact. Reclaimed wood offers unique character, sustainability benefits, and often greater stability due to years of aging, making it ideal for rustic or eco-friendly designs. New wood provides consistency, availability, and a wider selection of species, suited for projects requiring uniformity and specific structural requirements.
Reclaimed wood vs new wood Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com