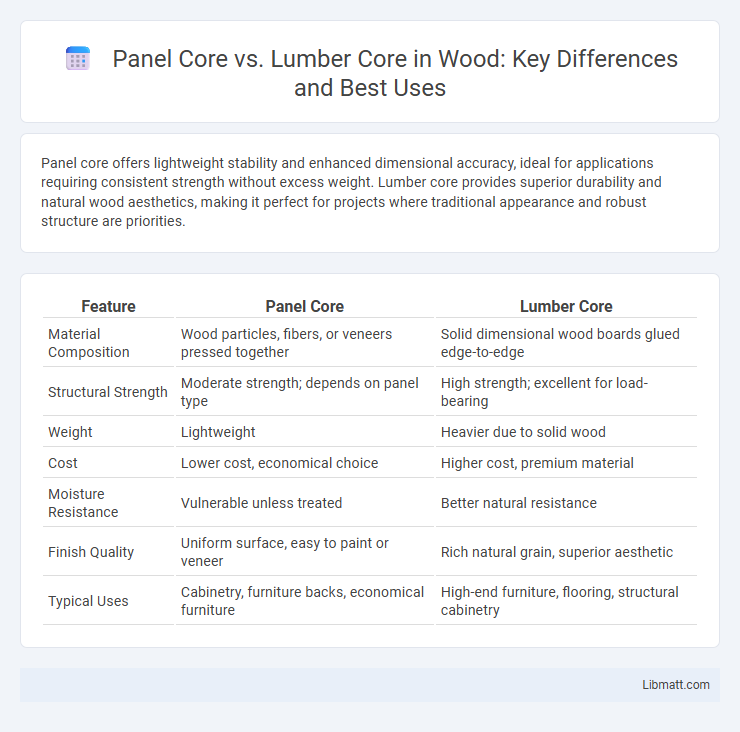
Panel core offers lightweight stability and enhanced dimensional accuracy, ideal for applications requiring consistent strength without excess weight. Lumber core provides superior durability and natural wood aesthetics, making it perfect for projects where traditional appearance and robust structure are priorities.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Panel Core | Lumber Core |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Wood particles, fibers, or veneers pressed together | Solid dimensional wood boards glued edge-to-edge |
| Structural Strength | Moderate strength; depends on panel type | High strength; excellent for load-bearing |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier due to solid wood |
| Cost | Lower cost, economical choice | Higher cost, premium material |
| Moisture Resistance | Vulnerable unless treated | Better natural resistance |
| Finish Quality | Uniform surface, easy to paint or veneer | Rich natural grain, superior aesthetic |
| Typical Uses | Cabinetry, furniture backs, economical furniture | High-end furniture, flooring, structural cabinetry |
Introduction to Panel Core and Lumber Core
Panel core features engineered wood layers fused together to enhance stability and strength, making it ideal for consistent performance in furniture and cabinetry. Lumber core consists of solid hardwood strips glued side by side, offering natural durability and the ability to hold fasteners effectively for framed and traditional cabinetry. Both cores serve structural purposes but differ in material composition and application based on performance and aesthetic preferences.
Defining Panel Core: Structure and Materials
Panel core refers to the inner layer of engineered wood products, typically composed of thin wood veneers or wood fibers bonded together to form a stable, lightweight, and durable core. This core enhances structural integrity and dimensional stability while reducing weight compared to solid lumber cores, which consist of solid wood pieces stacked or glued together. Panel cores are commonly used in furniture, cabinetry, and doors to balance strength, cost-effectiveness, and environmental impact.
Lumber Core Explained: Composition and Features
Lumber core refers to a solid wood center sandwiched between hardwood veneers, providing enhanced strength, durability, and resistance to warping compared to panel core. Its composition typically includes vertical grain wood staves glued edge-to-edge, offering a stable and high-quality foundation ideal for fine woodworking. Choosing lumber core ensures your furniture or cabinetry benefits from natural wood properties combined with superior structural integrity.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Panel core manufacturing involves layering thin sheets or veneers, which are bonded under heat and pressure to form a stable, uniform core ideal for engineered wood products. Lumber core, by contrast, is constructed from solid wood strips glued edge-to-edge, maintaining natural wood properties but requiring more precise milling and joining techniques. Both processes emphasize strength and dimensional stability, yet panel core benefits from more consistent thickness and surface smoothness due to its composite nature.
Strength and Durability Differences
Panel core doors typically feature a hollow or composite structure with engineered wood or MDF, offering moderate strength and durability suitable for interior use. Lumber core doors consist of a solid wood frame filled with high-density wood blocks, providing superior structural integrity and enhanced resistance to wear and impact. Choosing your door core depends on the desired balance between cost efficiency and long-lasting performance in high-traffic or exterior environments.
Weight and Workability: Which Is Easier to Handle?
Panel core materials, typically made from plywood or MDF, are lighter and offer better workability compared to lumber core, which consists of solid wood strips. The reduced weight of panel cores makes them easier to lift, cut, and install, enhancing efficiency in construction and cabinetry projects. Lumber core's heavier mass provides durability but can require more effort and specialized tools during handling and fabrication.
Cost Analysis: Panel Core vs Lumber Core
Panel core offers a cost-effective alternative to lumber core, typically lowering material and labor expenses due to its engineered construction and consistent dimensions. Lumber core tends to be more expensive because of higher raw wood costs and additional machining required for natural material variances. When evaluating cost analysis, your choice should factor in initial purchase price, durability, and long-term maintenance for accurate budget planning.
Common Applications and Best Uses
Panel core is commonly used in lightweight furniture, cabinetry, and interior doors due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of handling, making it ideal for applications where weight reduction is important. Lumber core, valued for its strength and durability, is preferred in high-end cabinetry, architectural millwork, and solid core doors where stability and long-term performance are crucial. Your choice between panel core and lumber core should depend on the specific structural demands and budget considerations of your project.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Panel core materials like plywood and MDF often use recycled wood fibers and adhesives that can contain formaldehyde, raising concerns about indoor air quality and long-term environmental effects. Lumber core, typically sourced from solid wood, offers greater sustainability when harvested from responsibly managed forests, as it is biodegradable and has a lower overall carbon footprint. Choosing lumber core reduces reliance on synthetic resins and promotes renewable resource utilization, contributing to more environmentally friendly furniture and construction products.
Choosing the Right Core for Your Project
Selecting the right core for your project depends on factors like durability, weight, and cost. Panel cores, such as plywood or MDF, offer consistent strength and stability, making them ideal for cabinetry and furniture that require a smooth finish. Lumber cores provide superior structural integrity and natural aesthetics, perfect for projects where solid wood appearance and long-term resilience are priorities for your build.
Panel core vs Lumber core Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com