An APU (Accelerated Processing Unit) integrates CPU and GPU cores on a single chip, offering balanced performance for everyday tasks and light gaming. Your choice depends on whether you need a cost-effective solution with basic graphics or a dedicated GPU for high-end gaming and intensive graphical workloads.
Table of Comparison
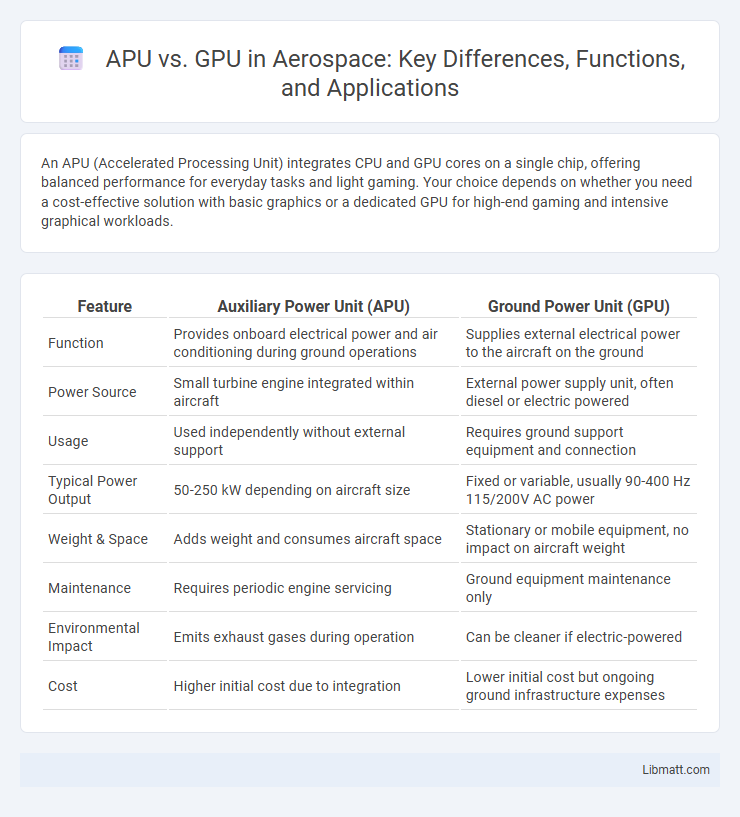
| Feature | Auxiliary Power Unit (APU) | Ground Power Unit (GPU) |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Provides onboard electrical power and air conditioning during ground operations | Supplies external electrical power to the aircraft on the ground |
| Power Source | Small turbine engine integrated within aircraft | External power supply unit, often diesel or electric powered |
| Usage | Used independently without external support | Requires ground support equipment and connection |
| Typical Power Output | 50-250 kW depending on aircraft size | Fixed or variable, usually 90-400 Hz 115/200V AC power |
| Weight & Space | Adds weight and consumes aircraft space | Stationary or mobile equipment, no impact on aircraft weight |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic engine servicing | Ground equipment maintenance only |
| Environmental Impact | Emits exhaust gases during operation | Can be cleaner if electric-powered |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to integration | Lower initial cost but ongoing ground infrastructure expenses |
Introduction to APU and GPU
An APU (Accelerated Processing Unit) integrates both the CPU (Central Processing Unit) and GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) on a single chip, enabling efficient processing for both general computing and graphics tasks. GPUs specialize in parallel processing with thousands of cores designed for rendering graphics and accelerating complex computations in gaming, AI, and scientific applications. The combination in APUs offers cost-effective and power-efficient solutions suitable for laptops and entry-level desktops, while discrete GPUs provide superior performance for high-end gaming and professional workloads.
What is an APU?
An APU (Accelerated Processing Unit) integrates both the CPU (Central Processing Unit) and GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) on a single chip, enhancing processing efficiency and reducing power consumption. This combination allows your computer to handle general computing tasks and graphics-intensive applications more seamlessly without needing a separate graphics card. APUs are especially beneficial in laptops and compact devices where space and energy efficiency are critical.
What is a GPU?
A GPU, or Graphics Processing Unit, is a specialized processor designed to accelerate rendering images, videos, and animations by performing rapid mathematical calculations, primarily for graphics tasks. Unlike a CPU, a GPU contains thousands of smaller cores optimized for parallel processing, making it highly efficient for handling complex visual data and graphics-intensive applications such as gaming, virtual reality, and video editing. Modern GPUs also support general-purpose computing tasks through technologies like CUDA and OpenCL, enabling accelerated performance in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and scientific simulations.
Key Differences Between APU and GPU
APUs integrate both the CPU and GPU cores on a single chip, offering improved power efficiency and lower latency for graphics processing compared to discrete GPUs. GPUs, designed as dedicated hardware units, deliver superior performance for complex parallel computations and are essential for high-end gaming, professional rendering, and AI workloads. The key difference lies in APUs providing a balanced solution for everyday computing with moderate graphics needs, while GPUs excel in intensive graphical and computational tasks.
Performance Comparison: APU vs GPU
APUs integrate both CPU and GPU cores on a single chip, providing efficient performance for everyday computing and light gaming by reducing latency and power consumption. Dedicated GPUs, however, offer superior graphics processing power, supporting high-end gaming, complex 3D rendering, and professional applications with faster frame rates and enhanced visual effects. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize cost-effective versatility or specialized, high-performance graphics.
Power Consumption and Efficiency
APUs (Accelerated Processing Units) combine CPU and GPU cores on a single chip, offering lower power consumption and improved energy efficiency compared to discrete GPUs due to integrated architecture and shared resources. GPUs generally consume more power as dedicated hardware designed for intensive parallel processing, making them less efficient for low to moderate workloads. In scenarios requiring continuous heavy graphics or compute tasks, GPUs deliver superior performance per watt, but APUs excel in balanced power efficiency for general computing and light gaming applications.
Cost Analysis: Which Is More Affordable?
APUs typically offer a more affordable solution by combining CPU and GPU capabilities on a single chip, reducing overall system costs and power consumption compared to separate GPU setups. Budget-conscious users and entry-level gamers benefit from APUs as they eliminate the need for an additional discrete graphics card, often lowering the initial purchase and maintenance expenses. However, discrete GPUs can provide better performance per dollar in high-end gaming and professional workloads, making them cost-effective for users requiring advanced graphics processing.
Use Cases: When to Choose APU or GPU
APUs excel in compact systems and budget builds by integrating CPU and GPU cores for light gaming, multimedia, and general computing with lower power consumption. Dedicated GPUs are essential for high-performance tasks like 3D rendering, advanced gaming, AI acceleration, and professional visual workloads requiring extensive parallel processing. Choose an APU for space-efficient, cost-effective solutions and a discrete GPU for maximum graphical power and specialized computational needs.
Future Trends in APU and GPU Technology
Future trends in APU and GPU technology emphasize increasing integration of AI and machine learning capabilities directly onto chips, enhancing real-time processing performance. Advances in chip fabrication, such as 3nm and beyond, drive higher energy efficiency and computational power for both APUs and GPUs, supporting next-gen gaming and professional workloads. The convergence of CPU and GPU architectures in APUs is expected to accelerate, enabling more versatile, compact, and cost-effective computing solutions across mobile and desktop platforms.
Conclusion: Which Is Right for You?
Choosing between an APU and a GPU depends on your computing needs and budget; APUs offer integrated graphics suitable for casual gaming and everyday tasks, while dedicated GPUs provide superior performance for high-end gaming, video editing, and 3D rendering. If space, power consumption, and cost are priorities, an APU delivers a balanced solution with decent graphics capabilities. For users requiring maximum graphics power and faster processing speeds, investing in a dedicated GPU is the optimal choice.
APU vs GPU Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com