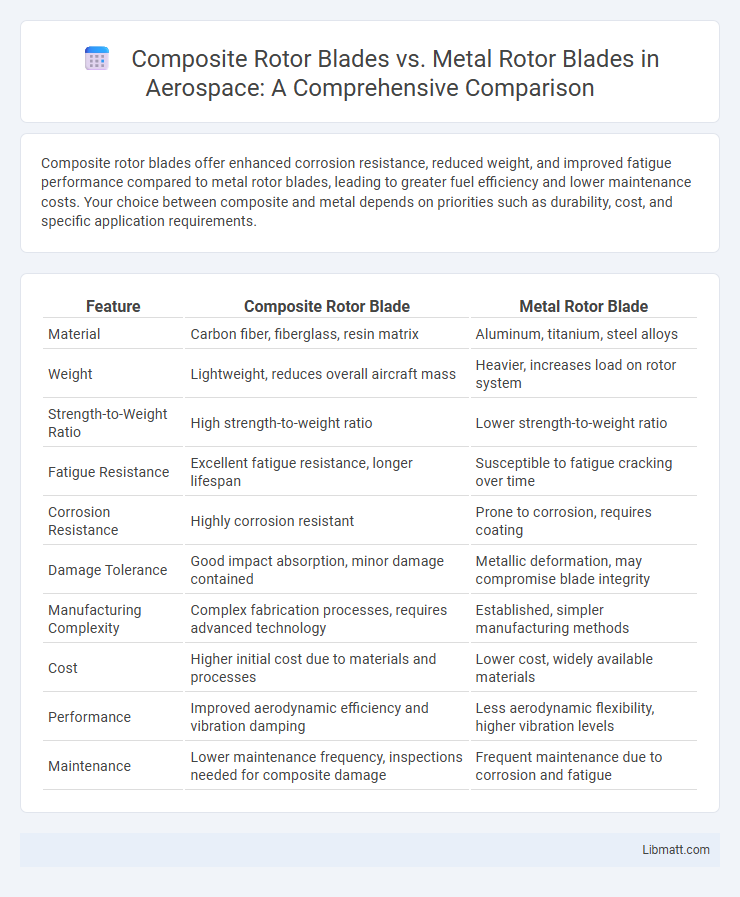
Composite rotor blades offer enhanced corrosion resistance, reduced weight, and improved fatigue performance compared to metal rotor blades, leading to greater fuel efficiency and lower maintenance costs. Your choice between composite and metal depends on priorities such as durability, cost, and specific application requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Composite Rotor Blade | Metal Rotor Blade |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Carbon fiber, fiberglass, resin matrix | Aluminum, titanium, steel alloys |
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces overall aircraft mass | Heavier, increases load on rotor system |
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | High strength-to-weight ratio | Lower strength-to-weight ratio |
| Fatigue Resistance | Excellent fatigue resistance, longer lifespan | Susceptible to fatigue cracking over time |
| Corrosion Resistance | Highly corrosion resistant | Prone to corrosion, requires coating |
| Damage Tolerance | Good impact absorption, minor damage contained | Metallic deformation, may compromise blade integrity |
| Manufacturing Complexity | Complex fabrication processes, requires advanced technology | Established, simpler manufacturing methods |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to materials and processes | Lower cost, widely available materials |
| Performance | Improved aerodynamic efficiency and vibration damping | Less aerodynamic flexibility, higher vibration levels |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance frequency, inspections needed for composite damage | Frequent maintenance due to corrosion and fatigue |
Introduction to Rotor Blade Materials
Composite rotor blades, typically made from carbon fiber reinforced polymers, offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced fatigue resistance compared to traditional metal rotor blades, usually constructed from aluminum or titanium alloys. The lightweight nature of composites improves aerodynamic efficiency and reduces centrifugal stresses, allowing for longer blade spans and increased performance in wind turbines and helicopters. Metal rotor blades remain valued for their toughness and ease of repair but are generally heavier and more prone to corrosion and fatigue over extended operational periods.
Overview of Metal Rotor Blades
Metal rotor blades, typically made from aluminum or titanium alloys, offer high strength, durability, and resistance to impact and corrosion. They provide reliable performance in harsh environments and maintain structural integrity under high stress conditions. However, metal blades are generally heavier and less flexible than composite rotor blades, which can affect efficiency and vibration damping.
Overview of Composite Rotor Blades
Composite rotor blades offer superior strength-to-weight ratios compared to traditional metal rotor blades, enhancing aircraft performance and fuel efficiency. These blades are made from advanced materials like carbon fiber and fiberglass, providing excellent fatigue resistance and flexibility under stress. Your rotorcraft benefits from reduced maintenance costs and improved aerodynamic efficiency with composite rotor blades, making them the preferred choice in modern aviation.
Weight Comparison: Composite vs. Metal
Composite rotor blades weigh significantly less than metal rotor blades due to advanced materials like carbon fiber and fiberglass, which offer high strength-to-weight ratios. This weight reduction enhances aircraft performance by improving fuel efficiency and maneuverability. Your choice of composite blades can lead to lower operational costs and increased payload capacity compared to traditional metal rotor blades.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Composite rotor blades exhibit superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced fatigue resistance compared to traditional metal rotor blades, making them more durable under cyclic loading conditions. Their ability to absorb and dissipate vibration reduces the risk of structural failure and extends service life, providing a reliable performance advantage. When evaluating your rotor blade options, composites offer improved longevity and resilience, crucial for demanding operational environments.
Fatigue Resistance and Lifespan
Composite rotor blades exhibit superior fatigue resistance compared to metal rotor blades due to their ability to absorb and dissipate stress more efficiently, resulting in fewer micro-cracks over time. This enhanced durability translates into a longer operational lifespan, reducing maintenance frequency and overall costs. Your choice of composite blades can significantly improve performance and longevity in demanding rotor applications.
Maintenance Requirements and Costs
Composite rotor blades generally require less maintenance than metal rotor blades due to their resistance to corrosion, fatigue, and environmental wear. Metal rotor blades often face higher maintenance costs caused by regular inspections, corrosion control, and repairs from metal fatigue or cracking. Your investment in composite blades can lead to reduced downtime and lower long-term maintenance expenses, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Performance Impact on Aircraft
Composite rotor blades offer significant performance advantages over metal rotor blades by reducing overall weight, which enhances fuel efficiency and increases payload capacity. Their superior fatigue resistance and damage tolerance improve durability and lower maintenance costs, resulting in greater operational availability for your aircraft. Enhanced aerodynamic properties of composite blades contribute to reduced vibration and noise levels, leading to smoother, more efficient flight performance.
Environmental and Corrosion Resistance
Composite rotor blades offer superior environmental and corrosion resistance compared to metal rotor blades due to their synthetic fiber reinforcement and resin matrix, which do not rust or degrade easily under exposure to moisture, salt, or chemicals. These blades maintain structural integrity and performance in harsh environmental conditions, reducing maintenance costs and extending service life. Your choice of composite blades ensures enhanced durability in marine and coastal applications where metal blades are prone to oxidation and corrosion damage.
Future Trends in Rotor Blade Technology
Composite rotor blades offer superior fatigue resistance, lighter weight, and enhanced aerodynamic efficiency compared to traditional metal rotor blades, driving future trends in aerospace technology. Advances in material science and manufacturing techniques will continue to optimize composite structures for improved durability and performance under extreme conditions. Your investment in composite rotor blade technology enhances fuel efficiency, reduces maintenance costs, and supports the industry's shift toward sustainable aviation solutions.
composite rotor blade vs metal rotor blade Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com