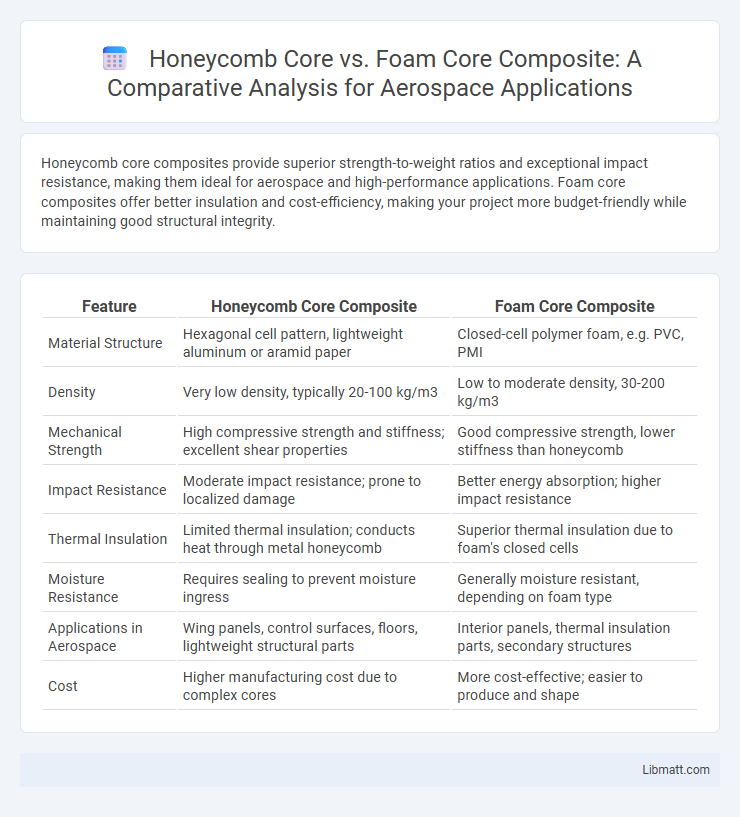
Honeycomb core composites provide superior strength-to-weight ratios and exceptional impact resistance, making them ideal for aerospace and high-performance applications. Foam core composites offer better insulation and cost-efficiency, making your project more budget-friendly while maintaining good structural integrity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Honeycomb Core Composite | Foam Core Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Structure | Hexagonal cell pattern, lightweight aluminum or aramid paper | Closed-cell polymer foam, e.g. PVC, PMI |
| Density | Very low density, typically 20-100 kg/m3 | Low to moderate density, 30-200 kg/m3 |
| Mechanical Strength | High compressive strength and stiffness; excellent shear properties | Good compressive strength, lower stiffness than honeycomb |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate impact resistance; prone to localized damage | Better energy absorption; higher impact resistance |
| Thermal Insulation | Limited thermal insulation; conducts heat through metal honeycomb | Superior thermal insulation due to foam's closed cells |
| Moisture Resistance | Requires sealing to prevent moisture ingress | Generally moisture resistant, depending on foam type |
| Applications in Aerospace | Wing panels, control surfaces, floors, lightweight structural parts | Interior panels, thermal insulation parts, secondary structures |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost due to complex cores | More cost-effective; easier to produce and shape |
Introduction to Composite Core Materials
Honeycomb core composites offer exceptional strength-to-weight ratios by utilizing a lightweight, hexagonal structure made of materials like aluminum or Nomex, ideal for aerospace and marine applications. Foam core composites, typically constructed from closed-cell polymer foams such as PVC or PET, provide excellent impact resistance and thermal insulation with reduced density. Both core types enhance the mechanical properties of sandwich panels by improving stiffness and durability while minimizing weight, but selection depends on specific performance requirements and environmental conditions.
Understanding Honeycomb Core Structures
Honeycomb core structures offer exceptional strength-to-weight ratios thanks to their hexagonal geometry, which efficiently distributes stress across the composite material. These cores provide superior impact resistance and stiffness compared to foam cores, making them ideal for aerospace, automotive, and marine applications. Understanding the properties of honeycomb cores helps you select the right composite construction to optimize performance and durability in your projects.
Overview of Foam Core Composites
Foam core composites consist of a lightweight foam core sandwiched between two composite face sheets, offering excellent stiffness-to-weight ratios ideal for aerospace, marine, and automotive applications. Common foam materials include polyurethane, PVC, and PET, each providing different mechanical properties and thermal resistance tailored for specific use cases. These composites provide efficient energy absorption, impact resistance, and thermal insulation, making them versatile for structural panels and lightweight load-bearing components.
Key Differences Between Honeycomb and Foam Cores
Honeycomb core composites feature a hexagonal structure made from materials like aluminum or Nomex, providing high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent impact resistance, while foam cores are typically made from PVC, polyurethane, or polystyrene, offering good insulation and ease of fabrication. Honeycomb cores excel in aerospace and automotive applications due to their superior stiffness and damage tolerance, whereas foam cores are favored for marine and lightweight structural panels where cost-effectiveness and thermal properties are critical. Your choice depends on required mechanical performance, weight constraints, and environmental conditions of the application.
Weight and Strength Comparison
Honeycomb core composites offer superior strength-to-weight ratios compared to foam core composites, making them ideal for high-performance applications requiring maximum stiffness with minimal weight. Foam cores are generally lighter but provide less structural strength and impact resistance, which may limit their use in heavy-load or high-stress environments. Your choice between these materials should consider the specific demands of weight efficiency and mechanical durability in your project.
Impact Resistance and Durability
Honeycomb core composites offer superior impact resistance due to their lightweight structure and high energy absorption capacity, making them ideal for aerospace and automotive applications. Foam core composites provide good durability with excellent resistance to compression and fatigue, but they generally exhibit lower impact resistance compared to honeycomb cores. Understanding these differences helps you select the optimal core material based on specific performance requirements in your composite design.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Properties
Honeycomb core composites excel in thermal insulation due to their efficient air trapping cells, significantly reducing heat transfer, while foam core composites offer superior acoustic insulation by absorbing sound waves within their porous structure. Your choice between honeycomb and foam core materials depends on whether thermal efficiency or noise reduction is the primary concern in your composite application. Balancing these properties ensures optimal performance tailored to specific environmental conditions and functional requirements.
Manufacturing and Cost Considerations
Honeycomb core composites offer superior strength-to-weight ratios but involve more complex manufacturing processes such as vacuum bagging and autoclave curing, leading to higher production costs. Foam core composites feature simpler fabrication methods like hand lay-up or resin infusion, reducing labor intensity and initial equipment investment. While honeycomb cores are more expensive upfront, they provide enhanced performance for aerospace and high-end applications, whereas foam cores suit cost-sensitive industries requiring quicker turnaround times.
Applications in Aerospace, Marine, and Construction
Honeycomb core composites offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and energy absorption, making them ideal for aerospace structures like aircraft panels and satellite components where weight reduction is critical. Foam core composites provide excellent thermal insulation and impact resistance, widely used in marine applications for boat hulls and decks to enhance buoyancy and durability. In construction, honeycomb cores contribute to lightweight, high-strength panels for facades and flooring, whereas foam cores facilitate thermal efficiency and sound insulation in building envelopes.
Choosing the Right Core for Your Project
Selecting the right core material for your composite project depends on factors like weight, strength, and application environment. Honeycomb cores excel in providing exceptional strength-to-weight ratios and impact resistance, ideal for aerospace and marine industries. Foam cores, while lighter and easier to shape, offer superior thermal insulation and are preferred in automotive and wind energy sectors where energy absorption and flexibility are critical.
Honeycomb Core vs Foam Core Composite Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com