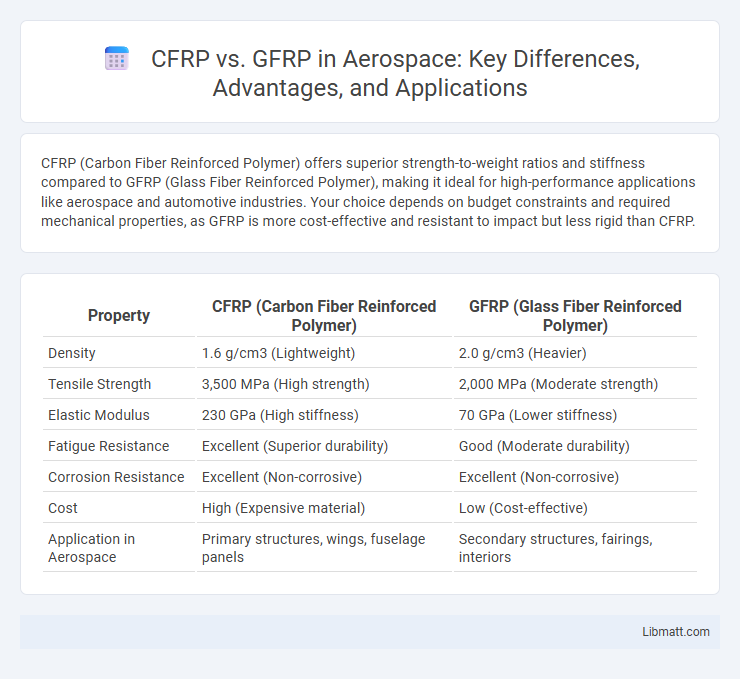
CFRP (Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer) offers superior strength-to-weight ratios and stiffness compared to GFRP (Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer), making it ideal for high-performance applications like aerospace and automotive industries. Your choice depends on budget constraints and required mechanical properties, as GFRP is more cost-effective and resistant to impact but less rigid than CFRP.
Table of Comparison
| Property | CFRP (Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer) | GFRP (Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 1.6 g/cm3 (Lightweight) | 2.0 g/cm3 (Heavier) |
| Tensile Strength | 3,500 MPa (High strength) | 2,000 MPa (Moderate strength) |
| Elastic Modulus | 230 GPa (High stiffness) | 70 GPa (Lower stiffness) |
| Fatigue Resistance | Excellent (Superior durability) | Good (Moderate durability) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (Non-corrosive) | Excellent (Non-corrosive) |
| Cost | High (Expensive material) | Low (Cost-effective) |
| Application in Aerospace | Primary structures, wings, fuselage panels | Secondary structures, fairings, interiors |
Introduction to CFRP and GFRP
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) and Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer (GFRP) are composite materials widely used in aerospace, automotive, and construction industries for their high strength-to-weight ratios. CFRP consists of carbon fibers embedded in a polymer matrix, offering superior stiffness, tensile strength, and thermal resistance compared to GFRP, which uses glass fibers and provides excellent corrosion resistance and lower costs. Understanding the fundamental differences between CFRP and GFRP helps you select the most suitable material based on mechanical performance, weight considerations, and budget constraints.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) consists of carbon fibers embedded in a polymer matrix, typically epoxy resin, while Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer (GFRP) uses glass fibers within a similar resin system. CFRP manufacturing involves processes such as autoclave curing and prepreg layering to achieve high strength-to-weight ratios, whereas GFRP is commonly produced through methods like hand lay-up, filament winding, and spray-up, offering cost-effective production. The distinctive fiber types and curing techniques directly influence the mechanical properties and applications of both composites.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
CFRP (Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer) offers superior tensile strength and stiffness compared to GFRP (Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer), making it ideal for high-performance applications requiring lightweight yet strong materials. GFRP provides better impact resistance and is generally more cost-effective, suitable for applications where flexibility and durability are prioritized over ultimate strength. Your choice between CFRP and GFRP should consider the specific mechanical property requirements such as strength-to-weight ratio, stiffness, and impact tolerance for optimal performance.
Weight and Density Differences
CFRP (Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer) offers significantly lower weight and density compared to GFRP (Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer), making it ideal for high-performance applications where weight reduction is critical. CFRP typically has a density around 1.6 g/cm3, whereas GFRP's density ranges from 2.0 to 2.6 g/cm3, resulting in notable weight savings for your projects. Choosing CFRP can improve efficiency and structural strength while minimizing overall mass.
Strength and Durability Assessment
CFRP (Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer) exhibits superior tensile strength and stiffness compared to GFRP (Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer), making it ideal for applications requiring high strength-to-weight ratios. Durability assessments reveal CFRP has excellent resistance to fatigue, corrosion, and environmental degradation, whereas GFRP can be more susceptible to moisture absorption and UV damage over time. Your choice between CFRP and GFRP should consider these performance differences based on the specific strength and longevity requirements of your project.
Cost Analysis: CFRP vs GFRP
Carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) typically has a higher initial cost compared to glass fiber reinforced polymer (GFRP) due to the expensive raw materials and complex manufacturing processes involved. GFRP offers a more budget-friendly option with lower material and production costs, making it suitable for large-scale applications where cost efficiency is critical. Your decision should weigh the performance benefits of CFRP against the economic advantages of GFRP for cost-effective project outcomes.
Applications in Various Industries
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) is extensively used in aerospace, automotive, and sports equipment industries due to its high strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness. Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer (GFRP) finds applications in construction, marine, and electrical industries because of its cost-effectiveness, corrosion resistance, and electrical insulation properties. Both materials enhance performance and durability but are selected based on specific industry requirements and environmental conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
CFRP (Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer) has a higher environmental impact than GFRP (Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer) due to energy-intensive production and limited recyclability, though it offers superior strength-to-weight ratio which may reduce overall resource use in certain applications. GFRP is more sustainable with lower embodied energy and better recyclability, making it preferable for projects prioritizing environmental responsibility. You should consider the lifecycle emissions and end-of-life options of both materials to align with your sustainability goals.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and higher stiffness compared to Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer (GFRP), making it ideal for high-performance applications in aerospace and automotive industries. However, CFRP is significantly more expensive and has lower impact resistance, leading to potential brittleness under sudden loads. GFRP provides cost-effective corrosion resistance and better flexibility, but it is heavier and less rigid, limiting its use in weight-critical components.
Choosing Between CFRP and GFRP
Choosing between CFRP (Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer) and GFRP (Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer) depends on your project's strength, weight, and cost requirements. CFRP offers superior tensile strength and stiffness with a lighter weight, making it ideal for high-performance applications such as aerospace and automotive industries. GFRP provides a more cost-effective solution with good corrosion resistance and durability, suitable for construction and marine applications where budget constraints are critical.
CFRP vs GFRP Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com