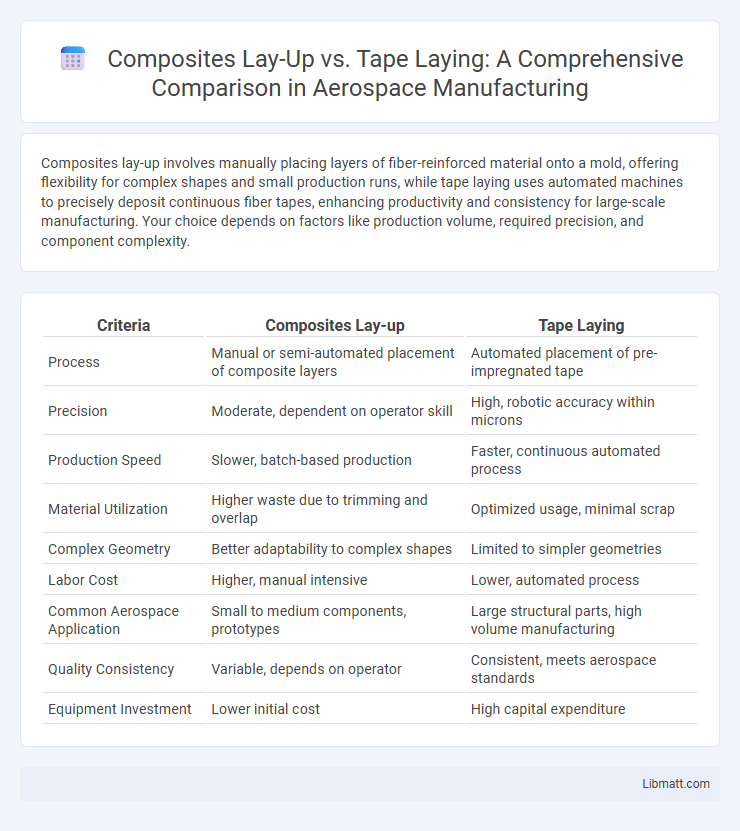
Composites lay-up involves manually placing layers of fiber-reinforced material onto a mold, offering flexibility for complex shapes and small production runs, while tape laying uses automated machines to precisely deposit continuous fiber tapes, enhancing productivity and consistency for large-scale manufacturing. Your choice depends on factors like production volume, required precision, and component complexity.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Composites Lay-up | Tape Laying |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Manual or semi-automated placement of composite layers | Automated placement of pre-impregnated tape |
| Precision | Moderate, dependent on operator skill | High, robotic accuracy within microns |
| Production Speed | Slower, batch-based production | Faster, continuous automated process |
| Material Utilization | Higher waste due to trimming and overlap | Optimized usage, minimal scrap |
| Complex Geometry | Better adaptability to complex shapes | Limited to simpler geometries |
| Labor Cost | Higher, manual intensive | Lower, automated process |
| Common Aerospace Application | Small to medium components, prototypes | Large structural parts, high volume manufacturing |
| Quality Consistency | Variable, depends on operator | Consistent, meets aerospace standards |
| Equipment Investment | Lower initial cost | High capital expenditure |
Introduction to Composite Manufacturing Techniques
Composite manufacturing techniques like lay-up and tape laying are essential for producing high-performance materials used in aerospace, automotive, and marine industries. Lay-up involves manually placing fiber reinforcements onto a mold, providing flexibility for complex shapes, while tape laying uses automated machines to precisely lay pre-impregnated tape, ensuring consistency and reducing labor costs. Your choice between these methods depends on factors such as production volume, part complexity, and material performance requirements.
Overview of Lay-Up and Tape Laying Methods
Composite lay-up involves manually placing fiber reinforcement materials, such as fabrics or pre-pregs, onto a mold in predetermined orientations to build composite structures layer by layer. Tape laying uses automated machinery to precisely deposit narrow tapes of composite material, enabling faster production and improved consistency in fiber alignment. Both methods are critical in aerospace and automotive industries, with lay-up favored for complex, small-batch parts and tape laying suited for high-volume, large-scale manufacturing.
Material Selection for Lay-Up vs Tape Laying
Material selection for composites lay-up typically favors prepreg fabrics that allow manual placement and flexibility in fiber orientation, ideal for complex shapes and low-volume production. Tape laying uses unidirectional prepreg tapes, providing precise fiber alignment and consistent thickness, crucial for high-performance aerospace components requiring structural integrity. Your choice depends on the required mechanical properties, production speed, and part complexity, with tape laying excelling in automation and repeatability.
Process Workflow Comparison
Composites lay-up involves manually placing and aligning fabric layers on a mold, offering flexibility but requiring skilled labor and time-intensive inspection. Tape laying uses automated machinery to deposit narrow tape strips precisely, enhancing consistency and speed while reducing material waste. The process workflow for tape laying integrates computer-controlled programming for accurate patterning, whereas lay-up relies more heavily on operator expertise and manual adjustments.
Equipment and Tooling Differences
Composites lay-up typically involves manual or semi-automated tools such as hand rollers, spreaders, and vacuum bags, allowing for flexible and cost-effective production of complex shapes. Tape laying, on the other hand, employs sophisticated automated machines with robotic arms and tension control systems designed for precision and high repeatability in large-scale manufacturing. Your choice depends on the scale of production and the accuracy required, as tape laying offers superior consistency while composites lay-up allows greater adaptability for custom designs.
Precision and Automation in Each Method
Tape laying offers superior automation and precision through computer-controlled placement of continuous composite tapes, ensuring consistent fiber alignment and minimal human error. In contrast, composites lay-up relies more on manual processes, which can introduce variability in fiber orientation and thickness, although skilled technicians can achieve high precision in complex geometries. Your choice between these methods will impact production speed and quality consistency, with tape laying favoring large-scale, repeatable manufacturing and lay-up suited for lower volume, customized parts.
Structural Performance: Lay-Up vs Tape Laying
Composites lay-up offers greater flexibility in fiber orientation and resin distribution, enhancing customized structural performance in complex geometries. Tape laying provides higher precision and automation, resulting in consistent fiber placement and improved mechanical properties such as strength and stiffness. Your choice between lay-up and tape laying impacts the durability and load-bearing capacity of the final composite structure.
Cost and Production Efficiency Analysis
Tape laying offers higher production efficiency through automated placement of continuous fiber tapes, reducing labor costs and minimizing human error compared to manual composites lay-up. Composites lay-up remains cost-effective for low-volume or custom parts due to lower initial equipment investment and greater flexibility. Your choice depends on balancing upfront capital spending against long-term throughput gains and consistency requirements.
Application Areas and Industry Use Cases
Composites lay-up is widely used in aerospace, automotive, and marine industries for low to medium volume production, offering flexibility in complex shapes and customized parts. Tape laying technology excels in high-performance aerospace and wind energy applications where automated precision and high throughput are critical for producing large, structural components with superior mechanical properties. Industries such as defense and industrial equipment leverage tape laying for enhanced material consistency and repeatability in advanced composite manufacturing.
Future Trends in Composite Fabrication Methods
Automated tape laying (ATL) is advancing with increased precision and speed, enabling the production of large, complex aerospace components with improved fiber alignment and reduced material waste. Composites lay-up techniques are evolving through integration with robotics and AI-driven quality control systems, enhancing consistency and reducing labor costs. Future trends emphasize hybrid approaches combining ATL and traditional lay-up for optimized structural performance and manufacturing efficiency in automotive and aerospace industries.
Composites lay-up vs Tape laying Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com