Active radar emits radio waves and detects their reflections from objects, providing precise range and velocity information, while passive radar relies on detecting signals from existing transmissions, offering a covert advantage by not revealing its position. Your choice depends on whether stealth and low detectability or accurate target tracking and range measurement are more critical for the application.
Table of Comparison
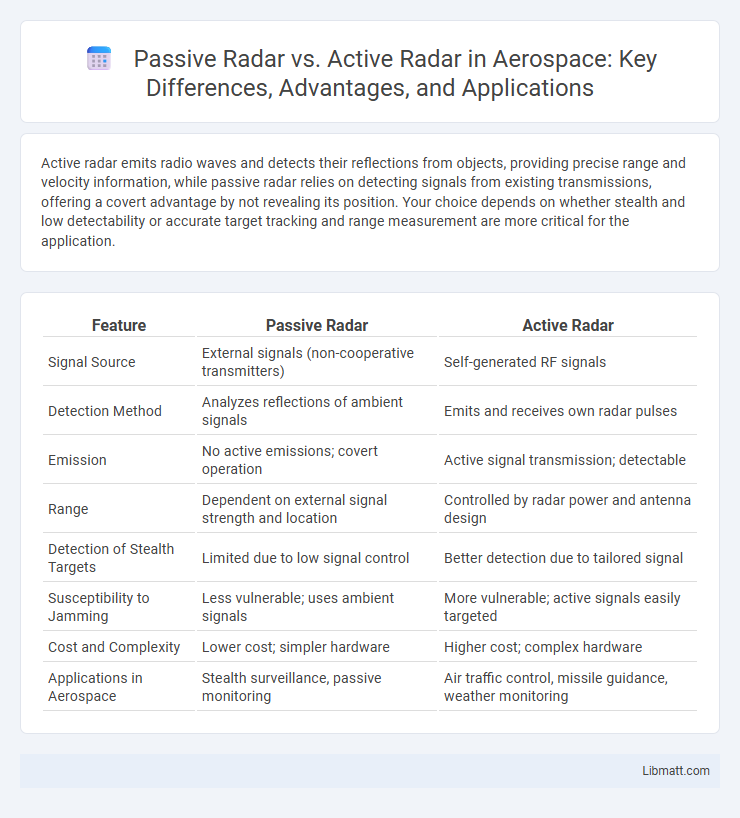
| Feature | Passive Radar | Active Radar |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Source | External signals (non-cooperative transmitters) | Self-generated RF signals |
| Detection Method | Analyzes reflections of ambient signals | Emits and receives own radar pulses |
| Emission | No active emissions; covert operation | Active signal transmission; detectable |
| Range | Dependent on external signal strength and location | Controlled by radar power and antenna design |
| Detection of Stealth Targets | Limited due to low signal control | Better detection due to tailored signal |
| Susceptibility to Jamming | Less vulnerable; uses ambient signals | More vulnerable; active signals easily targeted |
| Cost and Complexity | Lower cost; simpler hardware | Higher cost; complex hardware |
| Applications in Aerospace | Stealth surveillance, passive monitoring | Air traffic control, missile guidance, weather monitoring |
Introduction to Passive and Active Radar
Passive radar detects and tracks targets by analyzing reflected signals from non-cooperative sources like commercial broadcasts, providing stealthy surveillance without emitting signals. Active radar transmits its own radio waves and measures the reflections to determine target location and velocity, offering precise range and direction information. Passive radar excels in covert operations and electronic countermeasure resistance, while active radar delivers higher accuracy and real-time target tracking.
Fundamental Principles of Radar Technologies
Active radar systems emit radio waves that reflect off objects, calculating distance and speed based on returned signals, while passive radar relies on detecting and analyzing signals from external sources like commercial broadcasts or communication signals without transmitting its own. The fundamental difference lies in active radar's energy transmission, enabling direct target illumination, whereas passive radar leverages ambient signals to covertly monitor surroundings. Your choice depends on operational needs, such as stealth and energy efficiency, with passive radar offering advantages in undetectability and resistance to jamming.
How Passive Radar Systems Work
Passive radar systems detect and track objects by analyzing reflected signals from non-cooperative sources such as commercial broadcast towers, FM radio, or TV signals, rather than emitting their own signals. These systems rely on multiple receiver stations to measure the time difference of arrival and Doppler shifts of the signals reflected off targets, enabling accurate localization without revealing the radar's position. Your advantage lies in stealth and reduced energy consumption, as passive radar operates without transmitting detectable signals, making it harder to intercept or jam.
How Active Radar Systems Operate
Active radar systems transmit radio waves that reflect off objects, returning signals detected by the radar receiver to determine target location and velocity. These systems emit high-frequency electromagnetic pulses and analyze the time delay and Doppler shifts to create precise images and track moving targets. The robustness and reliability of active radar make it essential for applications such as air traffic control, weather monitoring, and military surveillance.
Key Differences Between Passive and Active Radar
Passive radar systems detect targets by analyzing reflections of signals from third-party sources without emitting their own signals, resulting in stealthier operations and reduced risk of detection. Active radar systems emit their own radio waves and measure reflections to locate objects, providing more precise range and velocity data but at the expense of potential detectability. Key differences include energy emission, detection range accuracy, vulnerability to jamming, and operational complexity, with passive radar excelling in covert surveillance while active radar offers superior target characterization.
Advantages of Passive Radar
Passive radar offers significant advantages such as enhanced stealth capabilities since it does not emit signals, making detection by adversaries extremely difficult. It leverages existing electromagnetic signals from commercial broadcasts or communication networks, reducing infrastructure costs and power consumption. Your defense system can benefit from reduced electronic interference and increased survivability in contested environments using passive radar technology.
Advantages of Active Radar
Active radar offers significant advantages by emitting its own radio signals, enabling precise target detection and range measurement regardless of external signal availability. This technology provides higher resolution and better tracking capabilities, making it reliable in various weather conditions and complex environments. Your radar system benefits from increased accuracy and real-time data, essential for effective navigation and surveillance.
Limitations and Challenges of Each Radar Type
Passive radar faces limitations such as reliance on external radio frequency sources, making it vulnerable to gaps in signal coverage and reduced detection capability in low-emission environments. Active radar encounters challenges including higher power consumption, susceptibility to electronic countermeasures like jamming, and the risk of revealing its location due to emitted signals. Your choice between passive and active radar must consider these factors to align with operational needs and environmental constraints.
Applications in Defense and Civil Sectors
Passive radar excels in defense applications by detecting stealth targets and minimizing electromagnetic emissions, enhancing covert surveillance and electronic warfare capabilities. Active radar is widely used in civil sectors for air traffic control, weather monitoring, and navigation due to its ability to provide precise range and velocity data through emitted signals. Your choice between passive and active radar depends on mission requirements, balancing stealth needs with the demand for high-resolution, real-time target tracking.
Future Trends in Radar Technology
Future trends in radar technology emphasize the integration of passive radar systems with advanced signal processing and machine learning algorithms to enhance detection accuracy and reduce energy consumption. Active radar continues to evolve with improvements in phased array antennas and cognitive radar capabilities, enabling adaptive waveform design and real-time environmental awareness. Hybrid radar architectures combining passive and active elements are expected to offer significant advantages in stealth detection, electronic countermeasure resistance, and spectrum efficiency.
Passive radar vs Active radar Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com