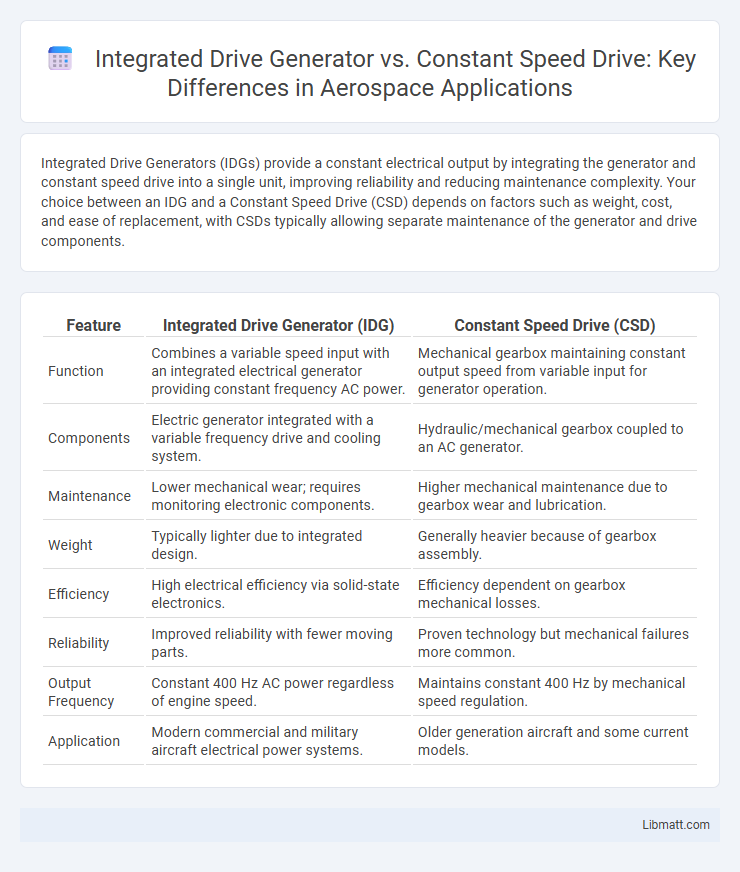
Integrated Drive Generators (IDGs) provide a constant electrical output by integrating the generator and constant speed drive into a single unit, improving reliability and reducing maintenance complexity. Your choice between an IDG and a Constant Speed Drive (CSD) depends on factors such as weight, cost, and ease of replacement, with CSDs typically allowing separate maintenance of the generator and drive components.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Integrated Drive Generator (IDG) | Constant Speed Drive (CSD) |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Combines a variable speed input with an integrated electrical generator providing constant frequency AC power. | Mechanical gearbox maintaining constant output speed from variable input for generator operation. |
| Components | Electric generator integrated with a variable frequency drive and cooling system. | Hydraulic/mechanical gearbox coupled to an AC generator. |
| Maintenance | Lower mechanical wear; requires monitoring electronic components. | Higher mechanical maintenance due to gearbox wear and lubrication. |
| Weight | Typically lighter due to integrated design. | Generally heavier because of gearbox assembly. |
| Efficiency | High electrical efficiency via solid-state electronics. | Efficiency dependent on gearbox mechanical losses. |
| Reliability | Improved reliability with fewer moving parts. | Proven technology but mechanical failures more common. |
| Output Frequency | Constant 400 Hz AC power regardless of engine speed. | Maintains constant 400 Hz by mechanical speed regulation. |
| Application | Modern commercial and military aircraft electrical power systems. | Older generation aircraft and some current models. |
Overview of Integrated Drive Generator (IDG) and Constant Speed Drive (CSD)
The Integrated Drive Generator (IDG) combines a constant speed drive and an electrical generator into a single unit, maintaining a stable output frequency by decoupling engine speed variations from generator operation. The Constant Speed Drive (CSD) is a mechanical device that ensures the generator receives input at a fixed speed, allowing the generator to produce consistent electrical power despite changes in engine RPM. Both systems are essential for aircraft electrical power generation, with the IDG offering a more compact and maintenance-efficient solution compared to the traditionally separate CSD and generator arrangement.
Key Functional Differences Between IDG and CSD
The Integrated Drive Generator (IDG) combines a generator and a Constant Speed Drive (CSD) into a single unit, providing a stable electrical output by maintaining constant generator speed despite variable engine RPM. Unlike the CSD, which mechanically adjusts input speed through a hydraulic coupling to ensure consistent generator speed, the IDG integrates the drive and generation components, reducing weight and maintenance complexity. Key functional differences include the IDG's integrated design offering streamlined operation and simplified installation, while the CSD serves solely as a speed regulator requiring a separate generator unit.
Components and Construction of IDG Systems
Integrated Drive Generator (IDG) systems feature a constant speed drive mechanism combining a hydraulic or mechanical system with an electrical generator in a single unit, ensuring stable generator output despite variable engine speeds. Key components include a hydraulic coupling or torsional spring assembly to regulate input speed, a slip ring assembly for continuous electrical connection, and the electrical generator itself, which converts mechanical energy into electrical power. Your aircraft's IDG system is designed to provide reliable power by integrating lubrication, cooling, and drive mechanisms within a compact housing, differentiating it from the simpler construction of constant speed drives (CSD) that focus solely on maintaining consistent output speed.
Components and Construction of CSD Systems
Constant Speed Drive (CSD) systems primarily consist of a hydraulic pump, a turbine, a reduction gearbox, and a control mechanism designed to maintain a constant output speed regardless of engine RPM variations. The hydraulic pump, powered by the engine, drives the turbine connected to the generator shaft, ensuring stable electrical power output essential for aircraft systems. Compared to Integrated Drive Generators (IDG), which combine the CSD and generator in one unit, CSD systems focus on modular components that offer flexibility in maintenance and replacement while delivering consistent speed regulation.
Operational Principles of Integrated Drive Generators
Integrated Drive Generators (IDGs) operate by using an integrated constant speed drive mechanism to maintain a generator shaft speed at a fixed value regardless of engine speed fluctuations, ensuring consistent electrical frequency output. This unit combines a variable-speed input shaft linked to the aircraft engine with a hydraulic or mechanical system that controls the rotation speed of the generator, enabling stable power supply for aircraft systems. Understanding the operational principles of IDGs helps you appreciate their reliability in delivering constant voltage and frequency, critical for avionics and onboard electrical loads.
Operational Principles of Constant Speed Drives
Constant Speed Drives (CSD) regulate engine speed by using a hydromechanical or electronic system to maintain a fixed output rotational speed regardless of input variations. They function by adjusting the transmission ratio between the engine and the driven accessory, ensuring stable and consistent operation critical for aircraft generators. This precise control contrasts with Integrated Drive Generators (IDG), where the generator and the drive are combined into a single unit integrating both mechanical and electrical regulation.
Efficiency and Performance Comparison: IDG vs CSD
Integrated Drive Generators (IDGs) offer superior efficiency by combining the generator and constant speed drive into a single unit, reducing weight and maintenance needs compared to traditional Constant Speed Drives (CSDs). IDGs maintain optimal engine speed, ensuring consistent electrical power output with minimal energy loss, enhancing overall aircraft performance. Your choice between IDG and CSD impacts operational reliability and fuel efficiency, with IDGs generally providing better performance in modern aviation systems.
Maintenance Requirements and Reliability Analysis
Integrated Drive Generators (IDGs) require regular maintenance, including oil changes and inspections due to their complex mechanical components, which can affect overall reliability if not properly serviced. Constant Speed Drives (CSDs), while simpler in design, also necessitate periodic maintenance to ensure hydraulic fluid integrity and component wear resistance, contributing to consistent operational reliability. Your choice between IDG and CSD should consider the balance between maintenance intensity and long-term reliability based on specific aircraft system demands.
Applications in Modern Aircraft Electrical Systems
Integrated Drive Generators (IDGs) are widely used in modern aircraft electrical systems to provide a stable and consistent 115V, 400Hz power supply by combining a generator with a constant speed drive unit. Unlike Constant Speed Drives (CSDs) alone, IDGs simplify power generation by integrating both components, ensuring reliable electrical power regardless of engine speed variations. Your aircraft benefits from the enhanced efficiency and reduced maintenance requirements offered by IDGs in systems powering avionics, lighting, and flight control electronics.
Future Trends in Aircraft Power Generation Technologies
Future trends in aircraft power generation technologies emphasize the shift from Constant Speed Drive (CSD) systems to Integrated Drive Generators (IDG) due to enhanced efficiency and reduced maintenance requirements. IDGs incorporate electronic control units that optimize power output and improve fault detection compared to traditional mechanical CSDs. Your aviation operations can benefit from adopting IDG technology as it supports more reliable and lighter electrical systems, aligning with the evolution towards more electric aircraft architectures.
Integrated Drive Generator vs Constant Speed Drive Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com