Radar altimeters measure altitude by sending radio waves to the ground and calculating the time it takes for the signal to return, providing accurate altitude readings above terrain for low-altitude flight. Your barometric altimeter, on the other hand, estimates altitude by measuring atmospheric pressure, which can be affected by weather changes and requires regular calibration for precise altitude tracking.
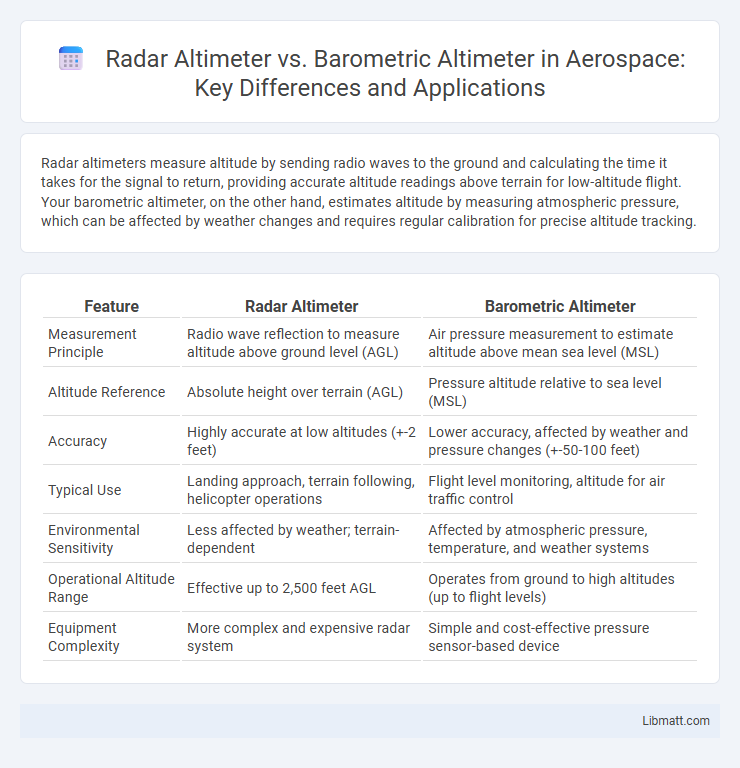
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Radar Altimeter | Barometric Altimeter |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Principle | Radio wave reflection to measure altitude above ground level (AGL) | Air pressure measurement to estimate altitude above mean sea level (MSL) |
| Altitude Reference | Absolute height over terrain (AGL) | Pressure altitude relative to sea level (MSL) |
| Accuracy | Highly accurate at low altitudes (+-2 feet) | Lower accuracy, affected by weather and pressure changes (+-50-100 feet) |
| Typical Use | Landing approach, terrain following, helicopter operations | Flight level monitoring, altitude for air traffic control |
| Environmental Sensitivity | Less affected by weather; terrain-dependent | Affected by atmospheric pressure, temperature, and weather systems |
| Operational Altitude Range | Effective up to 2,500 feet AGL | Operates from ground to high altitudes (up to flight levels) |
| Equipment Complexity | More complex and expensive radar system | Simple and cost-effective pressure sensor-based device |
Introduction to Altimeters
Radar altimeters measure altitude by sending radio waves to the ground and calculating the time it takes for the signal to return, providing precise height above terrain, especially useful in low-altitude flight. Barometric altimeters estimate altitude by measuring atmospheric pressure, which decreases with elevation, offering reliable data for general altitude reference but requiring calibration for weather changes. Your aircraft's flight system often integrates both to ensure accurate altitude readings under varying flight conditions.
What is a Radar Altimeter?
A radar altimeter measures altitude by emitting radio waves directly toward the ground and calculating the time it takes for the signals to reflect back, providing precise real-time height above terrain data. Unlike barometric altimeters that rely on atmospheric pressure changes and require calibration, radar altimeters offer accurate low-altitude readings unaffected by weather conditions. This makes radar altimeters crucial for applications such as aircraft landing systems, terrain-following flight, and helicopter operations.
What is a Barometric Altimeter?
A barometric altimeter measures altitude by detecting changes in atmospheric pressure, which decreases with increasing elevation. It provides altitude data relative to sea level using an internal barometer calibrated to standard atmospheric pressure. Unlike radar altimeters that measure altitude above ground level via radio waves, barometric altimeters rely on pressure variations and are widely used in aviation for determining flight levels.
How Radar Altimeters Work
Radar altimeters operate by emitting radio waves toward the ground and measuring the time it takes for the signals to reflect back, providing precise altitude above terrain data. These devices calculate absolute height by analyzing the round-trip travel time of the radar pulses, enabling accurate readings even at low altitudes or over uneven surfaces. Their functionality contrasts with barometric altimeters, which estimate altitude based on atmospheric pressure changes.
How Barometric Altimeters Work
Barometric altimeters measure altitude by detecting changes in atmospheric pressure, which decreases with increasing elevation. Your device calculates height above sea level by comparing the current pressure to a standard reference value, allowing for relatively accurate altitude readings under stable weather conditions. Unlike radar altimeters that use radio waves, barometric altimeters rely on air pressure variations, making them sensitive to weather changes and requiring periodic calibration.
Accuracy Comparison: Radar vs Barometric Altimeters
Radar altimeters provide higher accuracy by measuring the actual distance from an aircraft to the ground using radio waves, typically within a few feet. Barometric altimeters estimate altitude based on atmospheric pressure, which can be affected by weather changes and temperature, leading to less precise readings. Your flight safety benefits from radar altimeters' precise altitude measurements, especially during low-level operations or landing approaches.
Use Cases and Applications
Radar altimeters provide precise altitude measurements above ground level, making them essential for low-altitude flight operations, terrain-following navigation, and automated landing systems in aviation. Barometric altimeters are widely used for general altitude reference based on atmospheric pressure, suitable for high-altitude cruising, air traffic control, and hiking or mountaineering activities. The radar altimeter's accuracy in real-time terrain detection contrasts with the barometric altimeter's reliance on pressure changes, influencing their respective application contexts.
Advantages of Radar Altimeters
Radar altimeters provide precise altitude measurements above ground level by emitting radio waves and measuring their reflection time, which is especially crucial for low-altitude flight and landing. They are less affected by atmospheric pressure variations compared to barometric altimeters, offering consistent and reliable readings in diverse weather conditions. Their real-time accuracy enhances safety during critical maneuvers such as approach and terrain following in aviation.
Advantages of Barometric Altimeters
Barometric altimeters provide continuous altitude readings by measuring atmospheric pressure, allowing for reliable tracking during flight without reliance on external signals. These altimeters are typically less expensive and simpler in design compared to radar altimeters, making them widely used in general aviation and portable devices. Their ability to function effectively at high altitudes and in various weather conditions enhances safety and operational efficiency for pilots.
Choosing the Right Altimeter for Your Needs
Radar altimeters provide precise altitude measurements by bouncing radio waves off the ground, making them ideal for low-altitude navigation and terrain following. Barometric altimeters rely on atmospheric pressure, offering reliable altitude data at higher elevations and during standard flight conditions. Choosing the right altimeter depends on your specific needs, such as whether accuracy near the ground or overall altitude trends are most critical.
radar altimeter vs barometric altimeter Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com